Deploy infrastructure with vendor-supported methods
This guide explains how to deploy Camunda 8 infrastructure components using vendor-supported deployment methods as an alternative to the Bitnami subcharts. This approach provides production-grade, officially maintained deployment solutions for PostgreSQL, Elasticsearch, and Keycloak.
Overview
Starting with Camunda 8.8, we continue to strengthen our commitment to robust, production-ready deployments based on solid foundations.
As outlined in our strategy, Camunda reinforces building deployments on solid foundations—primarily managed PostgreSQL and Elasticsearch services, along with external OIDC providers. However, we understand that managed infrastructure components aren't always available in your organization's service catalog.
This guide demonstrates how to integrate these infrastructure components using official deployment methods that don't depend on Bitnami subcharts. Instead, we use vendor-supported deployment approaches—the recommended way to deploy and manage these services in production environments.
If you prefer to continue using Bitnami subcharts, you can enable them by using Bitnami Enterprise images. See Install Bitnami enterprise images for detailed instructions.
Why use vendor-supported deployment methods?
Using official vendor-supported methods provides several advantages over traditional subcharts:
- Vendor maintenance: Each deployment method is maintained by the respective project team (Elastic, CloudNativePG community, Keycloak team) with dedicated engineering resources
- Production-grade features: Built-in management, monitoring, and scaling capabilities designed for enterprise environments
- Enterprise support: Official support channels, dedicated vendor support teams, and comprehensive documentation
- Security-focused: Regular updates and CVE patches from upstream maintainers with specialized security teams
- Advanced lifecycle management: Automated upgrades, failover, and disaster recovery capabilities
- Best practices implementation: Following upstream recommended deployment patterns established by vendor experts
- Vendor expertise: Access to specialized knowledge and troubleshooting from the teams that build these technologies
- Future-proof architecture: Doesn't depend on deprecated Bitnami subcharts, ensuring long-term maintainability
Prerequisites
Before proceeding with this guide, ensure you have:
- Kubernetes cluster: A functioning cluster with
kubectlaccess and block-storage persistent volumes - Cluster admin privileges: Required to install Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs) and operators
- Command-line tools:
kubectlconfigured to access your clusterhelmCLI for deploying Camunda Platformopensslfor generating random passwordsenvsubstcommand (part ofgettextpackage) for environment variable substitution
Architecture overview
This deployment approach separates infrastructure management from application deployment:
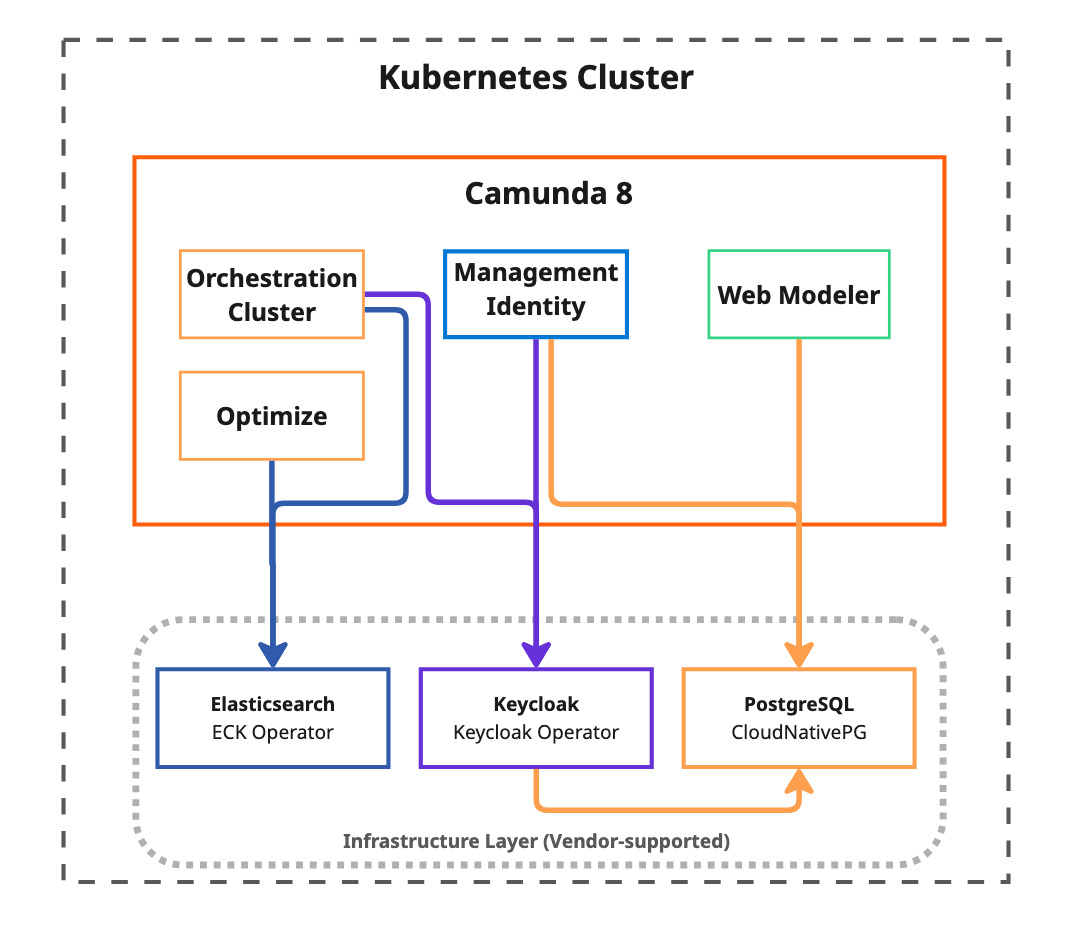
Infrastructure components
This approach uses three vendor-supported infrastructure components, each maintained by their respective project teams:
| Component | Purpose | Official Documentation |
|---|---|---|
| PostgreSQL with CloudNativePG | Production-grade PostgreSQL clusters for Keycloak, Management Identity, and Web Modeler databases | CloudNativePG Documentation |
