Google Gemini connector
The Google Gemini connector is available for 8.7.0 or later.
The Google Gemini connector is an outbound connector that allows you to access Gemini multimodal models from Google. It is capable of understanding virtually any input, and can combine different types of information in a BPMN process.
Create a Google Gemini connector task
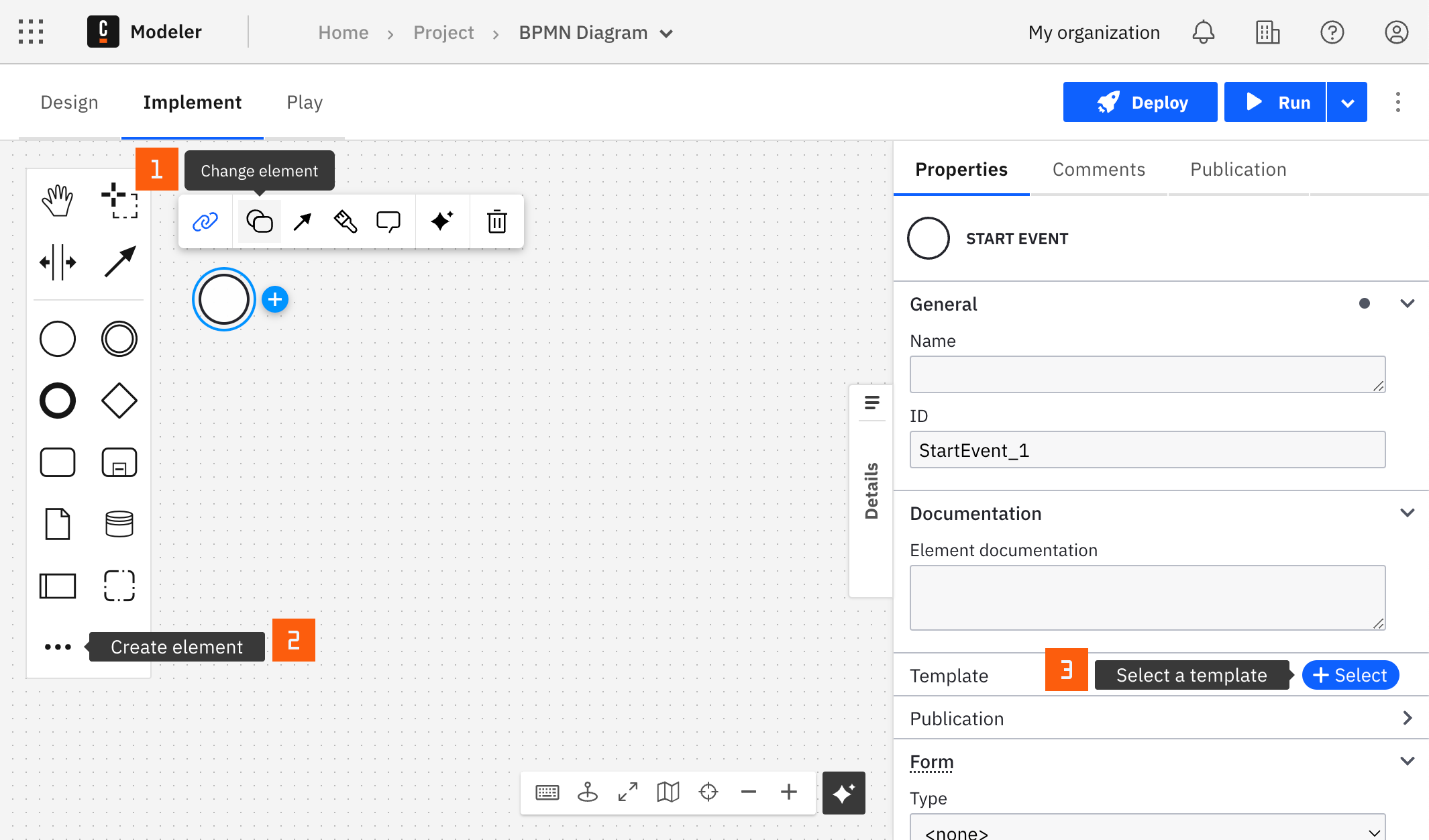
You can apply a connector to a task or event via the append menu. For example:
- From the canvas: Select an element and click the Change element icon to change an existing element, or use the append feature to add a new element to the diagram.
- From the properties panel: Navigate to the Template section and click Select.
- From the side palette: Click the Create element icon.
After you have applied a connector to your element, follow the configuration steps or see using connectors to learn more.
Make your Google Gemini connector executable
To execute this connector, ensure all mandatory fields are correctly filled.
All the mandatory and non-mandatory fields and required settings depending on the operation selection you choose are covered in the upcoming sections.
Authentication
Choose an authentication type from the Type dropdown. For details on authentication types, see Google authentication types.
Project ID
Enter your google cloud project identifier.
Region
Enter the region where your project is located. For example, us-central1 (lowa), us-west1 (Oregon).
Model
Select a model from the dropdown. The following models are currently supported:
- gemini-1.5-flash-001
- gemini-1.5-flash-002
- gemini-1.5-pro-001
- gemini-1.5-pro-002
- gemini-1.0-pro-001
- gemini-1.0-pro-002
- gemini-1.0-pro-vision-001
Prompt
Enter a prompt as a FEEL expression, providing text and media.
