Build your first AI agent
Get started with Camunda agentic orchestration by building and running your first AI agent.
About
AI agents represent the practical implementation of agentic process orchestration within Camunda, combining the flexibility of AI with the reliability of traditional process automation.
In Camunda, an AI agent refers to an automation solution that uses ad-hoc sub-processes to perform tasks with non-deterministic behavior.
In this guide, you will:
- Run your AI agent using Camunda 8 SaaS or locally with Camunda 8 Self-Managed.
- Use an AI Agent connector to provide interaction and reasoning capabilities to the AI agent.
- Use an ad-hoc sub-process to define the tools the AI agent should use.
- Integrate a Large Language Model (LLM) into your AI agent.
After completing it, you will have an example AI agent running in Camunda 8.
Prerequisites
To build your first AI agent, see the prerequisites below depending on:
- Your working environment.
- Your chosen model.
Camunda 8 environment
To run your agent, you must have Camunda 8 (version 8.8 or newer) running, using either:
- Camunda 8 SaaS. For example, sign up for a free SaaS trial account.
- Camunda 8 Self-Managed. For example, follow Run your first local project.
Supported models
The AI Agent connector makes it easy to integrate LLMs into your process workflows, with out-of-the-box support for popular model providers such as Anthropic and Amazon Bedrock. It can also connect to any additional LLM that exposes an OpenAI-compatible API. See supported model providers for more details.
In this guide, you can try two use cases:
| Setup | Model provider | Model used | Prerequisites |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud | AWS Bedrock | Claude Sonnet 4 |
|
| Local | Ollama | GPT-OSS:20b |
|
Running LLMs locally requires substantial disk space and memory. GPT-OSS:20b requires more than 20GB of RAM to function and 14GB of free disk space to download.
Step 1: Install the model blueprint
To start building your first AI agent, you can use a Camunda model blueprint from Camunda marketplace.
In this guide, you will use the AI Agent Chat Quick Start model blueprint. Depending on your working environment, follow the corresponding steps below.
- SaaS
- Self-Managed
- In the blueprint page, click For SAAS and select or create a project to save the blueprint.
- The blueprint BPMN diagram opens in Web Modeler.
- In the blueprint page, click For SM and download the blueprint files from the repository.
If you’re using Camunda 8 Run and installed it using the starter package, the blueprint was already downloaded as part of it.
- Open the blueprint BPMN diagram in Desktop Modeler.
About the example AI agent process
The example AI agent process is a chatbot that you can interact with via a user task form.
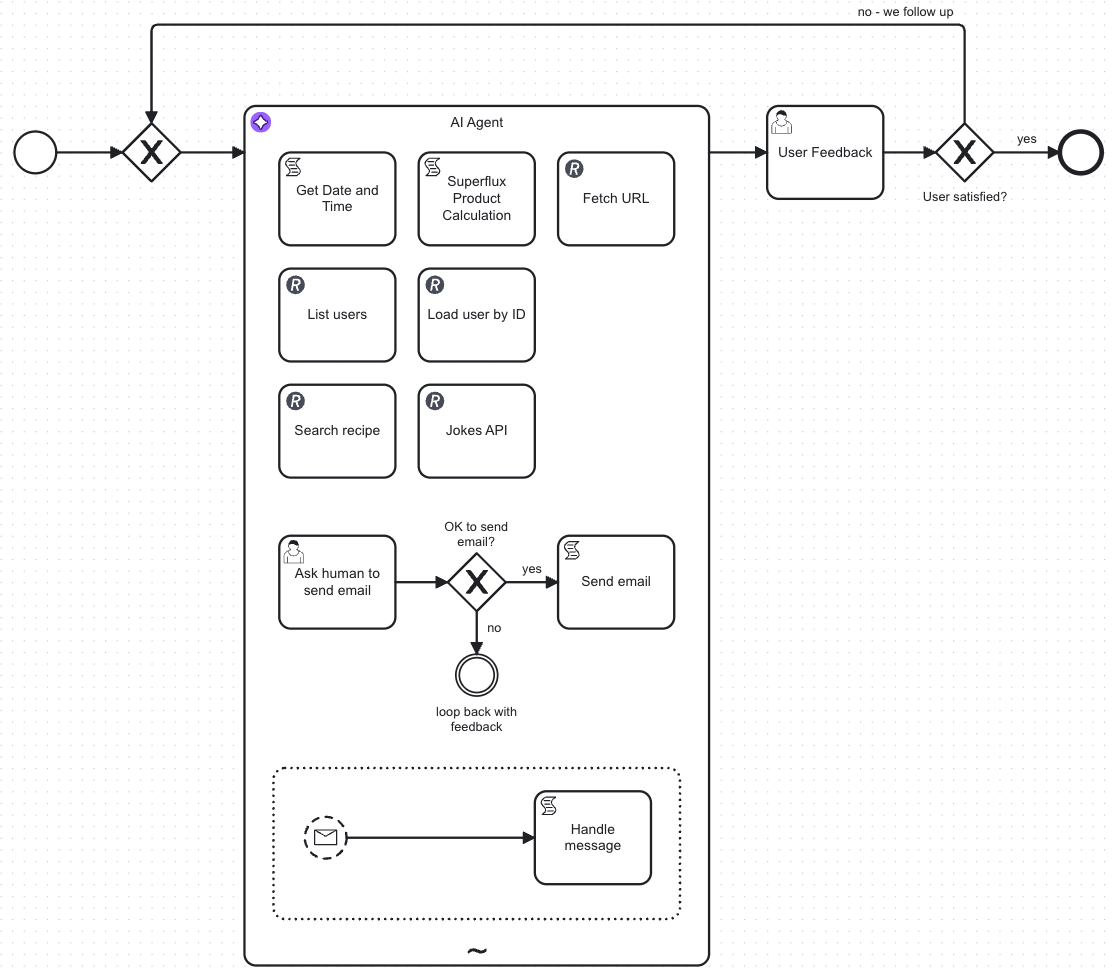
This process showcases how an AI agent can:
- Make autonomous decisions about which tasks to execute based on your input.