| Elasticsearch with ECK | Official Elasticsearch deployment for Zeebe records, Operate, Tasklist, and Optimize data storage | ECK Guide |
| Keycloak with Keycloak Operator | Automated OIDC authentication provider for Management Identity | Keycloak Operator Documentation |
Quick start
Step 1: Get deployment resources
All configuration files, deployment scripts, and automation tools referenced in this guide are available in the Camunda deployment references repository:
Repository: camunda-deployment-references
Quick deployment commands
loading...
Then execute:
# Set up environment (required for all deployments)
source ./0-set-environment.sh
# Review and deploy infrastructure components in order
# PostgreSQL deployment
cd postgresql/
cat deploy.sh # Review the deployment script
./deploy.sh
# Elasticsearch deployment
cd ../elasticsearch/
cat deploy.sh # Review the deployment script
./deploy.sh
# Keycloak deployment
cd ../keycloak/
cat deploy.sh # Review the deployment script
./deploy.sh
The deployment scripts (deploy.sh) contain all the necessary steps to install each component. You can either execute them directly or use them as reference for manual deployment or GitOps integration.
Step 2: Environment setup
All deployment scripts require environment variables to be set. This is a prerequisite for all subsequent steps:
loading...
Ensure you source this environment setup before running any deployment scripts in the following sections.
Step 3: Deployment overview
Each infrastructure component should be deployed individually in the following order:
| Order | Component | Dependencies | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PostgreSQL | None | Database clusters for Keycloak, Management Identity, and Web Modeler |
| 2 | Elasticsearch | None | Secondary storage for orchestration cluster components |
| 3 | Keycloak | PostgreSQL | Authentication and identity management |
| 4 | Camunda Platform | All above | Deploy using Helm with vendor-supported infrastructure |
While this guide demonstrates manual deployment using command-line tools, these same configurations can be automated using GitOps solutions like ArgoCD, Flux, or other Kubernetes deployment pipelines. All configuration files referenced in this guide are designed to work seamlessly with declarative deployment approaches.
PostgreSQL deployment
Overview
CloudNativePG is a CNCF project that provides the official Kubernetes deployment method for PostgreSQL. It's designed specifically for cloud-native environments with enterprise-grade features including automated backups, point-in-time recovery, and rolling updates.
Official documentation: CloudNativePG Documentation
Architecture
Our setup provisions three separate PostgreSQL clusters for different Camunda components. Use the latest PostgreSQL version listed in our supported environments matrix that is compatible across the required components:
- pg-identity: Database for Camunda Identity component
- pg-keycloak: Database for Keycloak identity service
- pg-webmodeler: Database for Web Modeler component
If you don't plan to use certain components (for example, Web Modeler), you can simply remove the corresponding cluster definition from the configuration before deployment. This allows you to deploy only the PostgreSQL clusters you actually need, reducing resource consumption.
