Helm chart dual-region operational procedure
Introduction
This operational blueprint procedure is a step-by-step guide on how to restore operations in the case of a total region failure. It explains how to temporarily restore functionality in the surviving region and how to ultimately do a full recovery to restore the dual-region setup.
The operational procedure builds on top of the dual-region AWS setup guidance, but is generally applicable for any dual-region setup. It has been also validated for the OpenShift dual-region setup guidance.
Before proceeding with the operational procedure, thoroughly review and understand the contents of the dual-region concept page. This page outlines various limitations and requirements pertinent to the procedure, which are crucial for successful execution.
Disclaimer
Running a dual-region configuration requires users to detect and manage any regional failures, and implement the operational procedure for failover and failback that matches their environment.
Prerequisites
- A dual-region Camunda 8 setup installed in two different regions, preferably derived from our AWS dual-region concept or OpenShift dual-region concept.
- In that guide, we're showcasing Kubernetes dual-region installation, based on the following tools:
- Helm for installing and upgrading the Camunda Helm chart.
- Kubectl to interact with the Kubernetes cluster.
- In that guide, we're showcasing Kubernetes dual-region installation, based on the following tools:
cURLor similar to interact with the Orchestration Cluster REST API.
Terminology
- Surviving region
- A surviving region refers to a region within a dual-region setup that remains operational and unaffected by a failure or disaster that affects other regions.
- Lost region
- A lost region is a region within a dual-region setup that becomes unavailable or unusable due to a failure or disaster.
- Recreated region
- A recreated region is a region within a dual-region setup that was previously lost but has been restored or recreated to resume its operational state.
- We assume this region does not contain Camunda 8 deployments or related persistent volumes. Ensure this is the case before executing the failover procedure.
Procedure
We use the same procedure to handle the loss of both active and passive regions. For clarity, this section focuses on the scenario where the passive region is lost while the active region remains operational. The same procedure will be valid in case of active region loss.
Temporary Loss Scenario: If a region loss is temporary — such as from transient network issues — Zeebe can handle this situation without initiating recovery procedures, provided there is sufficient free space on the persistent disk. However, processing may halt due to a loss of quorum during this time.
Key steps to handle passive region loss
- Traffic rerouting: Use DNS to reroute traffic to the surviving active region. (Details on managing DNS rerouting depend on your specific DNS setup and are not covered in this guide.)
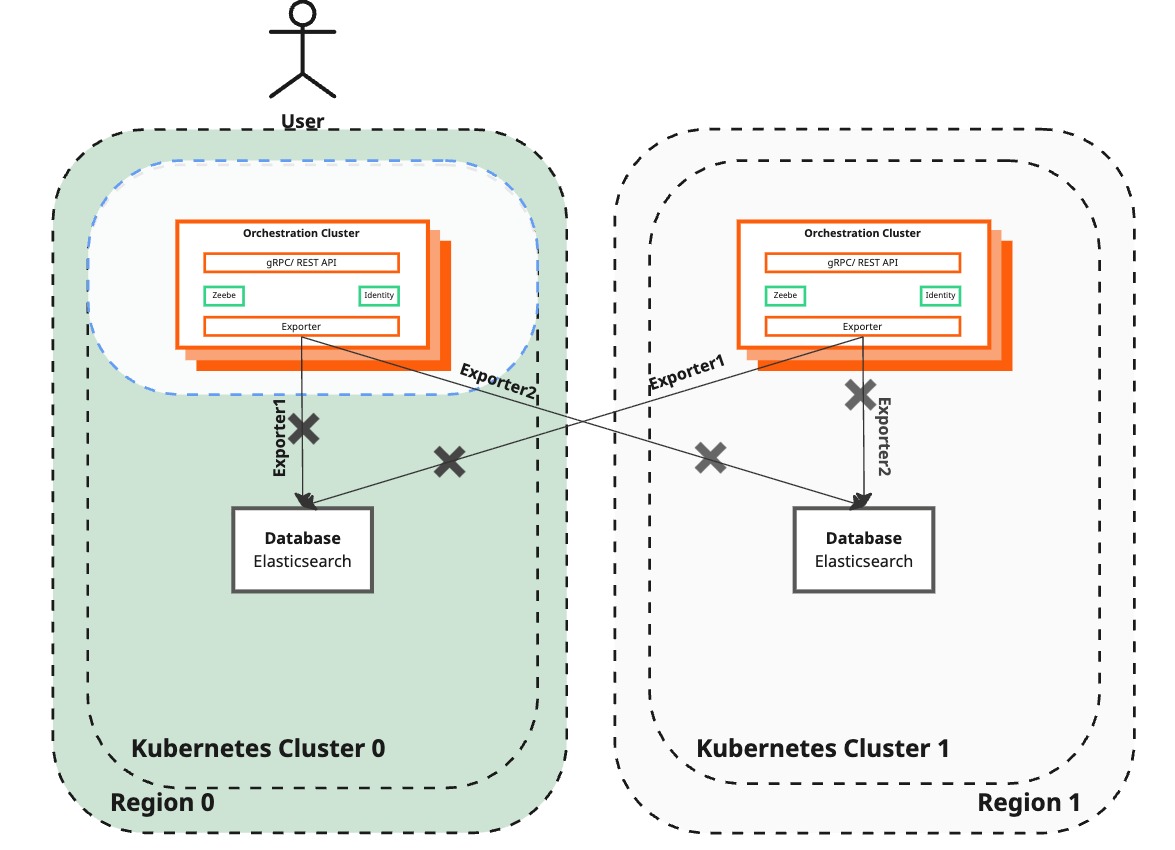
- Failover phase: Temporarily restores Camunda 8 functionality by removing the lost brokers and handling the export to the unreachable Elasticsearch instance.
- Failback phase: Fully restores the failed region to its original functionality. This phase requires the region to be ready for the redeployment of Camunda 8.
For the failback procedure, the recreated region must not include any active Camunda 8 deployments or residual persistent volumes associated with Camunda 8 or its Elasticsearch instance. It is essential to initiate a clean deployment to prevent data replication and state conflicts.
In the following examples, direct API calls are used because authentication methods may vary depending on your embedded Identity configuration.
The Management API (default port 9600) is not secured by default.
The v2 REST API (default port 8080) requires authentication, described in the API authentication guide.
Prerequisites
The following procedures assume the following dual-region deployment for:
-
AWS: the deployment has been created using AWS setup guide and you have your own copy of the c8-multi-region repository and previously completed changes in the
camunda-values.ymlto adjust them in your setup. Follow the dual-region cluster deployment guide to install Camunda 8, configure a dual-region setup, and have the general environment variables (see environment prerequisites already set up). -
OpenShift: the deployment has been created using OpenShift setup guide and previously completed changes in your
generated-values-region-1.ymlandgenerated-values-region-2.ymlto adjust them in your setup.
The OpenShift guide references the cluster's context using CLUSTER_1_NAME and CLUSTER_2_NAME and the namespaces using CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_1 and CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_2.
This guide use a different convention, the convertion can be done as follow:Show OpenShift convertion
export CLUSTER_0="$CLUSTER_1_NAME"
export CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_0="$CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_1"
echo "CLUSTER_0=$CLUSTER_0"
echo "CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_0=$CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_0"
export CLUSTER_1="$CLUSTER_2_NAME"
export CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_1="$CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_2"
echo "CLUSTER_1=$CLUSTER_1"
echo "CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_1=$CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_1"
We will avoid referencing both scenarios of losing either region. Instead, we have generalized the commands and require a one-time setup to configure environment variables, enabling you to execute the procedure based on the surviving region and the one that needs to be recreated. Depending on which region you lost, select the correct tab below and export those environment variables to your terminal for a smoother procedure execution:
- Region 0 lost
- Region 1 lost
export CLUSTER_SURVIVING=$CLUSTER_1
export CLUSTER_RECREATED=$CLUSTER_0
export CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_SURVIVING=$CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_1
export CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_RECREATED=$CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_0
export REGION_SURVIVING=region1
export REGION_RECREATED=region0
echo "You have lost $CLUSTER_RECREATED, $CLUSTER_SURVIVING is still alive"
export CLUSTER_SURVIVING=$CLUSTER_0
export CLUSTER_RECREATED=$CLUSTER_1
export CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_SURVIVING=$CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_0
export CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_RECREATED=$CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_1
export REGION_SURVIVING=region0
export REGION_RECREATED=region1
echo "You have lost $CLUSTER_RECREATED, $CLUSTER_SURVIVING is still alive"
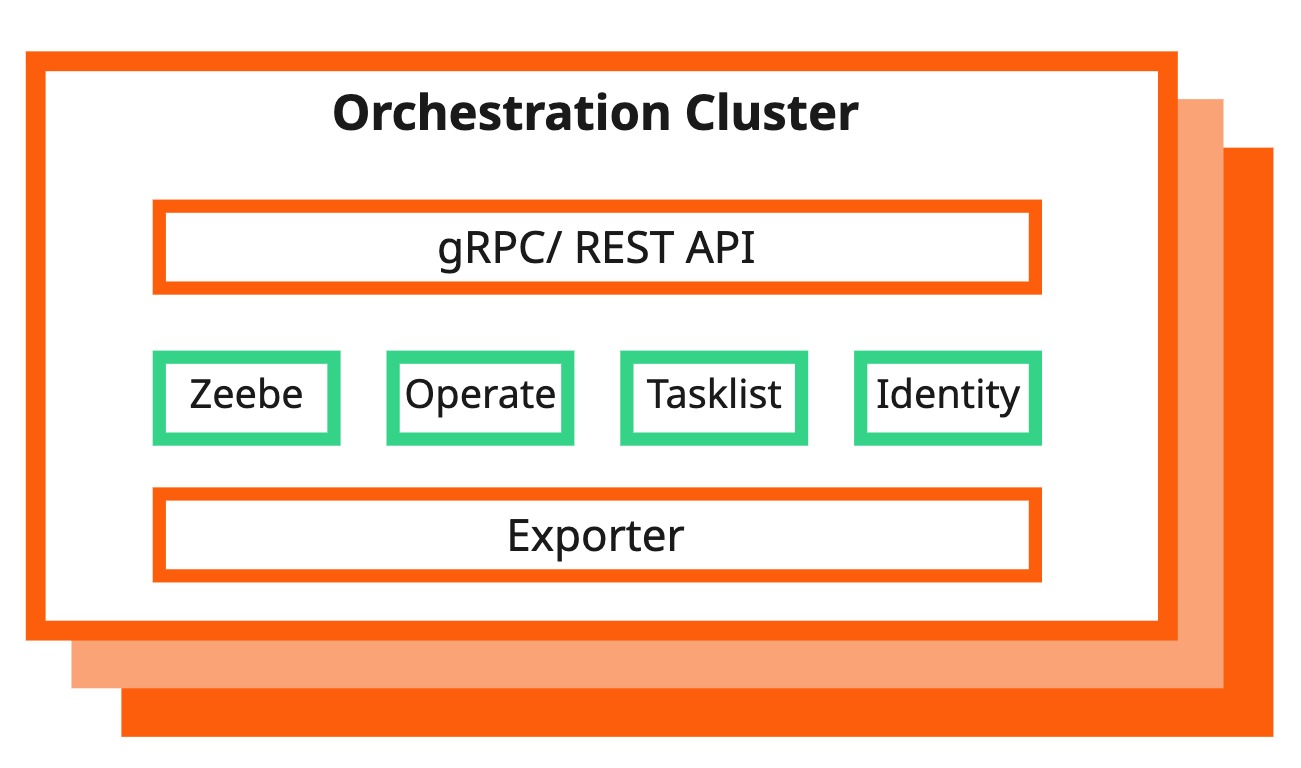
The camunda-zeebe-x pod represents the new architecture that contains the Orchestration Cluster and its components. It includes the former Zeebe Gateway, Operate, Tasklist, the new embedded Identity, and the new Camunda Exporter.
