What's new in Camunda 8.8
Learn about important changes in Camunda 8.8 to consider when planning your upgrade from Camunda 8.7.
This documentation is a work in progress and may contain incomplete, placeholder, or evolving content. While the core concepts introduced in Camunda 8.8 are stable, specific details are actively being refined.
Introducing Camunda 8.8
Camunda 8.8 introduces important architectural changes and enhancements to simplify deployment, improve maintainability, and empower both operations teams and developers.
Why upgrade to Camunda 8.8?
Upgrading to Camunda 8.8 delivers significant benefits:
-
Unified platform: Camunda 8.8 combines core components into a single Orchestration Cluster, reducing system complexity, centralizing operations, and simplifying both deployment and maintenance.
-
Enhanced productivity: This upgrade introduces streamlined identity and access management, a consolidated configuration model, and modernized & consolidated APIs and SDKs, making development, integration, and permission handling faster and more intuitive.
-
Increased efficiency: The new unified exporter architecture improves performance with accelerated data visibility in Operate and Tasklist, as well as available via query APIs. It also enables easier operation and administration, and improves resilience when deploying across multiple data centers.
To learn more about the benefits of upgrading to Camunda 8.8, see the blog posts streamlined deployment with Camunda 8.8 and introducing enhanced Identity Management in Camunda 8.8.
Summary of important changes
Important changes introduced in Camunda 8.8 are summarized as follows:
| What's new/changed | Summary |
| Orchestration Cluster | The Orchestration Cluster (previously automation cluster) is now the core Camunda 8 component. |
| Identity, authentication, and authorization | Identity management is now split into two scopes for improved access management, performance, and flexible integration with any OIDC-compatible Identity Provider:
|
| APIs & tools | New and changed APIs & tools are introduced in Camunda 8.8. |
The simplest Camunda 8.8 Self-Managed deployment runs as a single Java application or docker container.
- See release announcements, release notes, and the quality board for more detail on what's included in Camunda 8.8.
- Ready to upgrade? See our upgrade guides to learn more about upgrading from Camunda 8.7 to 8.8.
Orchestration Cluster
The primary architectural change is the consolidation of the core Zeebe, Operate, Tasklist, and Identity components into the Orchestration Cluster (a single unified deployable package). This impacts how Camunda 8 is deployed, managed, and scaled.