- Adapt its behavior dynamically using the context provided.
- Handle complex scenarios by selecting and combining different tools.
- Integrate seamlessly with other process components.
The example includes a form linked to the start event, allowing you to submit requests ranging from simple questions to more complex tasks, such as document uploads.
To make this agent reliable, treat each activity in the ad-hoc sub-process as a documented tool. Learn why this matters in AI agents: Why tool documentation in ad-hoc sub-processes matters.
For a runtime view of what the LLM decides vs. what Camunda orchestrates, see Design and architecture: How execution works in an AI agent.
For prompt configuration details, see AI Agent connector: System prompt, user prompt, and tool descriptions.
Step 2: Configure the AI Agent connector
Depending on your model choice, configure the AI Agent connector accordingly.
- AWS Bedrock
- Ollama
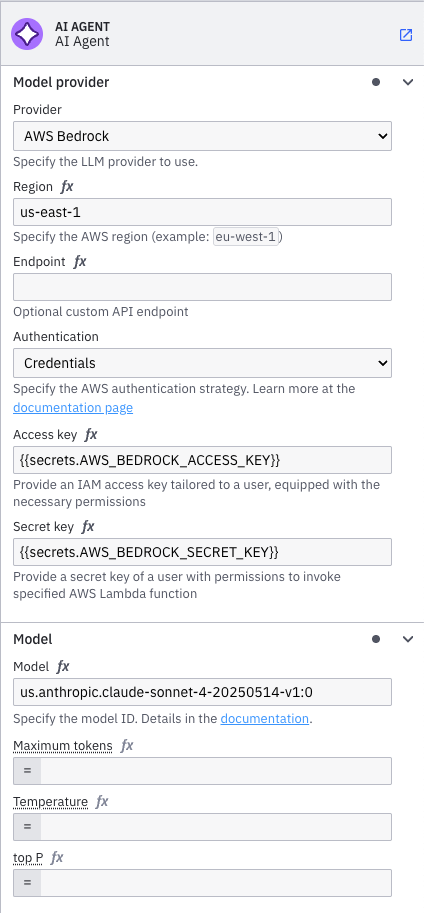
Configure the connector's authentication and template for AWS Bedrock.
Configure authentication
The example blueprint downloaded in step one is preconfigured to use AWS Bedrock. For authentication, it uses the following connector secrets:
AWS_BEDROCK_ACCESS_KEY: The AWS Access Key ID for your AWS account able to call the Bedrock Converse API.AWS_BEDROCK_SECRET_KEY: The AWS Secret Access Key for your AWS account.
You will configure these secrets differently depending on your working environment.
- SaaS
- Self-Managed
Configure the secrets using the Console.
Export the secrets as environment variables before starting the distribution. See Connector secrets for details.
See Amazon Bedrock model provider for more information about other available authentication methods.
Configure properties
In the blueprint BPMN diagram, the AI Agent connector template is applied to the AI Agent service task.
See AI Agent connector for more details.
You can keep the default configuration or adjust it to test other setups. To do so, use the properties panel:
Configure your local LLM with Ollama.
Set up Ollama
- Download and install: Follow Ollama's documentation for details.
- Confirm installation: Check the installed version in a terminal or command prompt by running
ollama --version. - Start the local server: Start it using the application, or run
ollama servein a terminal or command prompt. - Pull the GPT-OSS:20b model: If it isn't installed by default, run
ollama pull gpt-oss:20bin a terminal or command prompt to download the model. - Test: Ollama serves an API at
http://localhost:11434by default. To test it, open that URL in a browser or run this command in your terminal:
curl -X POST http://localhost:11434/v1/chat/completions \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"model":"gpt-oss:20b","messages":[{"role":"user","content":"Hello!"}]}'
Configure properties
The example blueprint downloaded in step one is preconfigured to use AWS Bedrock. Update the connector's configuration using the Model provider and Model sections to use Ollama instead.