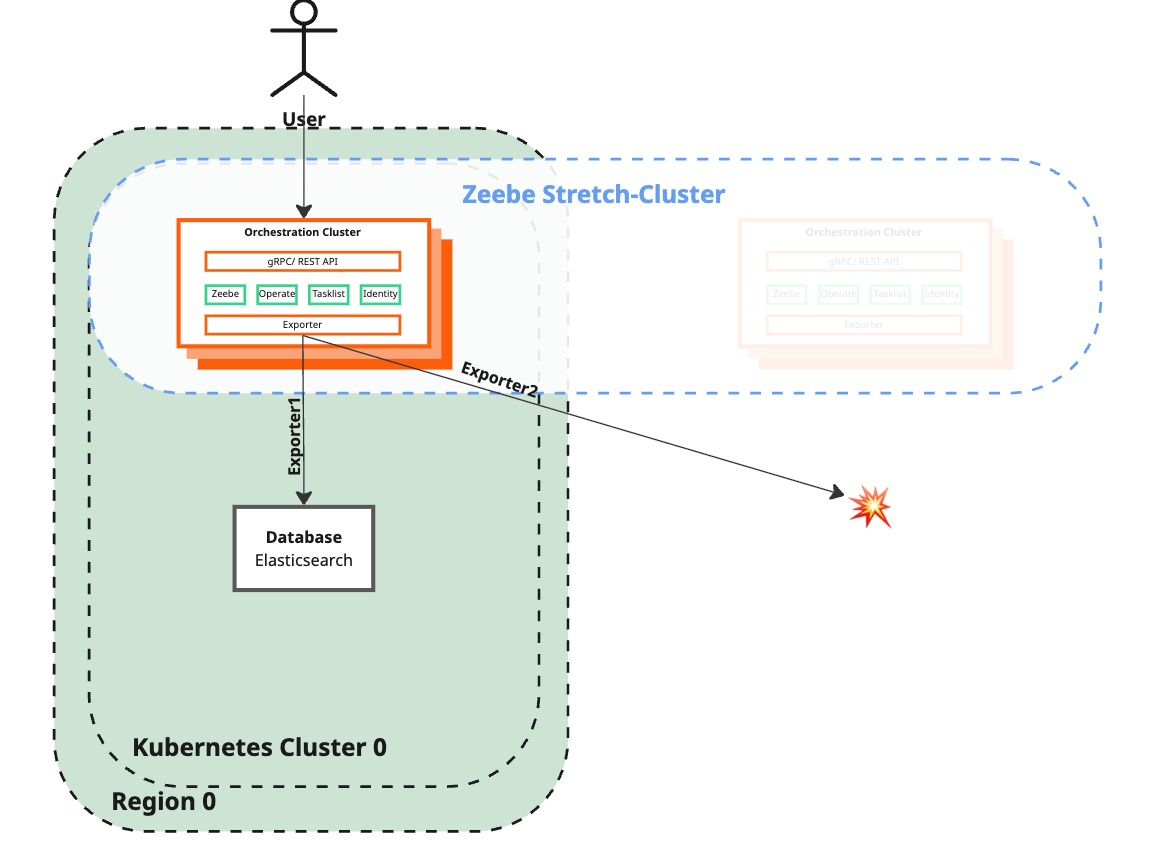
Failover phase
The Failover phase outlines steps for removing lost brokers, redistributing load, disabling Elasticsearch export to a failed region, and restoring user interaction with Camunda 8 to ensure smooth recovery and continued functionality.
- Step 1
- Step 2
Remove lost brokers from Zeebe cluster in the surviving region
Current state
Desired state
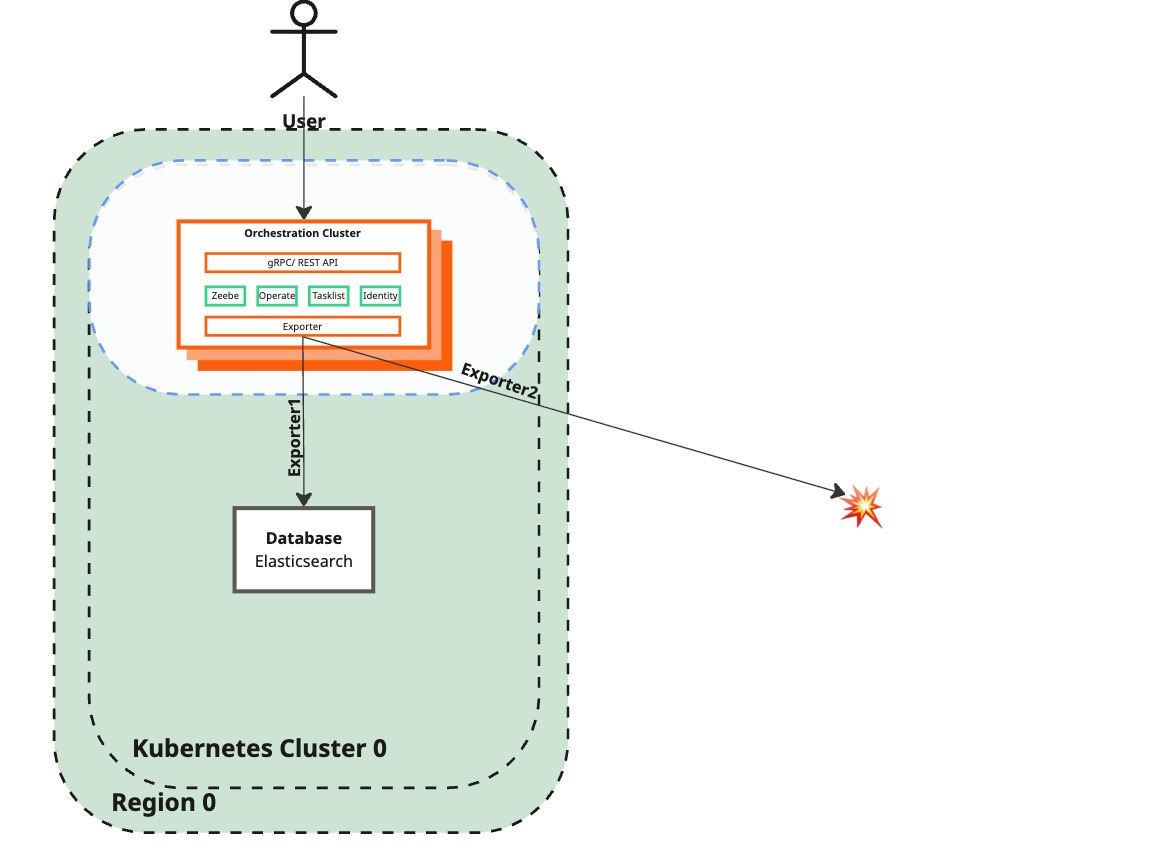
Description / Code
| Current state | Desired state |
|---|---|
| You have ensured that you fully lost a region and want to start the temporary recovery. One of the regions is lost, meaning Zeebe: - No data has been lost thanks to Zeebe data replication. - Is unable to process new requests due to losing the quorum - Stops exporting new data to Elasticsearch in the lost region - Stops exporting new data to Elasticsearch in the survived region | The lost brokers have been removed from the Zeebe cluster. Continued processing is enabled, and new brokers in the failback procedure will only join the cluster with our intervention. |
Procedure
Start with creating a port-forward to the Zeebe Gateway in the surviving region to the local host to interact with the Gateway.
The following alternatives to port-forwarding are possible:
- If the Zeebe Gateway is exposed to the outside of the Kubernetes cluster, you can skip port-forwarding and use the URL directly
execinto an existing pod (such as Elasticsearch), and executecurlcommands from inside of the podrunan Ubuntu pod in the cluster to executecurlcommands from inside the Kubernetes cluster
In our example, we went with port-forwarding to a localhost, but other alternatives can also be used.
-
Use the Orchestration Cluster REST API to retrieve the list of the remaining brokers
kubectl --context $CLUSTER_SURVIVING port-forward services/$CAMUNDA_RELEASE_NAME-zeebe-gateway 8080:8080 -n $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_SURVIVING
curl -L -X GET 'http://localhost:8080/v2/topology' \
-H 'Accept: application/json'
Example output
{
"brokers": [
{
"nodeId": 0,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-0.camunda-zeebe.camunda-london",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 1,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 6,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 7,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 8,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 2,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-1.camunda-zeebe.camunda-london",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 1,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 2,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 3,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 8,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 4,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-2.camunda-zeebe.camunda-london",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 2,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 3,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 4,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 5,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 6,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-3.camunda-zeebe.camunda-london",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 4,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 5,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 6,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 7,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
}
],
"clusterSize": 8,
"partitionsCount": 8,
"replicationFactor": 4,
"gatewayVersion": "8.8.0"
}
{
"brokers": [
{
"nodeId": 0,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-0.camunda-zeebe.camunda-london",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 1,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 6,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 7,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 8,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 2,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-1.camunda-zeebe.camunda-london",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 1,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 2,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 3,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 8,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 4,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-2.camunda-zeebe.camunda-london",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 2,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 3,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 4,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 5,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 6,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-3.camunda-zeebe.camunda-london",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 4,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 5,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 6,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 7,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
}
],
"clusterSize": 8,
"partitionsCount": 8,
"replicationFactor": 4,
"gatewayVersion": "8.8.0"
}
-
Port-forward the Zeebe Gateway service to access the Management REST API:
kubectl --context $CLUSTER_SURVIVING port-forward services/$CAMUNDA_RELEASE_NAME-zeebe-gateway 9600:9600 -n $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_SURVIVING -
Based on the Cluster Scaling APIs, send a request to the Zeebe Gateway to redistribute load to the remaining brokers and remove the lost ones. Depending on which region was lost, you must redistribute to either the even- or odd-numbered brokers. In this example,
region 1was lost, along with the odd-numbered brokers. Therefore, the load is redistributed to the even-numbered brokers. Run the appropriate command for the surviving region to remove the lost brokers and trigger redistribution. Removing the lost (odd-numbered) brokers will automatically redistribute partitions to the remaining (even-numbered) brokers.