The Orchestration Cluster (previously automation cluster) is now the core component of Camunda 8.
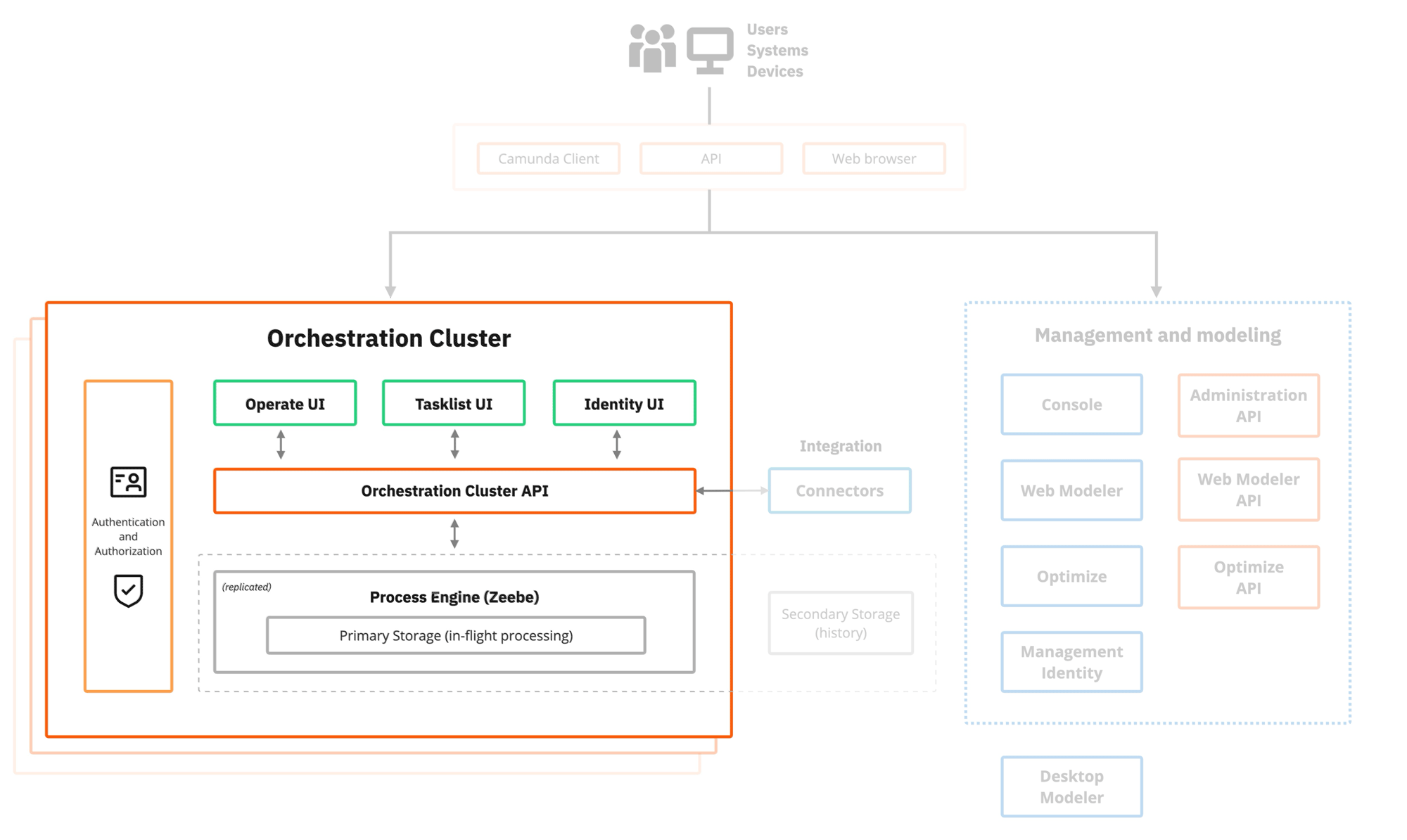
Zeebe, Operate, Tasklist, and Identity
In Camunda 8.8, Zeebe, Operate, Tasklist, and Identity are integrated into the Orchestration Cluster application as a single deployable artifact, distributed as a JAR file or Docker container.
- Zeebe is the workflow engine.
- Operate is used for monitoring and troubleshooting process instances running in Zeebe.
- Tasklist is used for interacting with user tasks (assigning, completing, and so on).
- Identity is used for managing the integrated Orchestration Cluster authentication and authorization.
In Camunda 8.7 and earlier, each component (Zeebe, Operate, Tasklist, and Identity) was deployed independently.
Unified Orchestration Cluster REST API
Camunda 8.8 introduces a single unified Orchestration Cluster REST API you can use to interact programmatically with the Orchestration Cluster.
- This replaces component APIs (Operate API, Tasklist API, Zeebe API, and much of Identity API) with a single set of endpoints.
- This unified API supports both organizational (SaaS) and Self-Managed deployments.
- This is now the default and recommended integration point for developers, operators, and automation solutions.
Unified Exporter
Camunda 8.8 introduces a new unified exporter architecture to improve cluster management and data migration. The new exporter architecture provides two dedicated Helm jobs for Identity migration and process application migration.
In Camunda 8.7 and earlier, dedicated importers/exporters were used for data flows between components (such as Elasticsearch import/export).
Unified component configuration
Camunda 8.8 introduces a unified configuration for Orchestration Cluster components where you can define all essential cluster and component behavior through a single, centralized configuration system.
In Camunda 8.7 and earlier, managing and configuring core components (Zeebe, Operate, Tasklist, Identity) was done separately.
Identity, authentication, and authorization
The Orchestration Cluster Identity component UI handles authentication and authorization for the Orchestration Cluster components and its resources.
With this 8.8 change, the source of truth for Identity and Access Management for the Orchestration Cluster (including Zeebe, Operate, Tasklist, and its APIs) is now the Orchestration Cluster itself. This removes the reliance on the separate Management Identity (formerly "Identity") component.