Installation
Prerequisites: Ensure environment variables are sourced (see Environment setup)
The PostgreSQL deployment follows these steps, automated via the postgresql/deploy.sh script:
loading...
Deployment steps performed by the script:
- Install CloudNativePG operator to
cnpg-systemnamespace - Generate PostgreSQL authentication secrets using
./set-secrets.sh - Deploy three PostgreSQL clusters from
postgresql-clusters.yml - Wait for readiness validation of all clusters
Operator Custom Resources
- PostgreSQL Clusters
This configuration creates three dedicated PostgreSQL clusters, each optimized for its specific use case.
Save as postgresql-clusters.yml:
loading...
Use cases:
pg-keycloak: Database for Keycloak authenticationpg-identity: Database for Management Identity componentpg-webmodeler: Database for Web Modeler component
Execution
- Kubernetes
- OpenShift
- Navigate to PostgreSQL directory:
cd postgresql/ - Review deployment script:
cat deploy.shto understand the deployment steps - Review cluster configuration:
cat postgresql-clusters.ymlto verify PostgreSQL cluster settings - Adapt configuration if needed: Modify
postgresql-clusters.ymlfor your specific requirements (resource limits, storage, etc.) - Execute deployment:
./deploy.sh
- Navigate to PostgreSQL directory:
cd postgresql/ - Review OpenShift deployment script:
cat deploy-openshift.shto understand the OpenShift-specific deployment steps - Review cluster configuration:
cat postgresql-clusters.ymlto verify PostgreSQL cluster settings - Adapt configuration if needed: Modify
postgresql-clusters.ymlfor your specific requirements (resource limits, storage, etc.) - Execute OpenShift deployment:
./deploy-openshift.sh
The deploy-openshift.sh script applies necessary Security Context Constraints (SCC) patches required for CloudNativePG to run properly on OpenShift platforms.
Camunda Helm configuration
The following configuration files integrate PostgreSQL clusters with Camunda components.
Save these files locally and include them in your Helm installation command.
- Management Identity
- Web Modeler
Configure Camunda Identity to use the PostgreSQL cluster.
Save as camunda-identity-values.yml:
loading...
Installation: Add -f camunda-identity-values.yml to your Helm install command.
Configure Web Modeler to use the PostgreSQL cluster.
Save as camunda-webmodeler-values.yml:
loading...
Installation: Add -f camunda-webmodeler-values.yml to your Helm install command.
Elasticsearch deployment
Overview
Elastic Cloud on Kubernetes (ECK) is the official Kubernetes deployment method for Elasticsearch, maintained by Elastic. ECK provides the vendor-recommended approach for deploying Elasticsearch in Kubernetes environments, automatically handling cluster deployment, scaling, upgrades, and security configuration.
Use the latest Elasticsearch version listed in our supported environments matrix and verify compatibility there before deploying.
Official documentation: ECK Guide
Architecture
The ECK deployment creates an Elasticsearch cluster with:
- Three multi-role nodes: Each node is master-eligible and also serves data, ingest, and coordinating roles (no separate master-only tier)
- Security configuration: TLS disabled for internal communication (can be enabled for production)
- Anti-affinity rules: Ensures nodes are distributed across different Kubernetes nodes
- Resource optimization: Configured for Camunda's specific requirements
This topology is an opinionated minimal baseline. Adjust node count/roles (e.g., add dedicated ingest, coordinating, or hot/warm tiers), JVM heap, storage class/size, security (TLS & auth), and other settings to match your workload characteristics, retention, and compliance requirements.
Elasticsearch as the secondary storage for Camunda 8:
Elasticsearch serves as the secondary storage for Camunda 8 orchestration cluster components, providing persistent storage and search capabilities.
Learn more about the secondary storage and how it supports advanced features like web applications, search APIs, process monitoring, task management, and analytics.
Installation
Prerequisites: Ensure environment variables are sourced (see Environment setup)
The Elasticsearch deployment follows these steps, automated via the elasticsearch/deploy.sh script:
loading...
Deployment steps performed by the script:
- Install ECK Custom Resource Definition
- Deploy ECK operator to
elastic-systemnamespace - Create Elasticsearch cluster from
elasticsearch-cluster.yml - Wait for cluster health validation
Operator Custom Resources
- Elasticsearch Cluster
This configuration creates a production-ready Elasticsearch cluster with security enabled.