- Redistribute to even brokers
- Redistribute to odd brokers
curl -XPATCH 'http://localhost:9600/actuator/cluster?force=true' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"brokers": {
"remove": [1,3,5,7]
}
}'
curl -XPATCH 'http://localhost:9600/actuator/cluster?force=true' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"brokers": {
"remove": [0,2,4,6]
}
}'
Using the force=true parameter reduces the replication factor accordingly.
Verification
Port-forwarding the Zeebe Gateway via kubectl and printing the topology should reveal that the cluster size has decreased to 4, partitions have been redistributed over the remaining brokers, and new leaders have been elected.
kubectl --context $CLUSTER_SURVIVING port-forward services/$CAMUNDA_RELEASE_NAME-zeebe-gateway 8080:8080 -n $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_SURVIVING
curl -L -X GET 'http://localhost:8080/v2/topology' \
-H 'Accept: application/json'
Example output
{
"brokers": [
{
"nodeId": 0,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-0.camunda-zeebe.camunda-london",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 1,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 6,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 7,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 8,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 2,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-1.camunda-zeebe.camunda-london",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 1,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 2,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 3,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 8,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 4,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-2.camunda-zeebe.camunda-london",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 2,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 3,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 4,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 5,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 6,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-3.camunda-zeebe.camunda-london",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 4,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 5,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 6,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 7,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
}
],
"clusterSize": 4,
"partitionsCount": 8,
"replicationFactor": 2,
"gatewayVersion": "8.8.0"
}
{
"brokers": [
{
"nodeId": 0,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-0.camunda-zeebe.camunda-london",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 1,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 6,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 7,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 8,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 2,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-1.camunda-zeebe.camunda-london",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 1,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 2,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 3,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 8,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 4,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-2.camunda-zeebe.camunda-london",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 2,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 3,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 4,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 5,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 6,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-3.camunda-zeebe.camunda-london",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 4,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 5,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 6,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 7,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
}
],
"clusterSize": 4,
"partitionsCount": 8,
"replicationFactor": 2,
"gatewayVersion": "8.8.0"
}
You can also use the Zeebe Gateway's REST API to ensure the scaling progress has been completed. For better output readability, we use jq.
kubectl --context $CLUSTER_SURVIVING port-forward services/$CAMUNDA_RELEASE_NAME-zeebe-gateway 9600:9600 -n $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_SURVIVING
curl -XGET 'http://localhost:9600/actuator/cluster' | jq .lastChange
Example output
{
"id": 2,
"status": "COMPLETED",
"startedAt": "2024-08-23T11:33:08.355681311Z",
"completedAt": "2024-08-23T11:33:09.170531963Z"
}
{
"id": 2,
"status": "COMPLETED",
"startedAt": "2024-08-23T11:33:08.355681311Z",
"completedAt": "2024-08-23T11:33:09.170531963Z"
}
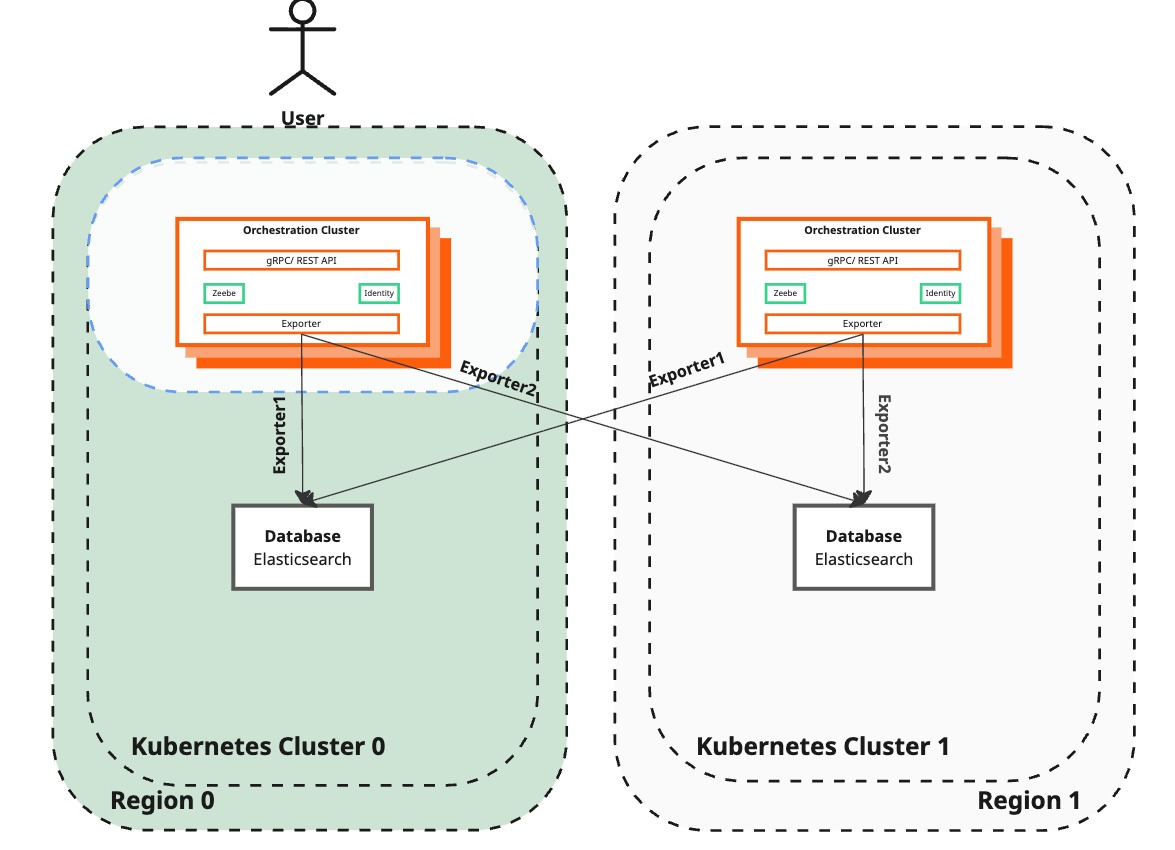
Configure Zeebe to disable the Elastic exporter to the lost region
Current state

Desired state
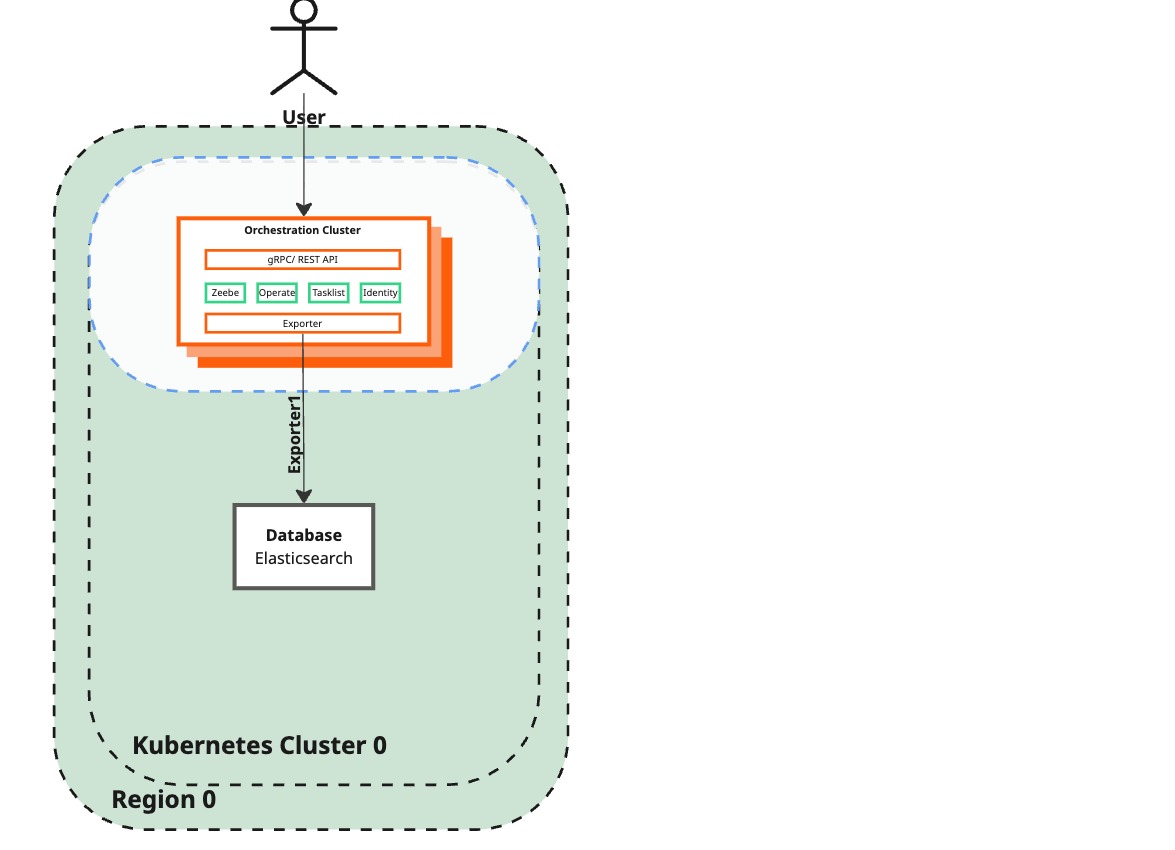
Description / Code
| Details | Current state | Desired state |
|---|---|---|
| Zeebe configuration | Zeebe brokers in the surviving region are still configured to point to the Elasticsearch instance of the lost region. Zeebe cannot continue exporting data. | Elasticsearch exporter to the failed region has been disabled in the Zeebe cluster. Zeebe can export data to Elasticsearch again. |
| User interaction | Regular interaction with Camunda 8 is not restored. | Regular interaction with Camunda 8 is restored, marking the conclusion of the temporary recovery. |
If you have upgraded from a previously migrated 8.7 system, you may still have the legacy elasticsearchregion0 and elasticsearchregion1 exporters configured.
- If both exporters are disabled, you can safely ignore them.
- If they are enabled (for example, because you’re using Optimize), apply the same logic to these exporters as described for the new ones in this guide.
