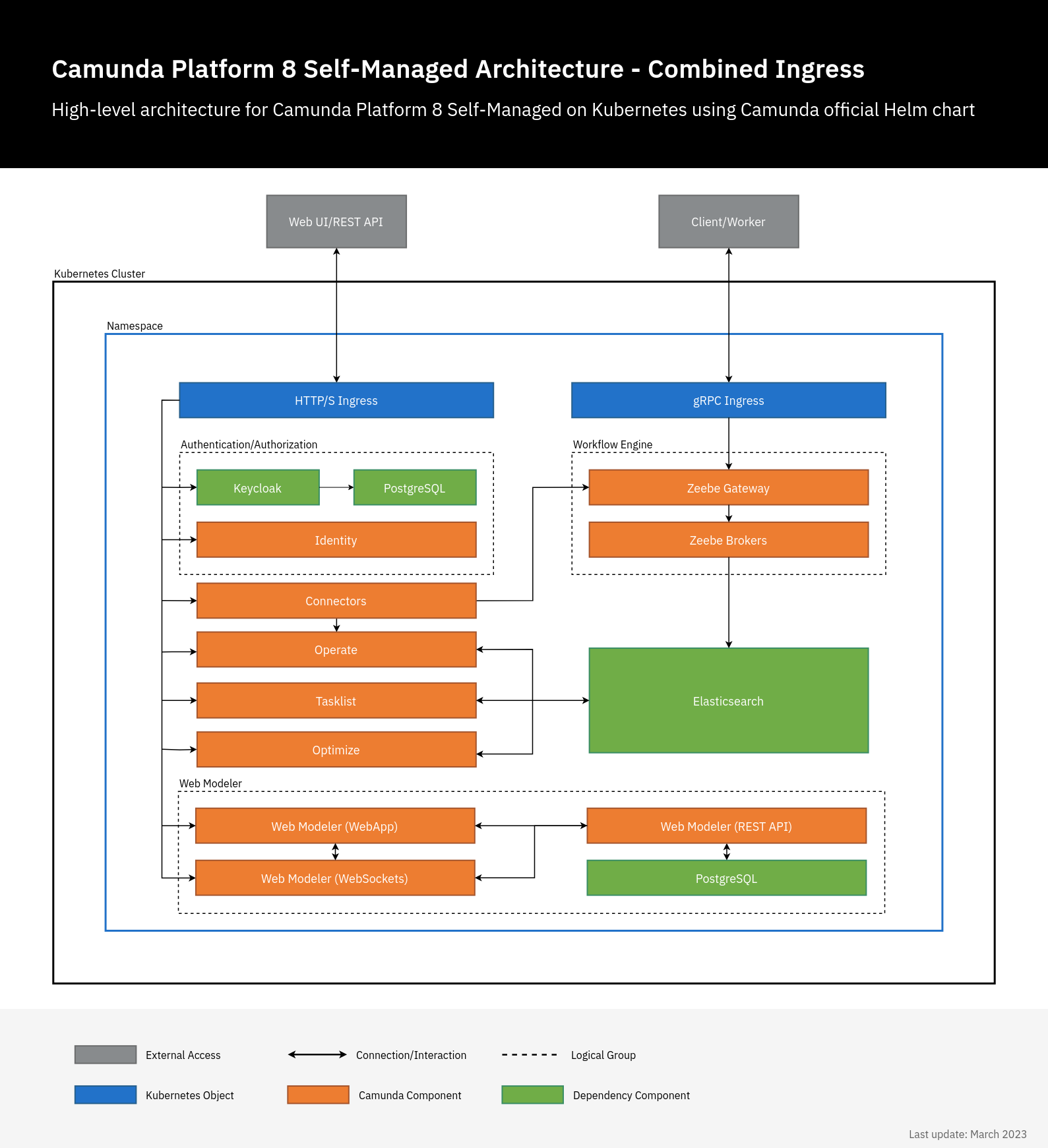
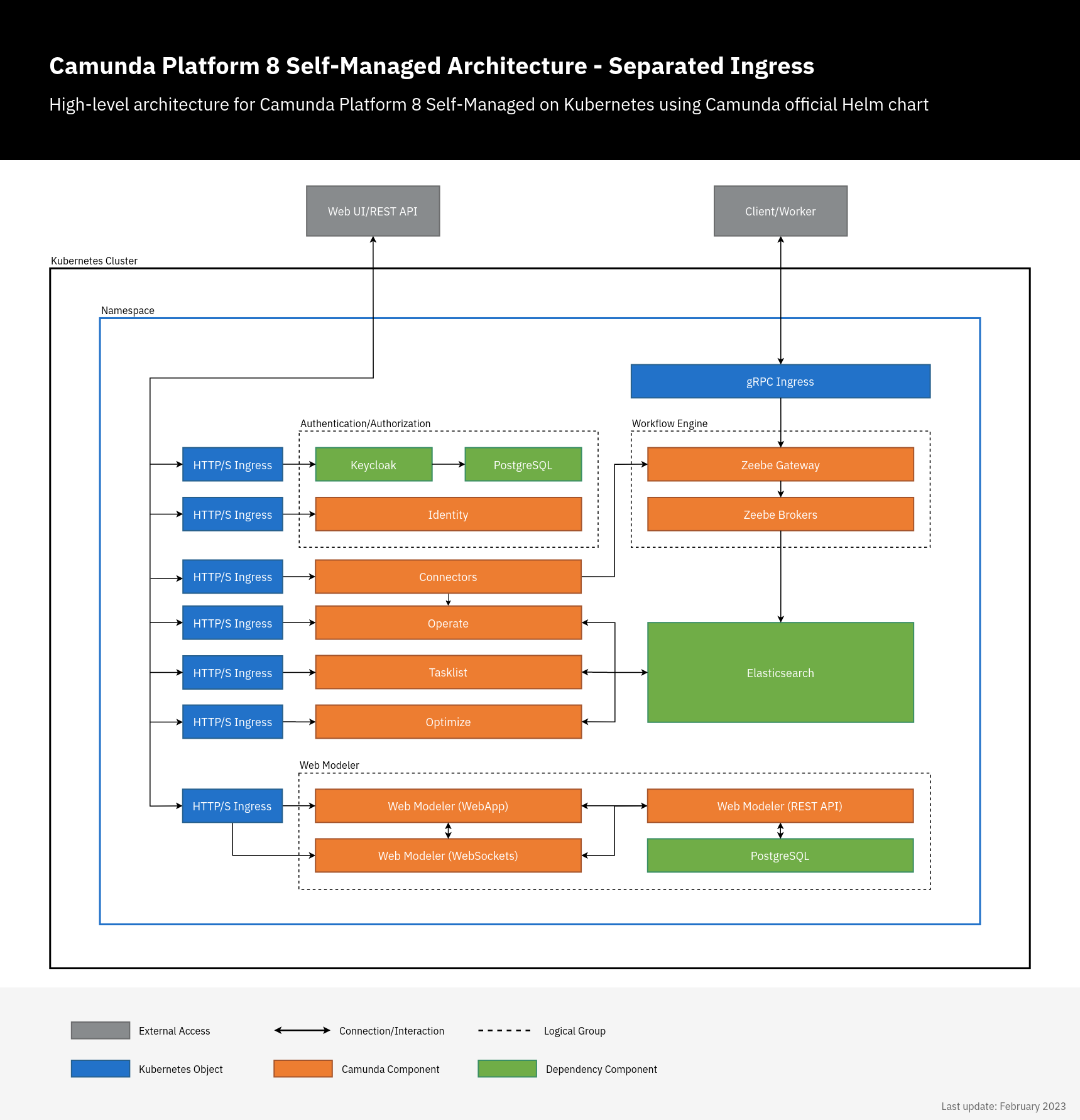
Combined and separated Ingress setup
Camunda 8 Self-Managed has multiple web applications and gRPC services. Both can be accessed externally using Ingress. There are two ways to do this:
- Combined setup: In this setup, there are two Ingress objects: one Ingress object for all Camunda 8 web applications using a single domain. Each application has a sub-path e.g.
camunda.example.com/operate, andcamunda.example.com/optimizeand another Ingress which uses gRPC protocol for Zeebe Gateway e.g.zeebe.camunda.example.com. - Separated setup: In this setup, each component has its own Ingress/host e.g.
operate.camunda.example.com,optimize.camunda.example.com,zeebe.camunda.example.com, etc.
There are no significant differences between the two setups. Rather, they both offer flexibility for different workflows.
Camunda 8 Helm chart doesn't manage or deploy Ingress controllers, it only deploys Ingress resources. Hence, this Ingress setup will not work without an Ingress controller running in your cluster.
Preparation
- An Ingress controller should be deployed in advance. The examples below use the ingress-nginx controller, but any Ingress controller could be used by setting
ingress.className. - TLS configuration is not handled in the examples because it varies between different workflows. It could be configured directly using
ingress.tlsoptions or via an external tool like Cert-Manager usingingress.annotations. For more details, check available configuration options.
Configuration
- Combined Ingress
- Separated Ingress
In this setup, a single Ingress/domain is used to access Camunda 8 web applications, and another for Zeebe Gateway. By default, all web applications use / as a base, so we just need to set the context path, Ingress configuration, and authentication redirect URLs.