Identity and Management Identity
In Camunda 8.8, Orchestration Cluster Identity and Management Identity are two separate components used for Identity management, each with distinct areas of responsibility.
| Identity | Management Identity |
|---|---|
Access and permission management for all Orchestration Cluster components: Zeebe, Operate, Tasklist, and the Orchestration Cluster REST and gRPC API.
| Continues to manage access for platform components such as Web Modeler, Console, and Optimize.
|
Who is affected by 8.8 Identity changes?
The 8.8 changes to Identity could affect different user roles in your Organization. For example:
| Role | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Administrators | Understand the new Identity setup and migration steps from Camunda 8.7. |
| Developers | Learn the new authorization concepts and required permissions for API access. |
| Information Security | Review and adapt to the new Identity architecture. |
Benefits
Orchestration Cluster Identity provides several advantages:
- Simplified identity management: The split between Orchestration Cluster Identity and Management Identity provides a clearer separation of concerns, making it easier to manage access for Orchestration Cluster components versus Web Modeler and Console.
- Unified access management: All identity and authorization features for the Orchestration Cluster components are now contained within the Orchestration Cluster, eliminating any dependency on Management Identity when orchestrating processes.
- Simplified deployment and improved availability: Removing the dependency on Management Identity streamlines deployment and increases availability by reducing potential points of failure.
- Consistent authorization model: The new model offers a unified approach to managing permissions across all Orchestration Cluster resources.
- Enhanced security: Granular access controls improve the overall security posture for cluster resources.
- Improved performance: Authorization checks are handled internally, reducing latency and improving performance.
- Flexible Identity Provider integration: Keycloak is now treated as a standard OIDC provider, making it easier to integrate with other Identity Provider and increasing flexibility for users.
Impact of Identity changes on your 8.7 deployment
The impact of these changes and what action you need to take depends on your deployment type. For example:
| Area | Impact |
|---|---|
| Authorization | The new authorization model introduces fine-grained access control for Orchestration Cluster resources, replacing the previous model. |
| Roles, tenants, and mapping rules | Now managed within Orchestration Cluster Identity, replacing the previous Management Identity setup. |
| User Task authorizations | User Task access restrictions only apply to the Tasklist v1 API. After switching to the v2 API with Tasklist, user task access restrictions do not apply. |
Each deployment type has a clear upgrade path and migration guidance to help administrators transition from Camunda 8.7 to Camunda 8.8.
Camunda 8 SaaS
Resource authorizations, groups, and roles formerly managed via Console are replaced by authorizations, groups, and roles managed within the cluster-specific Identity.
- These are automatically migrated during the Camunda 8.8 upgrade to preserve your existing Access Management configuration at the time of the update.
- After upgrading a cluster to 8.8, changes to resource authorizations and roles made in Console no longer affect the 8.8 cluster.
- Users and clients are created and managed in Console, with their authorizations managed via the Orchestration Cluster.
The following table summarizes where Identity entities are managed in Camunda 8.8 SaaS:
| Entity type | Managed via |
|---|---|
| Users | Console |
| Clients | Console |
| Roles | Orchestration Cluster Identity |
| Groups | Orchestration Cluster Identity |
| Authorizations | Orchestration Cluster Identity |
| Tenants | n/a (planned for future) |
| Mapping rules | n/a (managed by Camunda) |
Camunda 8 Self-Managed
After you deploy all Camunda 8 components in a Self-Managed environment, you will continue to use Management Identity for Web Modeler, Console, and Optimize, but use Orchestration Cluster Identity for Zeebe, Operate, Tasklist, and the Orchestration Cluster REST API.
-
Roles and permissions for Orchestration Cluster components (previously managed in Management Identity), are now replaced by the new authorizations and roles defined within Orchestration Cluster Identity.
-
The Identity Migration App that migrates these entities from Management Identity into Orchestration Cluster Identity must be run during your Camunda 8.7 to 8.8 upgrade. Instructions on enabling and configuring the Identity Migration App in the 8.7 to 8.8 migration guide are available for Helm and also docker-compose/bare Java deployments.