Procedure
-
Port-forward the service of the Zeebe Gateway for the management REST API
kubectl --context $CLUSTER_SURVIVING port-forward services/$CAMUNDA_RELEASE_NAME-zeebe-gateway 9600:9600 -n $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_SURVIVING -
List all exporters to find the corresponding ID. Alternatively, you can check your Helm chart
camunda-values.ymlfile, which lists the exporters as those that had to be configured explicitly.curl -XGET 'http://localhost:9600/actuator/exporters'Example output
[{"exporterId":"camundaregion0","status":"ENABLED"},{"exporterId":"camundaregion1","status":"ENABLED"}] -
Based on the Exporter APIs you will send a request to the Zeebe Gateway to disable the Elasticsearch exporter connected with the lost region.
curl -XPOST 'http://localhost:9600/actuator/exporters/camundaregion1/disable'
Verification
Port-forwarding the Zeebe Gateway via kubectl for the REST API and listing all exporters will reveal their current status.
kubectl --context $CLUSTER_SURVIVING port-forward services/$CAMUNDA_RELEASE_NAME-zeebe-gateway 9600:9600 -n $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_SURVIVING
curl -XGET 'http://localhost:9600/actuator/exporters'
Example output
[{"exporterId":"camundaregion0","status":"ENABLED"},{"exporterId":"camundaregion1","status":"DISABLED"}]
[{"exporterId":"camundaregion0","status":"ENABLED"},{"exporterId":"camundaregion1","status":"DISABLED"}]
Via the already port-forwarded Zeebe Gateway, you can also check the status of the change by using the Cluster API.
curl -XGET 'http://localhost:9600/actuator/cluster' | jq .lastChange
Example output
{
"id": 4,
"status": "COMPLETED",
"startedAt": "2024-08-23T11:36:14.127510679Z",
"completedAt": "2024-08-23T11:36:14.379980715Z"
}
{
"id": 4,
"status": "COMPLETED",
"startedAt": "2024-08-23T11:36:14.127510679Z",
"completedAt": "2024-08-23T11:36:14.379980715Z"
}
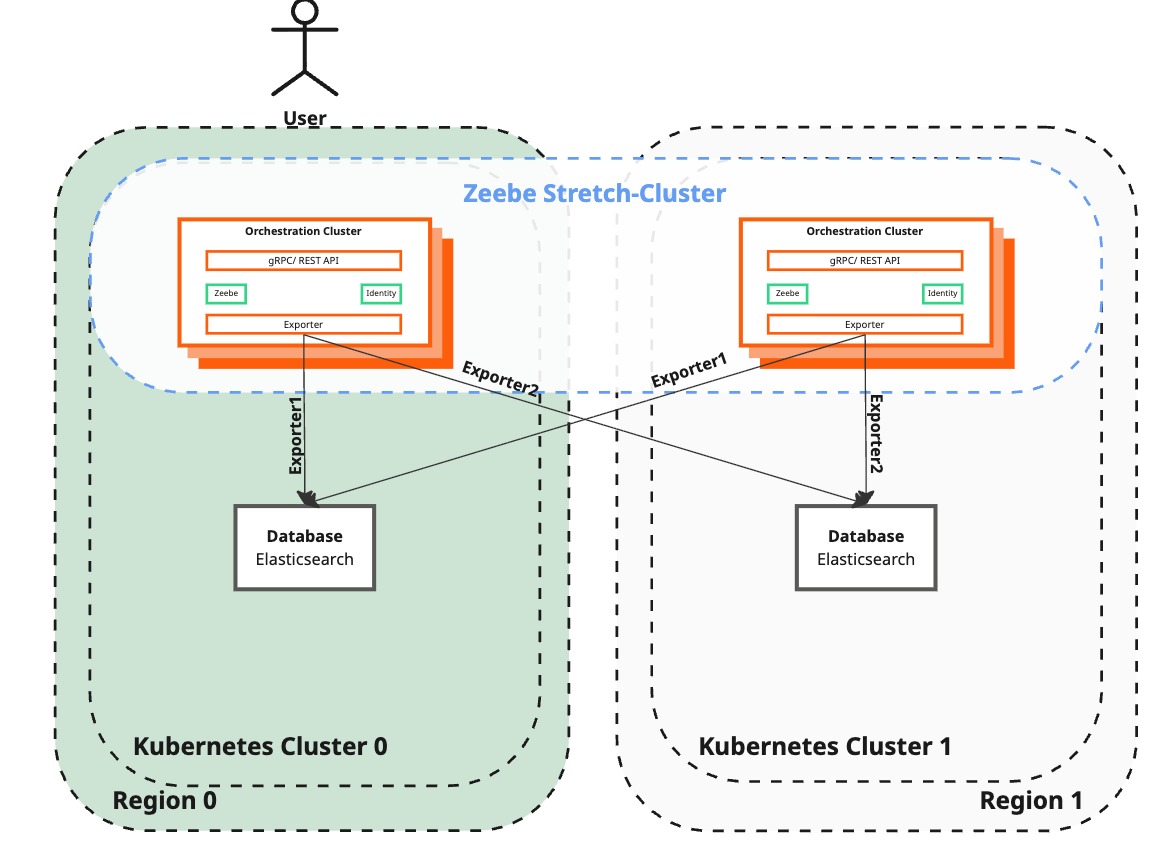
Failback phase
- Step 1
- Step 2
- Step 3
- Step 4
- Step 5
- Step 6
- Step 7
- Step 8
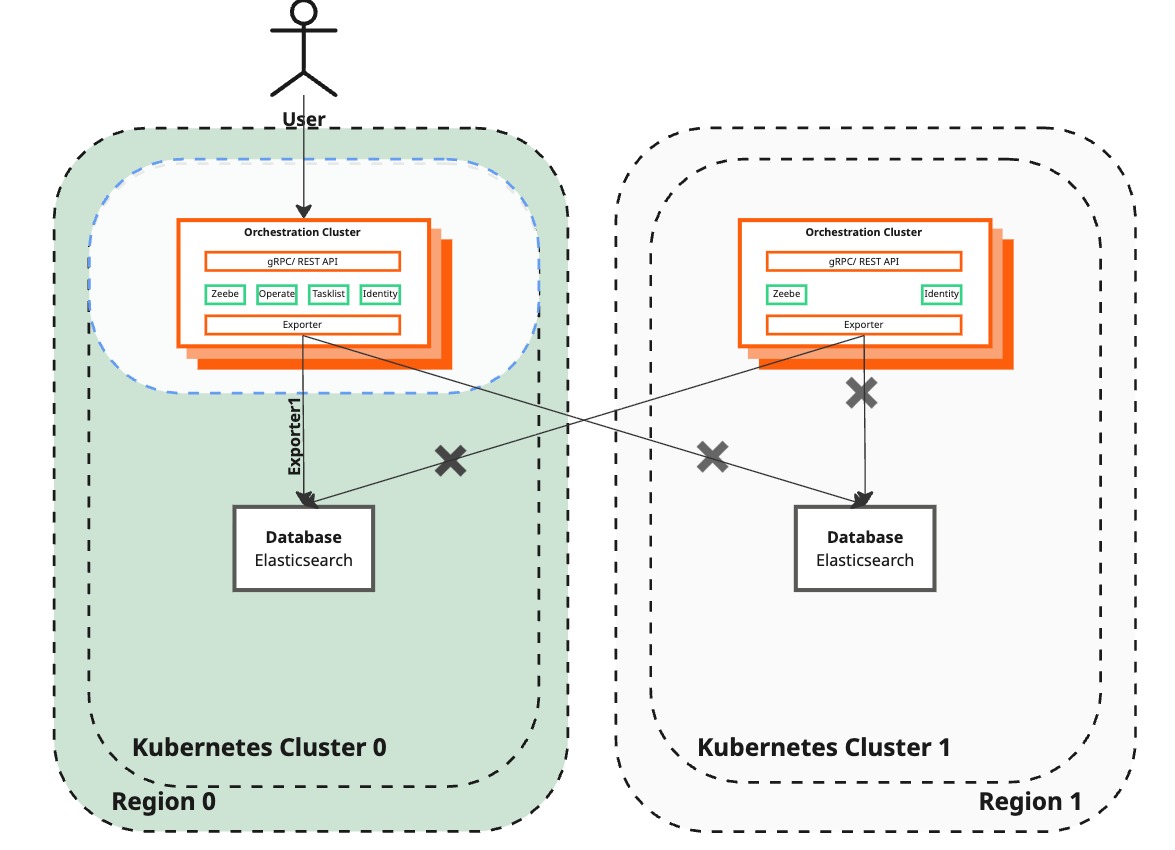
Deploy Camunda 8 in the newly created region
Current state

Desired state
Description / Code
| Details | Current state | Desired state |
|---|---|---|
| Camunda 8 | A standalone region with a fully functional Camunda 8 setup, including the Orchestration Cluster (Zeebe, Operate, Tasklist, Zeebe Gateway) and Elasticsearch. | Restore dual-region functionality by deploying Camunda 8 isolated to the Orchestration Cluster (Zeebe and Zeebe Gateway) and Elasticsearch in the newly restored region. Disable the standalone Schema Manager to prevent seeding Elasticsearch. |
| Operate and Tasklist | Operate and Tasklist are operational in the standalone region. | Keep Operate and Tasklist disabled in the restored region to avoid interference during the database backup and restore process. They will also be disabled in the following steps for the surviving region. |
Procedure
This step involves redeploying the recreated region using the same values files from the initial deployment.
The Helm command also disables Operate and Tasklist. These components will be re-enabled only after region recovery is complete. Keeping them disabled in the newly created region helps prevent data loss, as Operate and Tasklist may still rely on v1 APIs and functionality that are isolated to a single region. Disabling them also prevents user confusion, since no visible updates will appear for their actions while the exporters remain disabled in the following steps.
- EKS
- OpenShift
This procedure requires your Helm values file, camunda-values.yml, in aws/dual-region/kubernetes, used to deploy EKS Dual-region Camunda clusters.
Ensure that the values for ZEEBE_BROKER_EXPORTERS_CAMUNDAREGION0_ARGS_CONNECT_URL and ZEEBE_BROKER_EXPORTERS_CAMUNDAREGION1_ARGS_CONNECT_URL correctly point to their respective regions. The placeholder in ZEEBE_BROKER_CLUSTER_INITIALCONTACTPOINTS should contain the Zeebe endpoints for both regions, the result of the aws/dual-region/scripts/generate_zeebe_helm_values.sh.
This step is equivalent to applying for the region to be recreated:
The standalone Schema Manager must be disabled; otherwise, it will prevent a successful restore of the Elasticsearch backup later on. If you forget to disable it, you must manually remove all created indices in Elasticsearch in the restored region before restoring the backup.
