Camunda components flow control configuration
When internal requests are processed faster than the rate at which they are exported, backlogs of unexported records can occur. Flow control slows the write rate of new records through both static write limits and optional dynamic throttling, and prevents the stream from building an excessive backlog of records not yet exported.
For user commands, this will show up as increased backpressure, observed latency, and reduced throughput. Internal processing slows down as the stream processor waits longer for processing results to be written.
Write rate limiting applies to all new records, including processing results, user commands, inter-partition messages, and scheduled tasks.
Enable flow control
The write rate can be set as a static limit, which defines the upper rate at which records can be written. The dynamic limit, known as throttling, adjusts the write rate based on the exporting rate and backlog, and can be applied alongside the static limit.
A static write rate limit can prevent throughput peaks, and write rate throttling can keep the backlog stable by temporarily decreasing the static limit to keep the exporting backlog small. When configuring dynamic throttling, configuring a high static limit can help maintain a high write rate if the exporting can keep up.
These write limits are enabled by default in SaaS and disabled in Self-Managed. For most use cases, write rate limits can be enabled as needed if an issue arises.
Flow control is configured in your Zeebe Broker's application.yaml file. The default values can be found in the # flowControl section of the Zeebe Broker configuration templates.
zeebe:
broker:
flowControl:
write:
enabled: false
rampUp: 0
limit: 1000
throttling:
enabled: false
acceptableBacklog: 100000
minimumLimit: 100
resolution: 15s
The limit and in-flight count are calculated per partition.
| Field | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
rampUp | The time from startup during which the write limit is slowly increased until the configured limit. Useful for a warm-up period where a lower write rate is beneficial. This value is given in seconds and cannot be set null nor negative. | 0 |
limit | A static value to use as the write rate. This value cannot be null nor negative. | 1000 |
throttling | If enabled, throttling will additionally limit the write rate based on the exporting backlog. The exporting backlog is the quantity of records that were written, but not yet exported. An excessive exporting backlog is usually due to a mismatch of the rate of processed and exported records, or to degraded exporting capability. The throttling algorithm used takes into account the ratio between the acceptable backlog and the actual backlog. If the acceptable backlog is at least twice as long as the real backlog, the current rate is set as the limit. If the ratio between the acceptable backlog and current backlog is less than two, the rate is calculated by multiplying the ratio with the current exporting rate, with minimumLimit as the floor and limit as the ceiling. The intention is to proportionally increase or decrease the rate according to the ratio of the acceptable backlog and the actual backlog. If the acceptable backlog is larger than the current backlog, the rate is increased, and if the acceptable backlog is smaller than the current backlog, the rate is decreased. If the processing speed continues to outpace the exporting speed, the current backlog should stabilize around the acceptable backlog size. | enabled: false |
resolution | The frequency with which throttling is adjusted, given in seconds. Adjusting this value sets the speed at which the processing rate can respond to changes. | 15s |
The exporting rate is the number of exported records per second, averaged out over the last five minutes.
Configure temporary write limits
The flow control endpoint can be used to adjust the flow control configuration temporarily, without having to reset your clusters.
The flow control endpoint is intended as a temporary solution, and changes should be reverted after the issue is addressed. Permanent configuration changes should be made through the environment variables.
Configuring flow control through the available endpoint does not preserve the configuration in the broker state. If the broker restarts, any leader partition in this broker will revert to the defined configuration in the environment variables.
Fetch current configuration
The backup API can be reached via the /actuator management port, which is 9600 by default. The configured context path does not apply to the management port.
The following endpoint can be used to fetch the flow control configuration:
GET actuator/flowControl
Response
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 200 Accepted | The flow configuration was retrieved successfully. |
| 400 Bad Request | Indicates issues with the request. |
| 500 Server Error | All other errors. Refer to the returned error message for more details. |
Example request
curl -X GET 'localhost:9600/actuator/flowControl'
Example response
{
"1": {
"requestLimiter": {
"delegate": {
"limit": 100,
"minLimit": 1,
"maxLimit": 1000,
"backoffRatio": 0.9,
"expectedRTT": 200000000
}
},
"writeRateLimit": {
"enabled": true,
"limit": 4000,
"rampUp": 0.0,
"throttling": {
"enabled": true,
"acceptableBacklog": 100000,
"minRate": 100,
"resolution": 15.0
}
}
}
}
The writeRateLimit value can be null if it has not been defined yet.
Set a new configuration
To set a new flow control configuration, make a POST request to the actuator/flowControl endpoint.
This request will attempt to configure all partitions. Partitions might differ in configuration if, for example, a broker restarts and the leader partition reverts to the configuration defined in the environment variables.