-
Management Identity, Keycloak and Postgres are no longer needed for an Orchestration Cluster. They are only needed when using Web Modeler, Console or Optimize.
-
For the Orchestration Cluster, you can bring your own Identity Provider (for example, Keycloak, Microsoft EntraID, Okta) or use the built-in Basic Authentication method.
-
A special setup is no longer required for Keycloak as it is now integrated like any other Identity Provider via OpenID Connect (OIDC). Management Identity relies by default on Keycloak, but you can also configure it to use any OIDC-compatible Identity Provider.
-
The following table summarizes where Orchestration Cluster Identity entities are managed in Camunda 8.8 Self-Managed:
| Entity type | Managed via |
|---|---|
| Users | Identity Provider |
| Clients | Identity Provider |
| Roles | Orchestration Cluster Identity |
| Groups | Identity Provider |
| Authorizations | Orchestration Cluster Identity |
| Tenants | Orchestration Cluster Identity |
| Mapping Rules | Orchestration Cluster Identity |
Camunda 8 Self-Managed - Basic Authentication
If you are using built-in user management (Basic Authentication), Tasklist and Operate specific built-in user management (using ES/OS as storage) is no longer supported.
- Administrators must migrate their users manually into the Orchestration Cluster.
- You must ensure that usernames are identical, otherwise users will not be able to see their assigned tasks.
In a Basic Authentication setup, the Orchestration Cluster provides full functionality:
| Entity type | Managed via |
|---|---|
| Users | Orchestration Cluster Identity |
| Clients | n/a (not applicable for Basic Authentication) |
| Roles | Orchestration Cluster Identity |
| Groups | Orchestration Cluster Identity |
| Authorizations | Orchestration Cluster Identity |
| Tenants | Orchestration Cluster Identity |
| Mapping Rules | n/a (not applicable for Basic Authentication) |
APIs & tools
Changes to APIs & tools in 8.8 are summarized as follows:
| What's new/changed | Description |
|---|---|
| Orchestration Cluster REST API | The unified Orchestration Cluster REST API replaces the deprecated V1 component APIs, providing a unified interface for managing and interacting with the Orchestration Cluster. |
| Camunda Java Client | The Camunda Java Client is now the official Java library for connecting to Camunda 8 clusters, automating processes, and implementing job workers. It is designed for Java developers who want to interact programmatically with Camunda 8 via REST or gRPC, and is the successor to the Zeebe Java client. |
| Camunda Spring SDK | The Camunda Spring Boot SDK replaces the Spring Zeebe SDK. The SDK relies on the Camunda Java client, designed to enhance the user experience and introduce new features while maintaining compatibility with existing codebases. |
| Camunda Process Test | Camunda Process Test (CPT) is a Java library to test your BPMN processes and your process application. CPT is the successor of Zeebe Process Test. Our previous testing library is deprecated and will be removed with version 8.10. |
| Camunda user tasks | Camunda user tasks replace the deprecated job-based user tasks in Camunda 8.8, providing a more robust and flexible way to handle user tasks within process models. |
| Tasklist GraphQL API | The previously deprecated Tasklist GraphQL API is removed in Camunda 8.8. This change is part of the broader architectural evolution towards the Orchestration Cluster REST API, which provides a more unified and consistent interface for managing tasks and workflows. |
| Zeebe gRPC API endpoints | With the 8.8 release, the gRPC API continues but is being disabled by default starting with 8.10. |
To learn more about upgrading and migrating to 8.8, see the API & tools upgrade guide.
Upgrade guides
Camunda 8.8 lays the foundation for future releases. Upgrading ensures compatibility and access to improved features.
The following guides provide detailed information on how you can upgrade to Camunda 8.8.
| Guide | Description | Who is this guide for? |
|---|---|---|
| Self-Managed upgrade guide | Evaluate your infrastructure, understand operational changes, and choose the best update strategy for your environment. | Operations and platform administrators of Self-Managed installations. |
| API and SDK upgrade guide | Plan and execute an upgrade from Camunda 8.7 to 8.8, focusing on API and SDK transitions. |
|