There is no Helm chart option for this setting. Because orchestration.env is an array, it cannot be overwritten through an overlay and must be added manually on a temporary basis.
Edit the camunda-values.yml file in aws/dual-region/kubernetes to include the following under orchestration.env:
orchestration:
env:
- name: CAMUNDA_DATABASE_SCHEMAMANAGER_CREATESCHEMA
value: "false"
# ...
From the terminal context of aws/dual-region/kubernetes execute:
helm install $CAMUNDA_RELEASE_NAME camunda/camunda-platform \
--version $HELM_CHART_VERSION \
--kube-context $CLUSTER_RECREATED \
--namespace $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_RECREATED \
-f camunda-values.yml \
-f $REGION_RECREATED/camunda-values.yml \
--set orchestration.profiles.operate=false \
--set orchestration.profiles.tasklist=false
After successfully applying the recreated region, remove the temporary CAMUNDA_DATABASE_SCHEMAMANAGER_CREATESCHEMA environment variable.
Follow the installation steps recreated region:
-
Setting up the Camunda 8 Dual-Region Helm chart Optional if you already have your pre-configured
generated-values-file.yml -
Once your values file is generated from the installation step, install Camunda 8 only in the recreated region. Adjust the installation command to disable Operate and Tasklist:
--set orchestration.profiles.operate=false \
--set orchestration.profiles.tasklist=falseimportantThe standalone Schema Manager must be disabled; otherwise, it will prevent a successful restore of the Elasticsearch backup later on. If you forget to disable it, you must manually remove all created indices in Elasticsearch in the restored region before restoring the backup.
There is no Helm chart option for this setting. Because
orchestration.envis an array, it cannot be overwritten through an overlay and must be added manually on a temporary basis.Edit the
generated-values-region-1|2.yamlto include the following underorchestration.env:orchestration:
env:
- name: CAMUNDA_DATABASE_SCHEMAMANAGER_CREATESCHEMA
value: "false"
# ...Example command adapted from the installation step:
helm upgrade --install \
"$CAMUNDA_RELEASE_NAME" camunda/camunda-platform \
--version "$HELM_CHART_VERSION" \
--kube-context "$CLUSTER_RECREATED" \
--namespace "$CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_RECREATED" \
-f "<generated-values-region-1|2.yaml>" \
--set orchestration.profiles.operate=false \
--set orchestration.profiles.tasklist=falseAfter successfully applying the recreated region, remove the temporary
CAMUNDA_DATABASE_SCHEMAMANAGER_CREATESCHEMAenvironment variable again.
Verification
The following command will show the pods deployed in the newly created region.
kubectl --context $CLUSTER_RECREATED get pods -n $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_RECREATED
Half of the amount of your set clusterSize is used to spawn Zeebe brokers.
For example, in the case of clusterSize: 8, four Zeebe brokers are provisioned in the newly created region.
It is expected that the Zeebe broker pods will not reach the "Ready" state since they are not yet part of a Zeebe cluster and, therefore, not considered healthy by the readiness probe.
Port-forwarding the Zeebe Gateway via kubectl and printing the topology should reveal that the new Zeebe brokers are recognized but yet a full member of the Zeebe cluster.
kubectl --context $CLUSTER_SURVIVING port-forward services/$CAMUNDA_RELEASE_NAME-zeebe-gateway 8080:8080 -n $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_SURVIVING
curl -L -X GET 'http://localhost:8080/v2/topology' \
-H 'Accept: application/json'
Example output
{
"brokers": [
{
"nodeId": 0,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-0.camunda-zeebe.camunda-london",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 1,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 6,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 7,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 8,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 1,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-0.camunda-zeebe.camunda-paris",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 2,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-1.camunda-zeebe.camunda-london",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 1,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 2,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 3,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 8,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 3,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-1.camunda-zeebe.camunda-paris",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 4,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-2.camunda-zeebe.camunda-london",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 2,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 3,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 4,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 5,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 5,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-2.camunda-zeebe.camunda-paris",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 6,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-3.camunda-zeebe.camunda-london",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 4,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 5,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 6,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 7,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 7,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-3.camunda-zeebe.camunda-paris",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
],
"clusterSize": 4,
"partitionsCount": 8,
"replicationFactor": 2,
"gatewayVersion": "8.8.0"
}
{
"brokers": [
{
"nodeId": 0,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-0.camunda-zeebe.camunda-london",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 1,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 6,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 7,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 8,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 1,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-0.camunda-zeebe.camunda-paris",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 2,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-1.camunda-zeebe.camunda-london",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 1,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 2,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 3,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 8,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 3,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-1.camunda-zeebe.camunda-paris",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 4,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-2.camunda-zeebe.camunda-london",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 2,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 3,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 4,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 5,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 5,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-2.camunda-zeebe.camunda-paris",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 6,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-3.camunda-zeebe.camunda-london",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 4,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 5,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 6,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 7,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 7,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-3.camunda-zeebe.camunda-paris",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
],
"clusterSize": 4,
"partitionsCount": 8,
"replicationFactor": 2,
"gatewayVersion": "8.8.0"
}
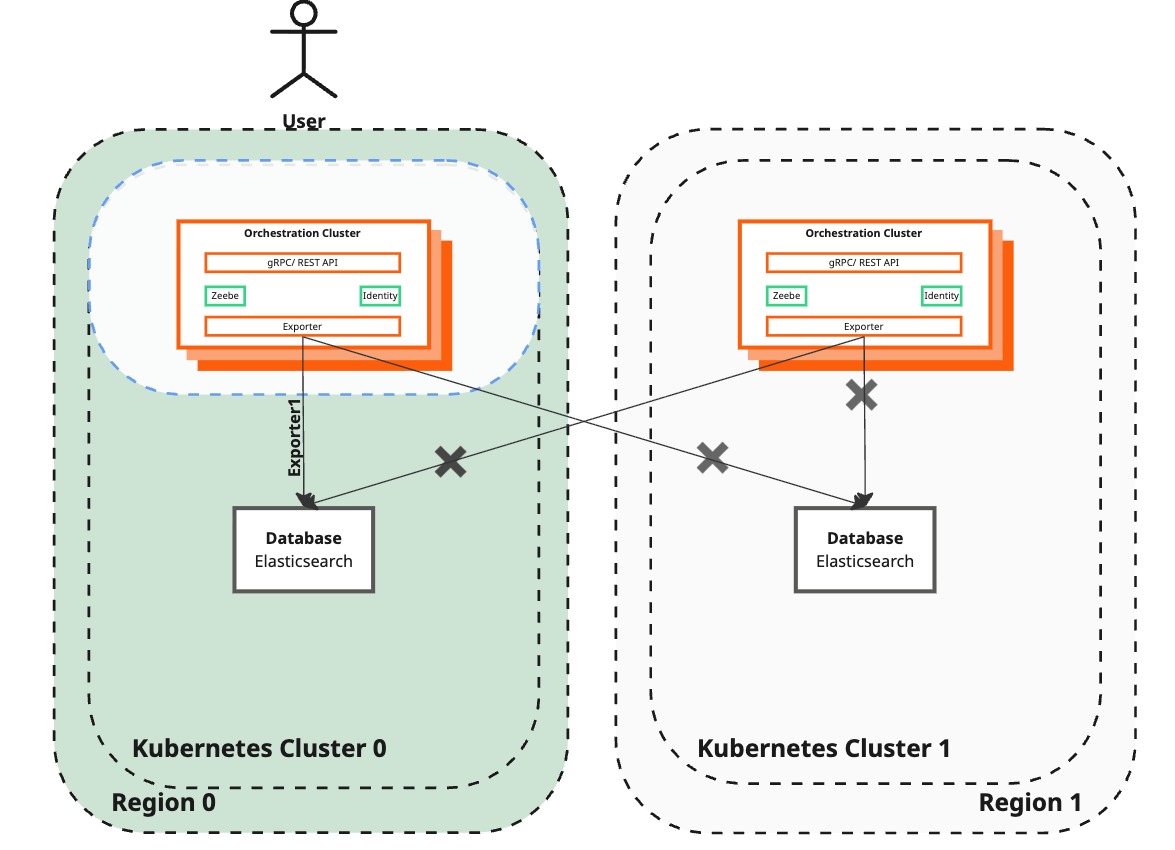
Deactivate Operate and Tasklist in the active region
Current state

Desired state
Description / Code
| Details | Current State | Desired State |
|---|---|---|
| Camunda 8 | The recovered region has been deployed with Operate and Tasklist disabled. Users can still access Operate and Tasklist through the surviving region. | Operate and Tasklist are turned off in the surviving region to avoid data loss during the backup procedure. |
How to get there
With the Orchestration Cluster, Operate and Tasklist are consolidated with the Zeebe Broker and Gateway into a single application.
Similar to Step 1, this step redeploys the active region using the same value files from the initial deployment.
Additionally, the Helm command disables Operate and Tasklist. These components will only be enabled at the end of the full region recovery again.
This step reduces the deployed application to the Zeebe Cluster and Elasticsearch only.
- EKS
- OpenShift
This procedure requires your Helm values file, camunda-values.yml, in aws/dual-region/kubernetes, used to deploy EKS dual-region Camunda clusters.
Ensure that the values for ZEEBE_BROKER_EXPORTERS_CAMUNDAREGION0_ARGS_CONNECT_URL and ZEEBE_BROKER_EXPORTERS_CAMUNDAREGION1_ARGS_CONNECT_URL correctly point to their respective regions. The placeholder in ZEEBE_BROKER_CLUSTER_INITIALCONTACTPOINTS should contain the Zeebe endpoints for both regions, generated by the aws/dual-region/scripts/generate_zeebe_helm_values.sh script.
This step is equivalent to applying the configuration for the recreated region:
If not already done, remove the CAMUNDA_DATABASE_SCHEMAMANAGER_CREATESCHEMA variable from the camunda-values.yml.