Save as elasticsearch-cluster.yml:
loading...
Execution
- Navigate to Elasticsearch directory:
cd ../elasticsearch/ - Review deployment script:
cat deploy.shto understand the deployment steps - Review cluster configuration:
cat elasticsearch-cluster.ymlto verify Elasticsearch cluster settings - Adapt configuration if needed: Modify
elasticsearch-cluster.ymlfor your specific requirements (node count, resources, security settings, etc.) - Execute deployment:
./deploy.sh
Camunda Helm configuration
The following configuration integrates ECK-managed Elasticsearch with Camunda components.
Save this file locally and include it in your Helm installation command.
- Elasticsearch Integration
Configure Camunda components to use the ECK-managed Elasticsearch.
Save as camunda-elastic-values.yml:
loading...
Use case: External Elasticsearch connection for all orchestration cluster components (Zeebe, Operate, Tasklist, Optimize).
Installation: Add -f camunda-elastic-values.yml to your Helm install command.
Keycloak deployment
Overview
The Keycloak Operator provides the official vendor-supported way to deploy and manage Keycloak instances on Kubernetes. Maintained by the Keycloak team, it provides the recommended approach for automated deployment, configuration, and lifecycle management.
Use the latest Keycloak version listed in our supported environments matrix.
We use the Camunda-maintained quay-optimized Keycloak image camunda/keycloak:quay-optimized-version as it bundles the Camunda Identity login theme, the /auth base path, the AWS JDBC wrapper, and pre-baked configuration.
Official documentation: Keycloak Operator Documentation
Architecture
The Keycloak deployment provides:
- Database integration: Connects to CloudNativePG-managed PostgreSQL cluster
- Authentication path: Configured to serve under
/authpath prefix - Flexible domain support: Options for local development, ingress-nginx, or OpenShift routes
- Resource optimization: Sized appropriately for typical Camunda authentication loads
- Custom Ingress management: Uses dedicated Ingress manifests integrated within the operator configuration for subpath management constraints
Ingress management
Due to subpath management constraints, the Keycloak operator's built-in Ingress configuration is disabled in favor of dedicated Ingress manifests. This approach provides better control over path routing and TLS certificate management when serving Keycloak under the /auth path prefix.
The dedicated Ingress configuration is integrated directly within the operator manifest to ensure proper deployment coordination and resource management.
Installation
Prerequisites:
- Ensure environment variables are sourced (see Environment setup)
- PostgreSQL must be deployed first (Keycloak requires database)
The Keycloak deployment follows these steps, automated via the keycloak/deploy.sh script:
loading...
Deployment steps performed by the script:
- Install Keycloak Custom Resource Definitions
- Deploy Keycloak operator to the target namespace
- Create Keycloak instance from the selected configuration file
- Wait for Keycloak readiness validation
Operator Custom Resources
- Local deployment
- nginx-ingress
- OpenShift Route
Basic Keycloak instance for local development.
Save as keycloak-instance-no-domain.yml:
loading...
Use case: Local development and testing without external domain.
In certain setups, Keycloak is configured to use its service name as the hostname, which may result in redirections. For local deployments, you need to add the Keycloak service name to your local hosts file (/etc/hosts on Linux and macOS) by adding the entry 127.0.0.1 keycloak-service and use this hostname to access Keycloak.
Production Keycloak instance with nginx-ingress.
Save as keycloak-instance-domain-nginx.yml:
loading...
Use case: Production deployment with external domain using nginx-ingress controller.
Keycloak instance configured for OpenShift Routes.
Save as keycloak-instance-domain-openshift.yml:
loading...
Use case: OpenShift deployment using native Route resources.
Execution
- Navigate to Keycloak directory:
cd ../keycloak/ - Review deployment script:
cat deploy.shto understand the deployment steps - Review instance configuration:
cat keycloak-instance-no-domain.ymlto verify Keycloak instance settings - Adapt configuration if needed: Choose appropriate instance configuration for your setup:
keycloak-instance-no-domain.ymlfor local developmentkeycloak-instance-domain-nginx.ymlfor nginx-ingresskeycloak-instance-domain-openshift.ymlfor OpenShift Routes
- Execute deployment:
./deploy.sh
Camunda Helm configuration
The following configurations integrate Keycloak with Camunda Identity.
Save the appropriate file locally based on your deployment setup and include it in your Helm installation command.
- Local setup
- Production setup
Configure Camunda to use Keycloak for local development.