POST actuator/flowControl
{
"write": {
"rampUp": <rampUp>,
"enabled": <enabled>,
"limit": <limit>,
"throttling": {
"enabled": <enabled>,
"acceptableBacklog": <acceptableBacklog>,
"minimumLimit": <minimumLimit>,
"resolution": <resolution>
}
}
}
Response
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 200 Accepted | The flow configuration request was processed correctly. |
| 400 Bad Request | Indicates issues with the request, for example, one of the fields contains an invalid type. |
| 500 Server Error | All other errors. For example, when the values set do not conform to the imposed restriction (such as minimumLimit being higher than limit). Refer to the returned error message for more details. |
Example request
curl -X POST 'localhost:9600/actuator/flowControl' -H "Content-Type: application/json" --data
'{
"write": {
"rampUp": 0,
"enabled": true,
"limit": 2000,
"throttling": {
"enabled": true,
"acceptableBacklog": 100000,
"minimumLimit": 200,
"resolution": 15
}
}
}'
Example response
{
"1": {
"requestLimiter": {
"delegate": {
"limit": 100,
"minLimit": 1,
"maxLimit": 1000,
"backoffRatio": 0.9,
"expectedRTT": 200000000
}
},
"writeRateLimit": {
"enabled": true,
"limit": 4000,
"rampUp": 0.0,
"throttling": {
"enabled": true,
"acceptableBacklog": 100000,
"minRate": 100,
"resolution": 15.0
}
}
}
}
The first value in the response (1 in the example) refers to the partition before the flow configuration is defined.
View write rate limits in Grafana
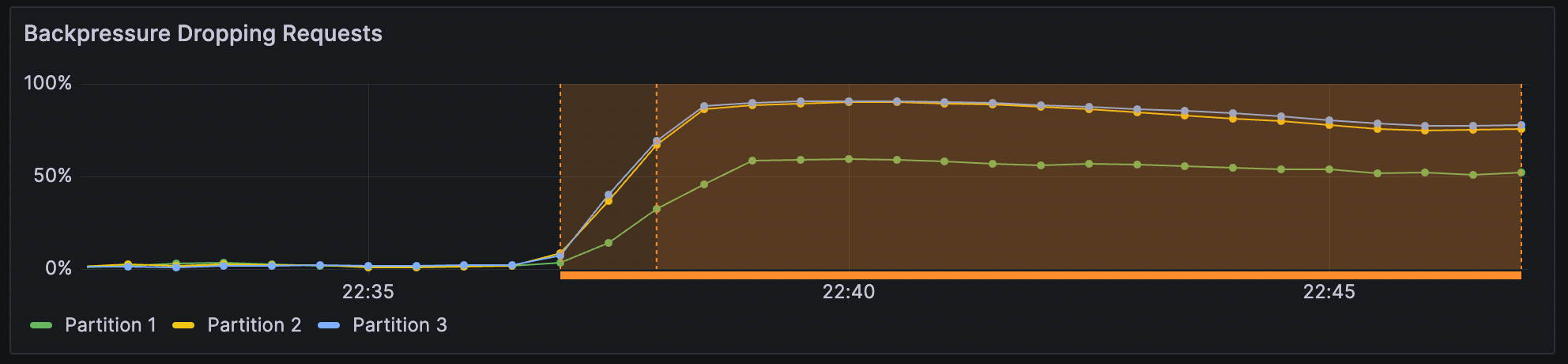
Throttling
Dynamic throttling, when actively acting on the current rate (and not only enabled), displays in Grafana with an underlying yellow bar for the period it was active.
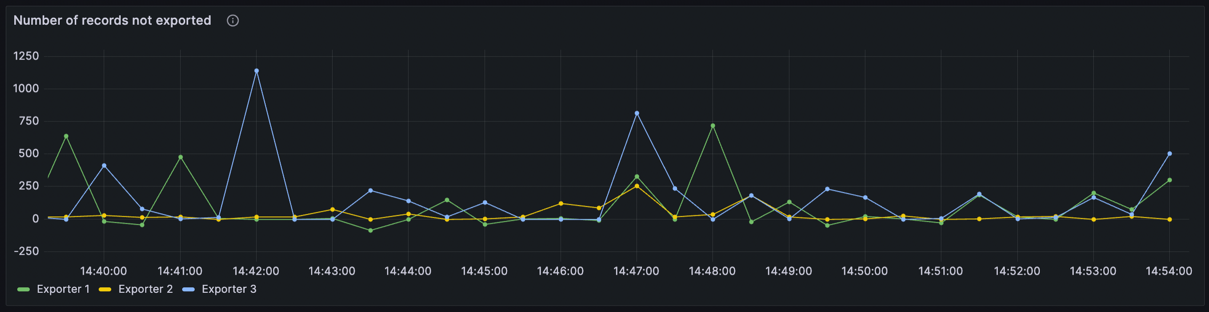
Exporting backlog
The exporting backlog panel is found under the Processing row and displays the number of records not yet exported per partition.