# Chart values for the Camunda 8 Helm chart in combined Ingress setup.
# This file deliberately contains only the values that differ from the defaults.
# For changes and documentation, use your favorite diff tool to compare it with:
# https://artifacthub.io/packages/helm/camunda/camunda-platform#parameters
# IMPORTANT: Make sure to change "camunda.example.com" to your domain.
global:
ingress:
enabled: true
className: nginx
host: "camunda.example.com"
identity:
auth:
publicIssuerUrl: "https://camunda.example.com/auth/realms/camunda-platform"
operate:
redirectUrl: "https://camunda.example.com/operate"
tasklist:
redirectUrl: "https://camunda.example.com/tasklist"
optimize:
redirectUrl: "https://camunda.example.com/optimize"
webModeler:
redirectUrl: "https://camunda.example.com/modeler"
identity:
contextPath: "/identity"
fullURL: "https://camunda.example.com/identity"
operate:
contextPath: "/operate"
optimize:
contextPath: "/optimize"
tasklist:
contextPath: "/tasklist"
webModeler:
# The context path is used for the web application that will be accessed by users in the browser.
# In addition, a WebSocket endpoint will be exposed on "[contextPath]-ws", e.g. "/modeler-ws".
contextPath: "/modeler"
zeebe-gateway:
ingress:
enabled: true
className: nginx
host: "zeebe.camunda.example.com"
The configuration above only contains the Ingress-related values under webModeler. Note the additional installation instructions and configuration hints.
Using the custom values file, deploy Camunda 8 as usual:
helm install demo camunda/camunda-platform -f values-combined-ingress.yaml
Once deployed, you can access the Camunda 8 components on:
- Web applications:
https://camunda.example.com/[identity|operate|optimize|tasklist|modeler]- Note: Web Modeler also exposes a WebSocket endpoint on
https://camunda.example.com/modeler-ws. This is only used by the application itself and not supposed to be accessed by users directly.
- Note: Web Modeler also exposes a WebSocket endpoint on
- Keycloak authentication:
https://camunda.example.com/auth - Zeebe Gateway:
grpc://zeebe.camunda.example.com
In this setup, each Camunda 8 component has its own Ingress/domain. There is no need to set the context since / is used as a default base. Here, we just need to set the Ingress configuration and authentication redirect URLs.
# Chart values for the Camunda 8 Helm chart in combined Ingress setup.
# This file deliberately contains only the values that differ from the defaults.
# For changes and documentation, use your favorite diff tool to compare it with:
# https://artifacthub.io/packages/helm/camunda/camunda-platform#parameters
# IMPORTANT: Make sure to change "camunda.example.com" to your domain.
global:
identity:
auth:
publicIssuerUrl: "https://keycloak.camunda.example.com/auth/realms/camunda-platform"
operate:
redirectUrl: "https://operate.camunda.example.com"
tasklist:
redirectUrl: "https://tasklist.camunda.example.com"
optimize:
redirectUrl: "https://optimize.camunda.example.com"
webModeler:
redirectUrl: "https://modeler.camunda.example.com"
identity:
ingress:
enabled: true
className: nginx
host: "identity.camunda.example.com"
fullURL: "https://identity.camunda.example.com"
keycloak:
ingress:
enabled: true
ingressClassName: nginx
hostname: "keycloak.camunda.example.com"
operate:
ingress:
enabled: true
className: nginx
host: "operate.camunda.example.com"
optimize:
ingress:
enabled: true
className: nginx
host: "optimize.camunda.example.com"
tasklist:
ingress:
enabled: true
className: nginx
host: "tasklist.camunda.example.com"
zeebe-gateway:
ingress:
enabled: true
className: nginx
host: "zeebe.camunda.example.com"
webModeler:
ingress:
enabled: true
className: nginx
webapp:
host: "modeler.camunda.example.com"
websockets:
host: "modeler-ws.camunda.example.com"
The configuration above only contains the Ingress-related values under webModeler. Note the additional installation instructions and configuration hints.
Using the custom values file, deploy Camunda 8 as usual:
helm install demo camunda/camunda-platform -f values-separated-ingress.yaml
Once deployed, you can access the Camunda 8 components on:
- Web applications:
https://[identity|operate|optimize|tasklist|modeler].camunda.example.com - Keycloak authentication:
https://keycloak.camunda.example.com - Zeebe Gateway:
grpc://zeebe.camunda.example.com
Ingress controllers
Ingress resources require the cluster to have an Ingress controller running. There are many options for configuring your Ingress controller. If you are using a cloud provider such as AWS or GCP, we recommend you follow their Ingress setup guides if an Ingress controller is not already pre-installed.
Example local configuration
An Ingress controller is also required when working on a local Camunda 8 installation. Take a look at an Ingress controller configuration using the ingress-nginx controller:
# ingress_nginx_values.yml
controller:
updateStrategy:
type: RollingUpdate
rollingUpdate:
maxUnavailable: 1
service:
type: NodePort
publishService:
enabled: false
To install this ingress-nginx controller to your local cluster, execute the following command:
helm install -f ingress_nginx_values.yml \
ingress-nginx ingress-nginx \
--repo https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx \
--version "4.9.0" \
--namespace ingress-nginx \
--create-namespace
Troubleshooting
If something is not working as expected, check the guide for general deployment troubleshooting.