Model provider
- Select OpenAI Compatible from the Provider dropdown.
- Enter
http://localhost:11434/v1in the API endpoint field. This is Ollama's default API URL. - No authentication or additional headers are required for the local Ollama API, so leave the remaining fields blank.
Model
- Enter
gpt-oss:20bin the Model field. This field is case-sensitive, so be sure to enter it in all lowercase.
When configuring connectors, use FEEL expressions, by clicking the fx icon, to reference process variables and create dynamic prompts based on runtime data.
Step 3: Test your AI agent
Deploy and run your AI agent in your Camunda cluster.
Whether you are testing your agent in Camunda 8 SaaS or locally with Camunda 8 Self-Managed, make sure you’re running a cluster with version 8.8 or higher.
Depending on your working environment, test your agent by following the corresponding steps below.
- SaaS
- Self-Managed
- Open Web Modeler.
- Select the Play tab.
- Select the cluster you want to deploy and play the process on.
- Open the Start form and add a prompt for the AI agent. For example, enter "Tell me a joke" in the How can I help you today? field, and click Start instance.
- The AI agent analyzes your prompt, decides what tools to use, and responds with an answer. Open the Task form to view the result.
- You can monitor the process execution in Operate.
- You can follow up with more prompts to continue testing the AI agent. Select the Are you satisfied with the result? checkbox when you want to finish your testing and complete the process.
Instead of using Play, you can also test the process within the Implement tab using Deploy & Run, and use Tasklist to complete the form.
- Deploy the process model to your local Camunda 8 environment using Desktop Modeler.
- Open Tasklist in your browser at http://localhost:8080/tasklist.
- On the Processes tab, find the
AI Agent Chat With Toolsprocess and click Start process. - In the start form, add a prompt for the AI agent. For example, enter "Tell me a joke" in the How can I help you today? field, and click Start process.
- The AI agent analyzes your prompt, decides what tools to use, and responds with an answer.
- Select the Tasks tab in Tasklist. When the AI agent finishes processing, you should see either a
User Feedbackor aAsk human to send emailtask waiting for you to complete. - You can monitor the process execution in Operate. Open it in your browser at http://localhost:8080/operate.
- You can follow up with more prompts to continue testing the AI agent. Select the Are you satisfied with the result? checkbox when you want to finish the process.
What to expect during execution
When you run the AI agent process:
- The AI agent receives your prompt and analyzes it together with the configured system prompt and tool descriptions.
- The LLM determines which tools from the ad-hoc subprocess should be activated.
- Camunda executes the selected BPMN activities.
- Tasks can execute in parallel or sequentially, depending on the agent's decisions and process state.
- Process variables are updated as each tool completes its execution.
- The agent may iterate through multiple tool calls to handle complex requests.
You can observe this dynamic behavior in real-time through Operate, where you'll see which tasks were activated and in what order.
Step 4: Add your first tool
You can customize your AI agent by adding tools. To do so, you typically follow these steps:
- Add a BPMN activity inside the ad-hoc sub-process.
- Configure the task implementation, including the connector, service task, user task, and DMN.
- Add a precise tool name and description, and define explicit input and output variables so the LLM can select and call the tool correctly.
- Use
fromAi()for typed inputs, and returntoolCallResultin the outputs.
As an example, you will now add a service task called Get order status inside the AI Agent ad-hoc sub-process.
- Use
fromAi()in the tool's input mapping so the LLM can provide structured inputs:
= {
customerEmail: fromAi(toolCall.customerEmail, "Customer email used to find the order", "string"),
orderId: fromAi(toolCall.orderId, "Order identifier to look up", "integer")
}
- Return the tool response by setting
toolCallResultin the result expression or output mapping:
= {
toolCallResult: {
orderId: orderId,
status: orderStatus,
message: "Order status retrieved successfully"
}
}
At runtime, each tool call produces one toolCallResult, and the ad-hoc multi-instance output collection aggregates them into toolCallResults for the AI Agent connector.
For your own tools, review the tasks already available to the agent in this blueprint and apply a similar pattern for fromAi() inputs and toolCallResult and toolCallResults outputs.
Next steps
Now that you’ve built your first Camunda AI agent, why not tailor it further?
For example:
- Add and configure more tools in the ad-hoc sub-process that the AI agent can use.
- Update the system prompt to adjust the AI agent's behavior.
- Experiment with different model providers and configurations in the AI Agent connector.
- Monitor your AI agents.
- Learn more about Camunda agentic orchestration and the AI Agent connector.
Register for the free Camunda 8 - Agentic Orchestration course to learn how to model, deploy, and manage AI agents in your end-to-end processes.