Multi-tenancy
Multi-tenancy in the context of Camunda 8 refers to the ability of Camunda 8 to serve multiple distinct tenants or clients within a single installation.
From version 8.3 onwards, Optimize has been enhanced to support multi-tenancy for Self-Managed setups. More information about the feature can be found in the multi-tenancy documentation.
Optimize imports the relevant tenant information from Zeebe records and retrieves each user's tenant authorizations from Identity, so that the logged-in users only have access to the data on tenants that they are authorized to see in Identity. Because tenant authorizations are cached in Optimize to improve performance, there could be a delay until any changes made to tenant authorizations in Identity are visible in Optimize.
Default tenant authorizations in Optimize
If multi-tenancy is enabled across components, users will be allowed to view any data from tenants for which they have authorizations configured in Identity.
If multi-tenancy is disabled in Optimize, all users will be allowed to view data from the <default> tenant only and no data from other tenants.
If multi-tenancy is enabled in Optimize, but disabled in Identity or Identity is not reachable for other reasons, users will not have any tenant authorizations in Optimize and will not be able to access the data of any tenants in Optimize.
Configuration
In a Self-Managed Camunda 8 environment, the following two configurations settings are required for multi-tenancy:
| YAML path | Environment variable | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| multitenancy.enabled | CAMUNDA_OPTIMIZE_MULTITENANCY_ENABLED | false | Enables the Camunda 8 multi-tenancy feature in Optimize. |
| security.auth.ccsm.baseUrl | CAMUNDA_OPTIMIZE_IDENTITY_BASE_URL | null | The base URL of Identity. |
The CAMUNDA_OPTIMIZE_MULTITENANCY_ENABLED environment variable enables the feature in Optimize. The multi-tenancy feature must be enabled in all other components as well using their respective multi-tenancy feature flags.
The CAMUNDA_OPTIMIZE_IDENTITY_BASE_URL environment variable has to be set to enable Optimize to retrieve tenant authorizations from Identity. If this base URL is not configured, Optimize will not be able to retrieve tenant authorizations and users will not be able to access any tenant's data in Optimize.
If required, the tenant authorization cache in Optimize can also be configured via these optional settings:
| YAML path | Environment variable | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| caches.cloudTenantAuthorizations.maxSize | CAMUNDA_OPTIMIZE_CACHES_CLOUD_TENANT_AUTHORIZATIONS_MAX_SIZE | 10000 | The maximum size of the Camunda 8 tenant authorizations cache. |
| caches.cloudTenantAuthorizations.defaultTtlMillis | CAMUNDA_OPTIMIZE_CACHES_CLOUD_TENANT_AUTHORIZATIONS_MIN_FETCH_INTERVAL_SECONDS | 300000 | The time in milliseconds the tenant authorizations will be cached. |
Troubleshooting
To ensure seamless integration and functionality, the multi-tenancy feature must also be enabled across all associated components if not configured in Helm so users can view any data from tenants for which they have authorizations configured in Identity.
Find more information (including links to individual component configuration) on the multi-tenancy concepts page.
Possible Camunda 7 multi-tenancy scenarios
As described in the Camunda 7 documentation, there are two possible multi-tenant scenarios which are also supported by Optimize: Single Camunda 7 process engine with tenant-identifiers and One Camunda 7 process engine per tenant.
Single Camunda 7 process engine with tenant-identifiers
Tenant-identifiers available in the Camunda 7 engine are automatically imported into Optimize and tenant-based access authorization is enforced based on the configured Tenant Authorizations within the Camunda 7. This means there is no additional setup required for Optimize in order to support this multi-tenancy scenario.
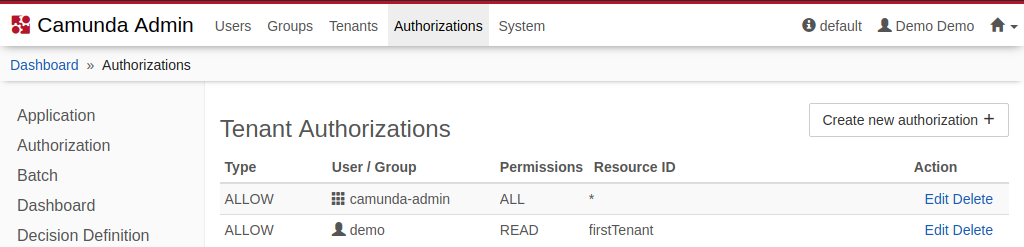
Users granted tenant access via the Camunda 7 will be able to create and see reports for that particular tenant in Optimize. In the following screenshot, the user demo is granted access to data of the tenant with the id firstTenant and will be able to select that tenant in the report builder. Other users, without the particular firstTenant authorization, will not be able to select that tenant in the report builder nor be able to see results of reports that are based on that tenant.
One Camunda 7 process engine per tenant
In the case of a multi-engine scenario where tenant-specific data is isolated by deploying to dedicated engines, there are no tenant identifiers present in the particular engines themselves. For a single Optimize instance that is configured to import from each of those engines to support this scenario, it is required to configure a defaultTenant for each of those engines.
The effect of configuring a defaultTenant per engine is that all data records imported from the particular engine where no engine-side tenant identifier is present this defaultTenant will be added automatically. Optimize users will be authorized to those default tenants based on whether they are authorized to access the particular engine the data originates from. So in this scenario, it is not necessary to configure any Tenant Authorizations in the Camunda 7 itself.
The following environment-config.yaml configuration snippet illustrates the configuration of this defaultTenant on two different engines.
...
engines:
"engineTenant1":
name: engineTenant1
defaultTenant:
# the id used for this default tenant on persisted entities
id: tenant1
# the name used for this tenant when displayed in the UI
name: First Tenant
...
"engineTenant2":
name: engineTenant2
defaultTenant:
# the id used for this default tenant on persisted entities
id: tenant2
# the name used for this tenant when displayed in the UI
name: Second Tenant
...
Optimize users who have a Optimize Application Authorization on both engines will be able to distinguish between data of both engines by selecting the corresponding tenant in the report builder.
Once a defaultTenant.id is configured and data imported, you cannot change it anymore without doing a full reimport as any changes to the configuration cannot be applied to already imported data records.