Save as camunda-keycloak-no-domain-values.yml:
loading...
Use case: Local development setup with port-forwarding access.
Installation: Add -f camunda-keycloak-no-domain-values.yml to your Helm install command.
Configure Camunda to use Keycloak with external domain.
Save as camunda-keycloak-domain-values.yml:
loading...
This configuration file contains ${CAMUNDA_DOMAIN} placeholder variables that must be replaced with your actual domain before deployment.
Options for domain injection:
- Automatic substitution: Use
envsubst < camunda-keycloak-domain-values.yml > camunda-keycloak-domain-values-final.yml(requiresCAMUNDA_DOMAINenvironment variable) - Manual replacement: Replace all instances of
${CAMUNDA_DOMAIN}with your actual domain name incamunda-keycloak-domain-values.yml
Use case: Production setup with external domain and proper OIDC configuration.
Installation: Add -f camunda-keycloak-domain-values.yml to your Helm install command.
Camunda deployment
With all infrastructure components deployed and configured, you can now deploy Camunda using the helm chart.
Prerequisites
Prerequisites:
- Ensure environment variables are sourced (see Environment setup)
- All infrastructure components (PostgreSQL, Elasticsearch, Keycloak) must be deployed first
- Save all configuration files from previous sections locally
Configuration files summary
Before deploying Camunda Platform, ensure you have saved all required configuration files locally. The files are organized by deployment phase:
Infrastructure deployment files (Custom Resources)
| Component | File Name | Purpose | Required for |
|---|---|---|---|
| PostgreSQL | postgresql-clusters.yml | PostgreSQL cluster definitions | Infrastructure deployment |
| Elasticsearch | elasticsearch-cluster.yml | Elasticsearch cluster definition | Infrastructure deployment |
| Keycloak (Local) | keycloak-instance-no-domain.yml | Local Keycloak instance | Infrastructure deployment |
| Keycloak (NGINX) | keycloak-instance-domain-nginx.yml | Production Keycloak with NGINX | Infrastructure deployment |
| Keycloak (OpenShift) | keycloak-instance-domain-openshift.yml | OpenShift Keycloak instance | Infrastructure deployment |
Camunda integration files (Helm values)
| Component | File Name | Purpose | Required for |
|---|---|---|---|
| Elasticsearch | camunda-elastic-values.yml | Connects to ECK-managed Elasticsearch | Camunda deployment |
| PostgreSQL (Identity) | camunda-identity-values.yml | Connects Identity to PostgreSQL cluster | Camunda deployment |
| PostgreSQL (Web Modeler) | camunda-webmodeler-values.yml | Connects Web Modeler to PostgreSQL cluster | Camunda deployment |
| Keycloak (Local) | camunda-keycloak-no-domain-values.yml | Local development OIDC configuration | Camunda deployment |
| Keycloak (Production) | camunda-keycloak-domain-values.yml | Production OIDC configuration | Camunda deployment |
Pre-deployment checklist
Before deploying Camunda Platform:
- All infrastructure components deployed (PostgreSQL, Elasticsearch, Keycloak)
- Configuration files saved locally from previous sections
- Authentication secrets generated (previous section)
Helm deployment
Deploy Camunda Platform using the infrastructure configuration files you saved from previous sections:
# Set the desired Helm chart version - see https://helm.camunda.io/camunda-platform/version-matrix/
export HELM_CHART_VERSION=13.0.0 # Replace with your desired version
For end-to-end configuration patterns (OIDC-enabled "Full Cluster" including Optimize, Web Modeler, Console, and Identity), see the Full Cluster section of our Helm installation guide.
- With external domain
- Local development
Deploy Camunda Platform with external domain configuration:
helm install "$CAMUNDA_RELEASE_NAME" camunda/camunda-platform \
--version $HELM_CHART_VERSION \
-f camunda-elastic-values.yml \
-f camunda-identity-values.yml \
-f camunda-webmodeler-values.yml \
-f camunda-keycloak-domain-values.yml \
-f camunda-values-identity-secrets.yml \
-n "$CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE"
Deploy Camunda Platform for local development:
helm install "$CAMUNDA_RELEASE_NAME" camunda/camunda-platform \
--version $HELM_CHART_VERSION \
-f camunda-elastic-values.yml \
-f camunda-identity-values.yml \
-f camunda-webmodeler-values.yml \
-f camunda-keycloak-no-domain-values.yml \
-f camunda-values-identity-secrets.yml \
-n "$CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE"
Order & precedence: The order of -f flags matters—later files override earlier ones, so place the most specific/override files (e.g. secrets, domain-specific settings) last.