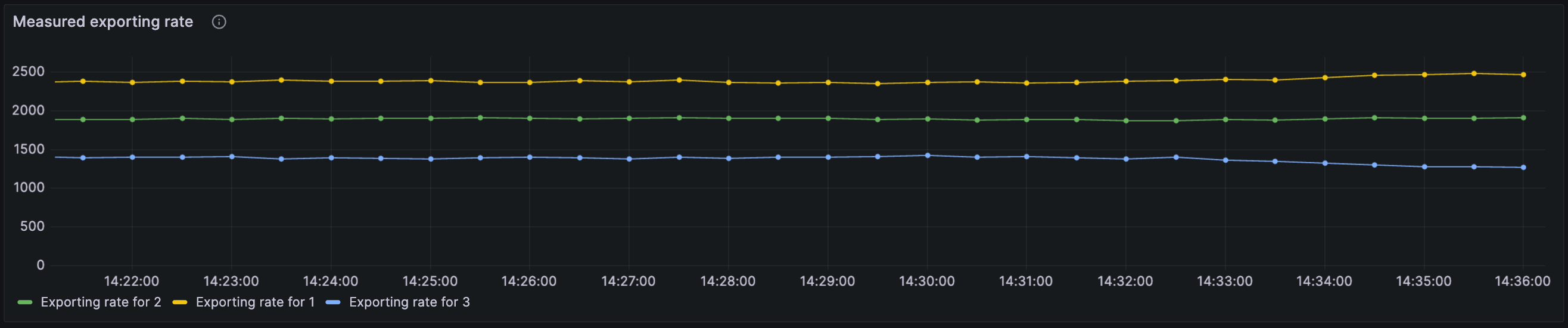
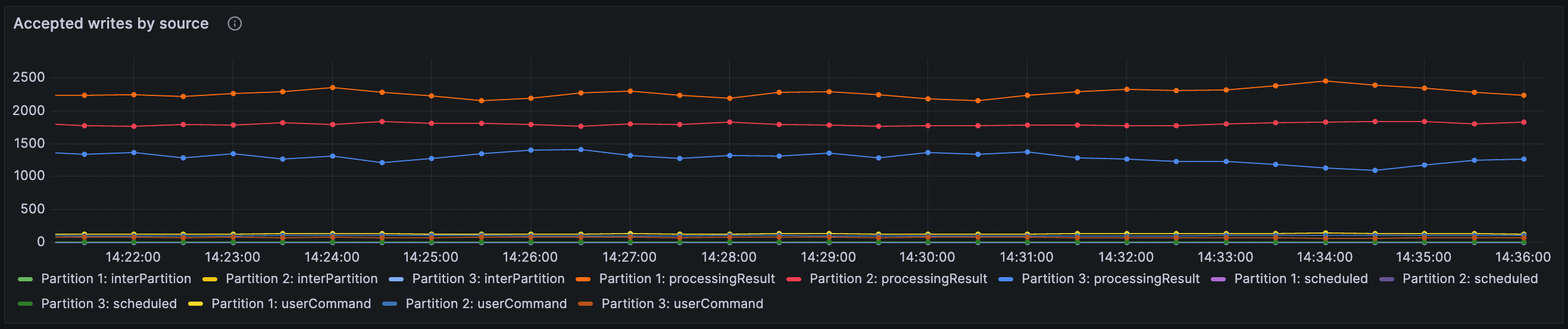
Exporting and write rate
The Measured exporting rate and Accepted writes by source panels are found under the Logstream row. The first shows the number of records accepted by flow control per second, organized by partition and write source (for example, processing result, scheduled tasks, etc.). The second displays measured average exporting rate which may be used to throttle write rate.
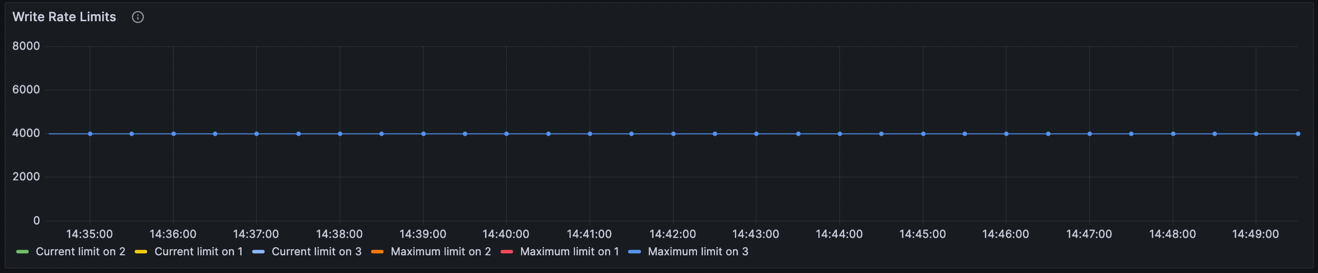
Write rate limit
The Write rate limits panel is under the Logstream row, and displays the current and maximum permissible write rate limit per partition.