Edit the camunda-values.yml in aws/dual-region/kubernetes and remove the following from orchestration.env:
orchestration:
env:
- name: CAMUNDA_DATABASE_SCHEMAMANAGER_CREATESCHEMA
value: "false"
# ...
From the aws/dual-region/kubernetes directory, run:
helm upgrade --install $CAMUNDA_RELEASE_NAME camunda/camunda-platform \
--version $HELM_CHART_VERSION \
--kube-context $CLUSTER_SURVIVING \
--namespace $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_SURVIVING \
-f camunda-values.yml \
-f $REGION_SURVIVING/camunda-values.yml \
--set orchestration.profiles.operate=false \
--set orchestration.profiles.tasklist=false
Follow the installation steps for the surviving region:
-
Set up the Camunda 8 Dual-Region Helm chart (optional if you already have your pre-configured
generated-values-file.yml) -
Once your values file is generated from the installation step, upgrade Camunda 8 only in the surviving region. Adjust the installation command to disable Operate and Tasklist:
--set orchestration.profiles.operate=false`
--set orchestration.profiles.tasklist=false`Example command adapted from the installation step:
helm upgrade --install \
"$CAMUNDA_RELEASE_NAME" camunda/camunda-platform \
--version "$HELM_CHART_VERSION" \
--kube-context "$CLUSTER_SURVIVING" \
--namespace "$CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_SURVIVING" \
-f "<generated-values-region-1|2.yaml>" \
--set orchestration.profiles.operate=false \
--set orchestration.profiles.tasklist=false
Verification
-
If the environment is exposed through an Ingress, verify that Operate and Tasklist are no longer accessible via the Ingress.
-
Check the logs of any
camunda-zeebe-Xpod to confirm that only a subset of profiles are active:kubectl --context $CLUSTER_SURVIVING logs camunda-zeebe-0 | grep "profiles are active"# The default are 5 profiles, so this confirms that Operate and Tasklist are not enabled
io.camunda.application.StandaloneCamunda - The following 3 profiles are active: "broker", "identity", "consolidated-auth" -
Alternatively, verify that the configuration does not list Operate and Tasklist as active profiles:
kubectl --context $CLUSTER_SURVIVING get cm camunda-zeebe-configuration-unified -oyaml | grep spring -A2spring:
profiles:
active: "broker,identity,consolidated-auth"
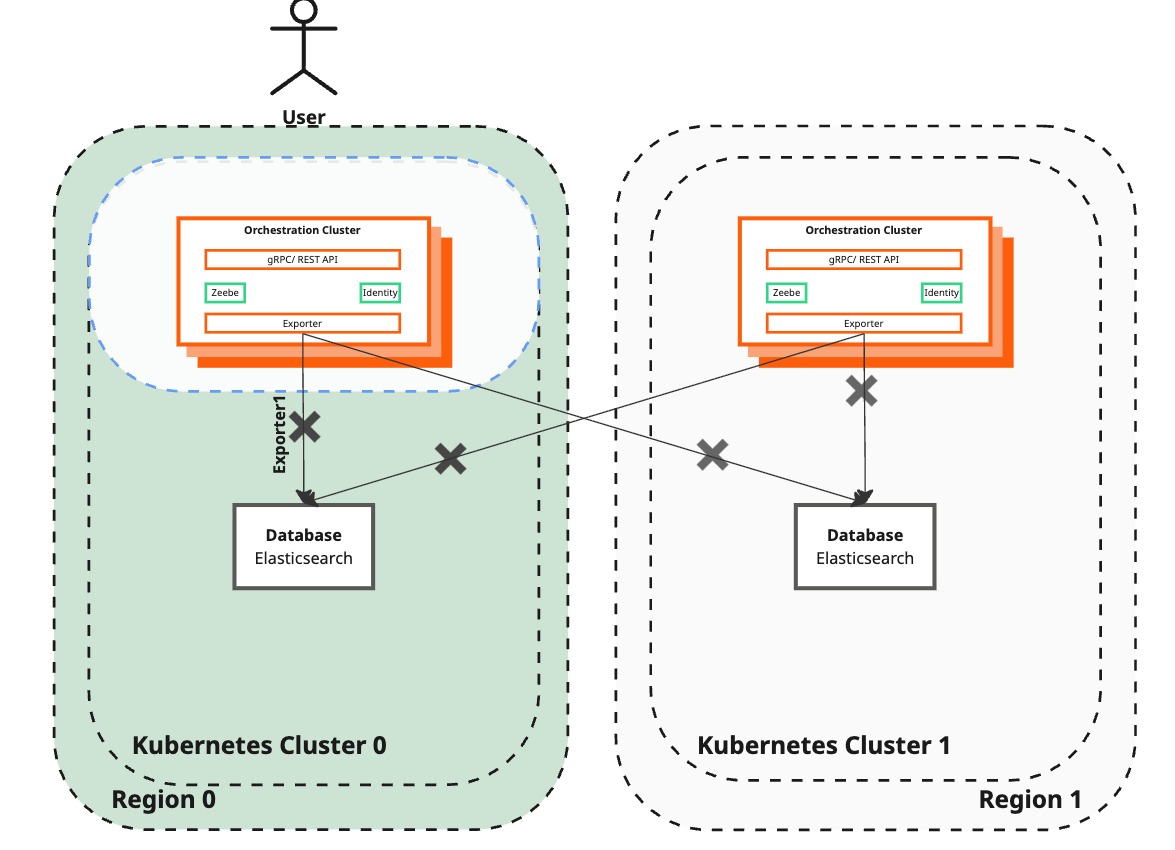
Pause Camunda exporters to Elasticsearch
Current state

Desired state
Description / Code
| Details | Current state | Desired state |
|---|---|---|
| Camunda 8 | The Orchestration Cluster is operating in a single region:
| Preparing the newly created region to take over and restore the dual-region setup. Stop Camunda exporters to prevent new data from being exported to Elasticsearch, allowing an Elasticsearch backup to be created. |
This step does not affect process instances. Process information may not be visible in Operate and Tasklist running in the affected instance.
Procedure
-
Disable the Camunda Exporter exporters in Zeebe using kubectl and the exporting API:
kubectl --context $CLUSTER_SURVIVING port-forward services/$CAMUNDA_RELEASE_NAME-zeebe-gateway 9600:9600 -n $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_SURVIVING
curl -i localhost:9600/actuator/exporting/pause -XPOST
# The successful response should be:
# HTTP/1.1 204 No Content
Verification
There is no API available to confirm the status of the Camunda exporters. A response code of 204 indicates that the disabling was successful. This is a synchronous operation.
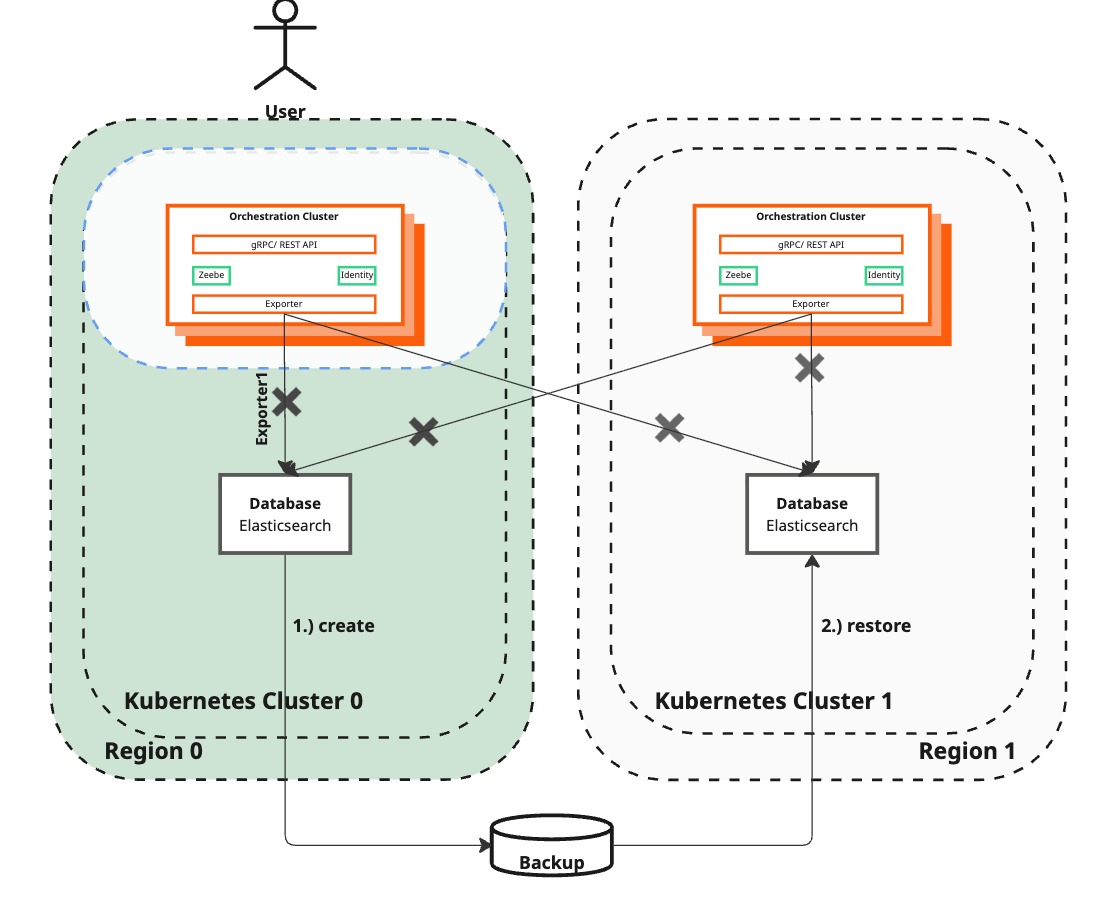
Create and restore Elasticsearch backup
Current state

Desired state
Description / Code
| Details | Current State | Desired State |
|---|---|---|
| Camunda 8 (Zeebe Cluster) | Reachable by end-users but not processing any new process instances nor reflecting User changes. This state allows for data backup without loss. | Remain not processing any new instances nor processing user inputs. |
| Elasticsearch Backup | No backup is in progress. | Backup of Elasticsearch in the surviving region is initiated and being restored in the recreated region, containing all necessary data. The backup process may take time to complete. |
How to get there
This builds on top of the AWS setup and assumes the S3 bucket was automatically created as part of the Terraform execution.
The procedure works for other Cloud providers and bare metal. You have to adjust the AWS S3-specific part depending on your chosen backup source for Elasticsearch. Consult the Elasticsearch documentation on snapshot and restore to learn more about this, and specifically the different supported types by Elasticsearch.