File origin: Every -f file corresponds to a configuration you saved in previous sections (Elasticsearch integration, PostgreSQL clusters, Keycloak, Identity secrets). Make sure they're present locally and reflect any custom adjustments before running the command.
Component flexibility: Drop files for components you don't deploy (for example, remove camunda-webmodeler-values.yml if you're not using Web Modeler) to reduce footprint.
Verification and troubleshooting
Verify infrastructure deployment
Check that all infrastructure components are running correctly:
- PostgreSQL
- Elasticsearch
- Keycloak
# Check PostgreSQL clusters
kubectl get clusters -n $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE
# Verify services
kubectl get svc -n $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE | grep "pg-"
# Check cluster status
kubectl describe cluster pg-identity -n $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE
# Check Elasticsearch cluster
kubectl get elasticsearch -n $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE
# Verify services
kubectl get svc -n $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE | grep "elasticsearch"
# Check cluster health
kubectl get elasticsearch elasticsearch -n $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE -o jsonpath='{.status.health}'
# Check Keycloak instance
kubectl get keycloak -n $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE
# Verify services
kubectl get svc -n $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE | grep keycloak
# Check readiness
kubectl get keycloak keycloak -n $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE -o jsonpath='{.status.conditions[?(@.type=="Ready")].status}'
Common issues and solutions
PostgreSQL cluster not starting
Symptoms: PostgreSQL pods stuck in pending or crash loop
Solutions:
- Verify persistent volume claims are bound:
kubectl get pvc -n $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE - Check node resources and storage availability
- Review CloudNativePG operator logs:
kubectl logs -n cnpg-system deployment/cnpg-controller-manager
Reference: CloudNativePG Troubleshooting
Elasticsearch cluster yellow/red status
Symptoms: Elasticsearch cluster health is not green
Solutions:
- Check disk space and memory allocation
- Verify all nodes are running:
kubectl get pods -n $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACE -l elasticsearch.k8s.elastic.co/cluster-name=elasticsearch - Review ECK operator logs:
kubectl logs -n elastic-system statefulset/elastic-operator
Reference: ECK Troubleshooting Guide
Keycloak authentication errors
Symptoms: Camunda components cannot authenticate with Keycloak
Solutions:
-
Verify Keycloak is accessible:
kubectl port-forward svc/keycloak-service 18080:8080 -n $CAMUNDA_NAMESPACEnoteThis uses
keycloak-service(the service name created by the Keycloak Operator) and port8080(Keycloak's internal port). This differs from Helm chart deployments which usecamunda-keycloakservice name and port80. -
Check client configurations in Keycloak admin console
-
Verify redirect URLs match your deployment setup
Reference: Keycloak Operator Documentation
Production considerations
Security
- Network policies: Implement network policies to restrict traffic between components
- TLS encryption: Enable TLS for all inter-component communication
- Secret management: Use external secret management systems in production
- RBAC: Configure proper role-based access control for infrastructure and applications
Backup and disaster recovery
- Elasticsearch: Perform backups using Camunda for Elastic (see Camunda backup guide).
- PostgreSQL: Configure automated backups using CloudNativePG's backup capabilities
- Keycloak: Configure regular exports of realm and user data
- Configuration: Store all configuration files in version control
Monitoring and observability
- Metrics: Enable Prometheus monitoring for all infrastructure components
- Logging: Aggregate logs from infrastructure and application components
- Alerting: Set up alerts for critical infrastructure events
Resource planning
- CPU and memory: Size clusters based on expected workload
- Storage: Plan for data growth and I/O requirements
- Network: Consider bandwidth requirements between components
Migration from subcharts
If you're migrating from existing Bitnami sub-chart deployments:
- Export data: Create backups of existing databases and Elasticsearch indices
- Deploy vendor-supported infrastructure: Install the vendor-supported infrastructure alongside existing deployment
- Migrate data: Transfer data to vendor-supported services
- Update configuration: Switch Camunda configuration to use new services
- Cleanup: Remove old sub-chart deployments once migration is complete
Additional resources
- CloudNativePG documentation
- Elastic Cloud on Kubernetes guide
- Keycloak Operator documentation
- Camunda 8 Helm chart parameters
- Kubernetes Operator pattern