- To provide text to Gemini, your expression should contain key "text" and text data. For example, "text" : "your text"
- To provide media to Gemini, your expression should contain key "mime" and mime type text, and key "uri" and media URI. For example, "mime": "mime type", "uri": "your URI".
For example:
= [{"text": "who is this video about"},
{"mime": "video/*", "uri": "https://youtu.be/..."}]
System instructions
Enter system instructions as a string, to determine how the model should respond.
To learn more about system instructions, refer to Google system instructions.
Grounding
Grounding connects the model output to the verifiable sources of information.
- This is useful in situations where accuracy and reliability are important.
- To use grounding, select the Grounding checkbox and input the path to the data store.
To learn more about grounding, refer to Google grounding overview.
Safety Filter Settings
You can adjust the likelihood of receiving a model response which might contain harmful content.
- Content is blocked based on the probability that it is harmful.
- To use safety filter settings, select the Safety Filter Settings checkbox and select the desired level from dropdown.
- By default, all filters are set to OFF.
To learn more about safety filters, refer to Google responsible AI safety filters and settings.
Add stop sequence
A stop sequence is a series of characters (including spaces) that stops response generation if encountered by the model.
The stop sequence should be inserted as a string list.
For example:
= ["text 1", "text 2"]
Temperature
The Temperature controls the randomness in token selection.
- A lower temperature is good when you expect a true or correct response. A temperature of
0means the highest probability token is usually selected. - A higher temperature can lead to diverse or unexpected results. Some models have a higher temperature max to encourage more random responses.
Output token limit
The Output token limit Determines the maximum amount of text output from a single prompt. A token is approximately four characters.
Seed
Setting a Seed value is useful if you make repeated requests and want the same model response.
Deterministic outcome isn’t guaranteed. Changing the model or other settings can cause variations in the response even when you use the same seed value.
Top-K
The Top-K specifies the number of candidate tokens when the model is selecting an output token.
- Use a lower value for less random responses and a higher value for more random responses.
- Only the gemini-1.0-pro-vision-001 model supports Top-K.
Top-P
The Top-P changes how the model selects tokens for output.
- Tokens are selected from the most probable to the least probable, until the sum of their probabilities equals the top-p value.
- For example, if tokens A, B, and C have a probability of .3, .2, and .1 and the top-p value is .5, then the model will select either A or B as the next token (using temperature).
- For the least variable results, set top-P to 0.
Functional call description
Function calling is a feature of Gemini models that makes it easier to get structured data outputs from generative models.
- The Functional call description must be provided in fell format.
- It is important that all types must be registered with capslock.
To learn more about function calling, refer to Google function calling.
For example:
[
{
"name": "get_exchange_rate",
"description":"Get the exchange rate for currencies between countries",
"parameters": {
"type": "OBJECT",
"properties": {
"currency_date": {
"type": "STRING",
"description": "A date that must always be in YYYY-MM-DD format or the value 'latest' if a time period is not specified"
},
"currency_from": {
"type": "STRING",
"description": "The currency to convert from in ISO 4217 format"
},
"currency_to": {
"type": "STRING",
"description": "The currency to convert to in ISO 4217 format"
}
},
"required":[
"currency_date",
"currency_from",
"currency_to"
]
}
}
]
Google authentication types
The Google Gemini connector currently supports two methods for authentication and authorization:
- Based on a short-lived JWT bearer token.
- Based on a refresh token.
Google supports multiple ways to obtain both types of token. Refer to the official Google OAuth documentation for current instructions, or see the examples below.
Example 1: Obtain JWT bearer token with a service account
The following code snippet is for demonstration purposes only and must not be used for real production systems due to security concerns. For production usage, follow the official Google guidelines.
Assuming you have created a service account and downloaded a JSON file with keys, run the following Python 3 snippet to print the JWT token in the terminal:
import google.auth
import google.auth.transport.requests
from google.oauth2 import service_account
# Scopes required to execute 'create' endpoind with Google Drive API
SCOPES = ['https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cloud-platform', 'https://www.googleapis.com/auth/generative-language.retriever']
# File with keys
SERVICE_ACCOUNT_FILE = 'google-service-account-creds.json'
credentials = service_account.Credentials.from_service_account_file(SERVICE_ACCOUNT_FILE, scopes=SCOPES)
auth_req = google.auth.transport.requests.Request()
credentials.refresh(auth_req)
# Print token
print(credentials.token)
Example 2: Obtain bearer and refresh token with OAuth client
The following code snippet is for demonstration purposes only and must not be used for real production systems due to security concerns. For production usage, follow the official Google guidelines.
Assuming you have created an OAuth client, you can download key files from the Google Console. Run the following Python 3 snippet to print the refresh token in the terminal:
from google_auth_oauthlib.flow import InstalledAppFlow
import pprint
SCOPES = ['https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cloud-platform', 'https://www.googleapis.com/auth/generative-language.retriever']
OAUTH_KEYS = './oauth-keys.json' # path to your file with OAuth credentials
def main():
flow = InstalledAppFlow.from_client_secrets_file(OAUTH_KEYS, SCOPES)
creds = flow.run_local_server(port=54948)
pprint.pprint(vars(creds))
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()