-
Determine the S3 bucket
- EKS
- OpenShift
Retrieve the name of the bucket via Terraform. Go to
aws/dual-region/terraformwithin the repository and retrieve the bucket name from the Terraform state:export S3_BUCKET_NAME=$(terraform output -raw s3_bucket_name)Retrieve the name of the bucket from the verify the pre-requisites step of OpenShift Dual-region step, it should be referenced as the
AWS_ES_BUCKET_NAMEvariable.Export it:
export S3_BUCKET_NAME="$AWS_ES_BUCKET_NAME" -
Configure Elasticsearch backup endpoint in the surviving namespace
CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_SURVIVING:ELASTIC_POD=$(kubectl --context $CLUSTER_SURVIVING get pod --selector=app\.kubernetes\.io/name=elasticsearch -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}' -n $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_SURVIVING)
kubectl --context $CLUSTER_SURVIVING exec -n $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_SURVIVING -it $ELASTIC_POD -c elasticsearch -- \
curl -XPUT 'http://localhost:9200/_snapshot/camunda_backup' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d'
{
"type": "s3",
"settings": {
"bucket": "'$S3_BUCKET_NAME'",
"client": "camunda",
"base_path": "backups"
}
}
' -
Create an Elasticsearch backup in the surviving namespace
CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_SURVIVING. Depending on the amount of data, this operation will take a while to complete. It also explicitly includes the global state, which is required during restore because it contains the Camunda index templates.# The backup will be called failback
kubectl --context $CLUSTER_SURVIVING exec -n $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_SURVIVING -it $ELASTIC_POD -c elasticsearch -- \
curl -XPUT 'http://localhost:9200/_snapshot/camunda_backup/failback?wait_for_completion=true' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"include_global_state": true}' -
Verify the backup has been completed successfully by checking all backups and ensuring the
stateisSUCCESS:kubectl --context $CLUSTER_SURVIVING exec -n $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_SURVIVING -it $ELASTIC_POD -c elasticsearch -- curl -XGET 'http://localhost:9200/_snapshot/camunda_backup/_all'Example output
{
"snapshots": [
{
"snapshot": "failback",
"uuid": "1S_C05K0RjqFyWMfjSKI_A",
"repository": "camunda_backup",
"version_id": 8525000,
"version": "8.18.0",
"indices": [
"camunda-usage-metric-tu-8.8.0_",
"tasklist-metric-8.3.0_",
"camunda-mapping-rule-8.8.0_",
"operate-job-8.6.0_",
"camunda-user-8.8.0_",
"camunda-usage-metric-8.8.0_",
"operate-import-position-8.3.0_",
"camunda-correlated-message-subscription-8.8.0_",
"operate-variable-8.3.0_",
"operate-message-8.5.0_",
"operate-decision-requirements-8.3.0_",
"operate-process-8.3.0_",
"camunda-authorization-8.8.0_",
"operate-decision-instance-8.3.0_",
"operate-list-view-8.3.0_",
"camunda-group-8.8.0_",
"operate-batch-operation-1.0.0_",
"tasklist-form-8.4.0_",
"tasklist-task-variable-8.3.0_",
"operate-metric-8.3.0_",
"camunda-web-session-8.8.0_",
"operate-sequence-flow-8.3.0_",
"tasklist-task-8.8.0_",
"tasklist-draft-task-variable-8.3.0_",
"operate-flownode-instance-8.3.1_",
"operate-event-8.3.0_",
"tasklist-import-position-8.2.0_",
"operate-decision-8.3.0_",
"operate-incident-8.3.1_",
"operate-operation-8.4.1_",
"camunda-role-8.8.0_",
"operate-post-importer-queue-8.3.0_",
"camunda-tenant-8.8.0_"
],
"data_streams": [],
"include_global_state": true,
"state": "SUCCESS",
"start_time": "2025-09-29T11:38:18.285Z",
"start_time_in_millis": 1759145898285,
"end_time": "2025-09-29T11:38:19.292Z",
"end_time_in_millis": 1759145899292,
"duration_in_millis": 1007,
"failures": [],
"shards": {
"total": 33,
"failed": 0,
"successful": 33
},
"feature_states": []
}
],
"total": 1,
"remaining": 0
} -
Configure Elasticsearch backup endpoint in the new region namespace
CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_RECREATED. It's essential to only do this step now as otherwise it won't see the backup:ELASTIC_POD=$(kubectl --context $CLUSTER_RECREATED get pod --selector=app\.kubernetes\.io/name=elasticsearch -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}' -n $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_RECREATED)
kubectl --context $CLUSTER_RECREATED exec -n $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_RECREATED -it $ELASTIC_POD -c elasticsearch -- curl -XPUT 'http://localhost:9200/_snapshot/camunda_backup' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
{
"type": "s3",
"settings": {
"bucket": "'$S3_BUCKET_NAME'",
"client": "camunda",
"base_path": "backups"
}
}
' -
Verify that the backup can be found in the shared S3 bucket:
kubectl --context $CLUSTER_RECREATED exec -n $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_RECREATED -it $ELASTIC_POD -c elasticsearch -- curl -XGET 'http://localhost:9200/_snapshot/camunda_backup/_all'The example output above should be the same since it's the same backup.
-
Restore Elasticsearch backup in the new region namespace
CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_RECREATED. Depending on the amount of data, this operation may take a while to complete.kubectl --context $CLUSTER_RECREATED exec -n $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_RECREATED -it $ELASTIC_POD -c elasticsearch -- \
curl -XPOST 'http://localhost:9200/_snapshot/camunda_backup/failback/_restore?wait_for_completion=true' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"include_global_state": true}' -
Verify that the restore has been completed successfully in the new region:
kubectl --context $CLUSTER_RECREATED exec -n $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_RECREATED -it $ELASTIC_POD -c elasticsearch -- curl -XGET 'http://localhost:9200/_snapshot/camunda_backup/failback/_status'Example output
This is only an example, and the values will differ for you. Ensure you see
state: "SUCCESS", and that the propertiesdoneandtotalhave equal values.{
"snapshots": [
{
"snapshot": "failback",
"repository": "camunda_backup",
"uuid": "1S_C05K0RjqFyWMfjSKI_A",
"state": "SUCCESS",
"include_global_state": true,
"shards_stats": {
"initializing": 0,
"started": 0,
"finalizing": 0,
"done": 33,
"failed": 0,
"total": 33
},
"stats": {
"incremental": {
"file_count": 145,
"size_in_bytes": 353953
},
"total": {
"file_count": 145,
"size_in_bytes": 353953
},
"start_time_in_millis": 1712058365525,
"time_in_millis": 1005
},
"indices": {
...
}
}
]
}
Initialize new Camunda exporter to the recreated region
Current state

Desired state
Description / Code
| Details | Current state | Desired state |
|---|---|---|
| Camunda 8 | Remains unreachable by end-users while restoring functionality. | Start a new exporter to the recreated region. Ensure that both Elasticsearch instances are populated for data redundancy. Separate the initialization step (asynchronous) and confirm completion before resuming the exporters. |
| Elasticsearch Backup | Backup has been created and restored to the recreated region. | N/A |
If you have upgraded from a previously migrated 8.7 system, you may still have the legacy elasticsearchregion0 and elasticsearchregion1 exporters configured.
- If both exporters are disabled, you can safely ignore them.
- If the old exporter is enabled in the survived region (for example, because you’re using Optimize), apply the same logic to these exporters as described for the new ones in this guide.
How to get there
-
Initialize the new exporter for the recreated region by sending an API request via the Zeebe Gateway:
kubectl --context $CLUSTER_SURVIVING port-forward services/$CAMUNDA_RELEASE_NAME-zeebe-gateway 9600:9600 -n $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_SURVIVING
curl -XPOST 'http://localhost:9600/actuator/exporters/camundaregion1/enable' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{"initializeFrom" : "camundaregion0"}'
Verification
Port-forwarding the Zeebe Gateway via kubectl for the REST API and listing all exporters will reveal their current status.
kubectl --context $CLUSTER_SURVIVING port-forward services/$CAMUNDA_RELEASE_NAME-zeebe-gateway 9600:9600 -n $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_SURVIVING
curl -XGET 'http://localhost:9600/actuator/exporters'
Example output
[{"exporterId":"camundaregion0","status":"ENABLED"},{"exporterId":"camundaregion1","status":"ENABLED"}]
[{"exporterId":"camundaregion0","status":"ENABLED"},{"exporterId":"camundaregion1","status":"ENABLED"}]
You can also check the status of the change using the Cluster API via the already port-forwarded Zeebe Gateway.
Ensure the status is "COMPLETED" before proceeding with the next step.
curl -XGET 'http://localhost:9600/actuator/cluster' | jq .lastChange
Example output
{
"id": 6,
"status": "COMPLETED",
"startedAt": "2024-08-23T12:54:07.968549269Z",
"completedAt": "2024-08-23T12:54:09.282558853Z"
}
{
"id": 6,
"status": "COMPLETED",
"startedAt": "2024-08-23T12:54:07.968549269Z",
"completedAt": "2024-08-23T12:54:09.282558853Z"
}
Reactivate Camunda exporter
Current state

Desired state
Description / Code
| Details | Current state | Desired state |
|---|---|---|
| Camunda 8 | Not reachable yet by end-users and currently not exporting any data. Exporters are enabled for both regions, with the operation confirmed to be completed. | Reactivate existing exporters that will allow Zeebe to export data to Elasticsearch again. |
How to get there
-
Reactivate the exporters by sending the exporting API activation request via the Zeebe Gateway:
kubectl --context $CLUSTER_SURVIVING port-forward services/$CAMUNDA_RELEASE_NAME-zeebe-gateway 9600:9600 -n $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_SURVIVING
curl -i localhost:9600/actuator/exporting/resume -XPOST
# The successful response should be:
# HTTP/1.1 204 No Content
Verification
There is currently no API available to confirm the reactivation of the exporters. Only the response code 204 indicates a successful resumption. This is a synchronous operation.
Add new brokers to the Zeebe cluster
Current state

Desired state
Description / Code
| Details | Current state | Desired state |
|---|---|---|
| Camunda 8 | Running in two regions, but not yet utilizing all Zeebe brokers. Operate and Tasklist remain unavailable, Elasticsearch exporters enabled. | Fully functional Zeebe cluster setup utilizing both regions, recovering the main dual-region benefits. |
How to get there
-
From the base Helm values file (
camunda-values.yml) inaws/dual-region/kubernetes, extract theclusterSizeandreplicationFactorvalues. You’ll need these when re-adding the brokers to the Zeebe cluster. -
Port-forward the Zeebe Gateway to access the management REST API. This allows you to send a Cluster API call to add the new brokers to the Zeebe cluster using the previously extracted
clusterSizeandreplicationFactor.In this example, the
clusterSizeis8and thereplicationFactoris4. Because the uneven brokers were lost, re-add them (brokers with IDs1, 3, 5, 7) and set the appropriatereplicationFactorin the request.kubectl --context $CLUSTER_SURVIVING port-forward services/$CAMUNDA_RELEASE_NAME-zeebe-gateway 9600:9600 -n $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_SURVIVING- Re-add uneven brokers
- Re-add even brokers
curl -XPATCH 'http://localhost:9600/actuator/cluster?force=true' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"brokers": {
"add": [1,3,5,7]
},
"partitions": {
"replicationFactor": 4
}
}'curl -XPATCH 'http://localhost:9600/actuator/cluster?force=true' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"brokers": {
"add": [0,2,4,6]
},
"partitions": {
"replicationFactor": 4
}
}'noteThis step can take longer depending on the cluster size, data volume, and current load.
Verification
Port-forwarding the Zeebe Gateway via kubectl for the REST API and checking the Cluster API endpoint will show the status of the last change.
kubectl --context $CLUSTER_SURVIVING port-forward services/$CAMUNDA_RELEASE_NAME-zeebe-gateway 9600:9600 -n $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_SURVIVING
curl -XGET 'http://localhost:9600/actuator/cluster' | jq .lastChange
Example output
{
"id": 6,
"status": "COMPLETED",
"startedAt": "2024-08-23T12:54:07.968549269Z",
"completedAt": "2024-08-23T12:54:09.282558853Z"
}
{
"id": 6,
"status": "COMPLETED",
"startedAt": "2024-08-23T12:54:07.968549269Z",
"completedAt": "2024-08-23T12:54:09.282558853Z"
}
Another way to confirm this is to use the v2 topology REST endpoint to see that partitions are actively re-distributed to the uneven members.
kubectl --context $CLUSTER_SURVIVING port-forward services/$CAMUNDA_RELEASE_NAME-zeebe-gateway 8080:8080 -n $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_SURVIVING
curl -L -X GET 'http://localhost:8080/v2/topology' \
-H 'Accept: application/json'
Example output
{
"brokers": [
{
"nodeId": 0,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-0.camunda-zeebe.camunda-london",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 1,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 6,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 7,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 8,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 1,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-0.camunda-zeebe.camunda-paris",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 1,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 6,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 7,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 8,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 2,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-1.camunda-zeebe.camunda-london",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 1,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 2,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 3,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 8,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 3,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-1.camunda-zeebe.camunda-paris",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 1,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 2,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 3,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 8,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 4,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-2.camunda-zeebe.camunda-london",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 2,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 3,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 4,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 5,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 5,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-2.camunda-zeebe.camunda-paris",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 2,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 3,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 4,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 5,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 6,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-3.camunda-zeebe.camunda-london",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 4,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 5,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 6,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 7,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 7,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-3.camunda-zeebe.camunda-paris",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 4,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 5,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 6,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 7,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
],
"clusterSize": 4,
"partitionsCount": 8,
"replicationFactor": 2,
"gatewayVersion": "8.8.0"
}
{
"brokers": [
{
"nodeId": 0,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-0.camunda-zeebe.camunda-london",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 1,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 6,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 7,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 8,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 1,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-0.camunda-zeebe.camunda-paris",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 1,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 6,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 7,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 8,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 2,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-1.camunda-zeebe.camunda-london",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 1,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 2,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 3,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 8,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 3,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-1.camunda-zeebe.camunda-paris",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 1,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 2,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 3,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 8,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 4,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-2.camunda-zeebe.camunda-london",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 2,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 3,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 4,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 5,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 5,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-2.camunda-zeebe.camunda-paris",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 2,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 3,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 4,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 5,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 6,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-3.camunda-zeebe.camunda-london",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 4,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 5,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 6,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 7,
"role": "leader",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
{
"nodeId": 7,
"host": "camunda-zeebe-3.camunda-zeebe.camunda-paris",
"port": 26501,
"partitions": [
{
"partitionId": 4,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 5,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 6,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
},
{
"partitionId": 7,
"role": "follower",
"health": "healthy"
}
],
"version": "8.8.0"
},
],
"clusterSize": 4,
"partitionsCount": 8,
"replicationFactor": 2,
"gatewayVersion": "8.8.0"
}
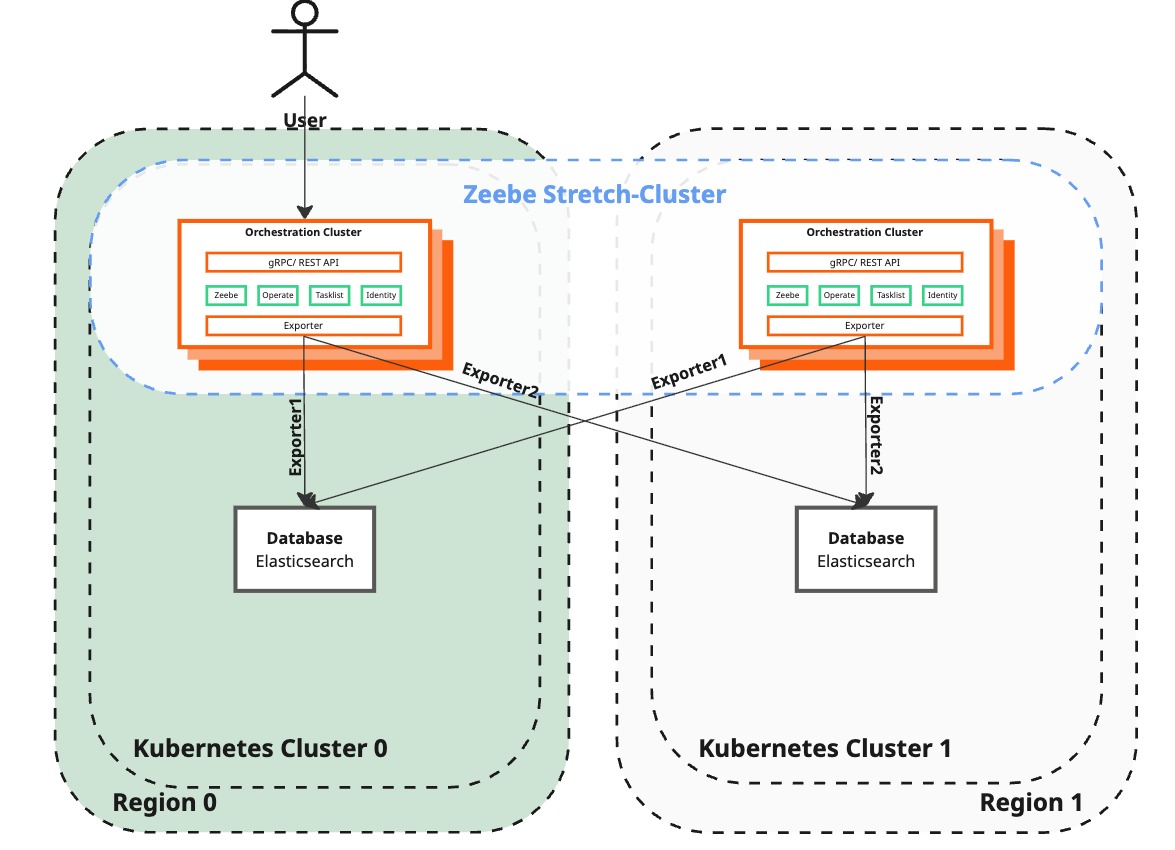
Start Operate and Tasklist
Current state

Desired state
Description / Code
| Details | Current state | Desired state |
|---|---|---|
| Camunda 8 | Remains unreachable by end-users while dual-region functionality is being restored. | Enable Operate and Tasklist in both the surviving and recreated regions to restore user interaction with Camunda 8. |
| User interaction | Users can interact with Zeebe cluster again. Dual-region functionality is restored, improving reliability and performance. | Users can fully utilize the Camunda 8 environment again. |
Procedure
This step is executed at this stage because the application must be redeployed — all components run within the same Kubernetes pod. Performing it earlier would block the automatic rollout, as readiness only complete once Zeebe brokers have joined the cluster. Executing it prematurely would therefore require manual intervention.
Reapply or upgrade the Helm release to enable and deploy Operate and Tasklist.
- EKS
- OpenShift
Assuming based on Step 1 and Step 2, the base Helm values file camunda-values.yml in aws/dual-region/kubernetes includes the adjustments for Elasticsearch and the Zeebe initial brokers.
Make sure to remove the CAMUNDA_DATABASE_SCHEMAMANAGER_CREATESCHEMA variable from camunda-values.yml.
Edit the camunda-values.yml in aws/dual-region/kubernetes and remove the following from the orchestration.env:
orchestration:
env:
- name: CAMUNDA_DATABASE_SCHEMAMANAGER_CREATESCHEMA
value: "false"
# ...
-
Upgrade the Camunda environment in the surviving region (
CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_SURVIVINGandREGION_SURVIVING) to deploy Operate and Tasklist:helm upgrade $CAMUNDA_RELEASE_NAME camunda/camunda-platform \
--version $HELM_CHART_VERSION \
--kube-context $CLUSTER_SURVIVING \
--namespace $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_SURVIVING \
-f camunda-values.yml \
-f $REGION_SURVIVING/camunda-values.yml -
Upgrade the environment in new region (
CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_RECREATEDandREGION_RECREATED) to deploy Operate and Tasklist:helm upgrade $CAMUNDA_RELEASE_NAME camunda/camunda-platform \
--version $HELM_CHART_VERSION \
--kube-context $CLUSTER_RECREATED \
--namespace $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_RECREATED \
-f camunda-values.yml \
-f $REGION_RECREATED/camunda-values.yml
Follow the installation instructions for both regions. You’ll need to apply helm upgrade on both CLUSTER_RECREATED and CLUSTER_SURVIVING.
Make sure to remove the CAMUNDA_DATABASE_SCHEMAMANAGER_CREATESCHEMA variable from camunda-values.yml.
Edit the generated-values-region-1|2.yml file and remove the following from the orchestration.env:
orchestration:
env:
- name: CAMUNDA_DATABASE_SCHEMAMANAGER_CREATESCHEMA
value: "false"
# ...
- Apply the initial installation on the two regions.
- Ensure that the services are exported correctly using
subctl. - This step re-enables Operate and Tasklist in both regions.
Verification
-
If the environment is exposed through an Ingress, verify that Operate and Tasklist are reachable again.
-
Check the logs of any
camunda-zeebe-Xpod to confirm the active profiles.Run this command for both the surviving and recreated clusters (
CLUSTER_RECREATEDandCAMUNDA_NAMESPACE_RECREATED):kubectl --context $CLUSTER_SURVIVING logs camunda-zeebe-0 | grep "profiles are active"# The default are 5 profiles, so this confirms that Operate and Tasklist are enabled
io.camunda.application.StandaloneCamunda - The following 5 profiles are active: "broker", "operate", "tasklist", "identity", "consolidated-auth" -
Alternatively, verify that the configuration lists Operate and Tasklist as active profiles:
kubectl --context $CLUSTER_SURVIVING get cm camunda-zeebe-configuration-unified -oyaml | grep spring -A2spring:
profiles:
active: "broker,operate,tasklist,identity,consolidated-auth"
Conclusion
Following this procedure ensures a structured and efficient recovery process that maintains operational continuity in dual-region deployments. Always manage dual-region environments carefully, and be prepared to follow these steps to perform a successful failover and failback.