Amazon EventBridge connector
- Amazon EventBridge connector
- Amazon EventBridge Webhook connector
The Amazon EventBridge connector integrates your BPMN service with Amazon EventBridge, enabling the sending of events from your workflows for further processing or routing to other AWS services. It provides seamless event-driven integration within your business processes.
For more information, refer to the Amazon EventBridge documentation.
Prerequisites
Before using the Amazon EventBridge connector, ensure you have the necessary permissions in your AWS account to send events to EventBridge. You will need an access key and secret key of a user with the appropriate permissions. Refer to the AWS documentation for more information.
Use Camunda secrets to avoid exposing your AWS IAM credentials as plain text. Refer to our documentation on managing secrets to learn more.
Create an Amazon EventBridge connector task
You can apply a connector to a task or event via the append menu. For example:
- From the canvas: Select an element and click the Change element icon to change an existing element, or use the append feature to add a new element to the diagram.
- From the properties panel: Navigate to the Template section and click Select.
- From the side palette: Click the Create element icon.
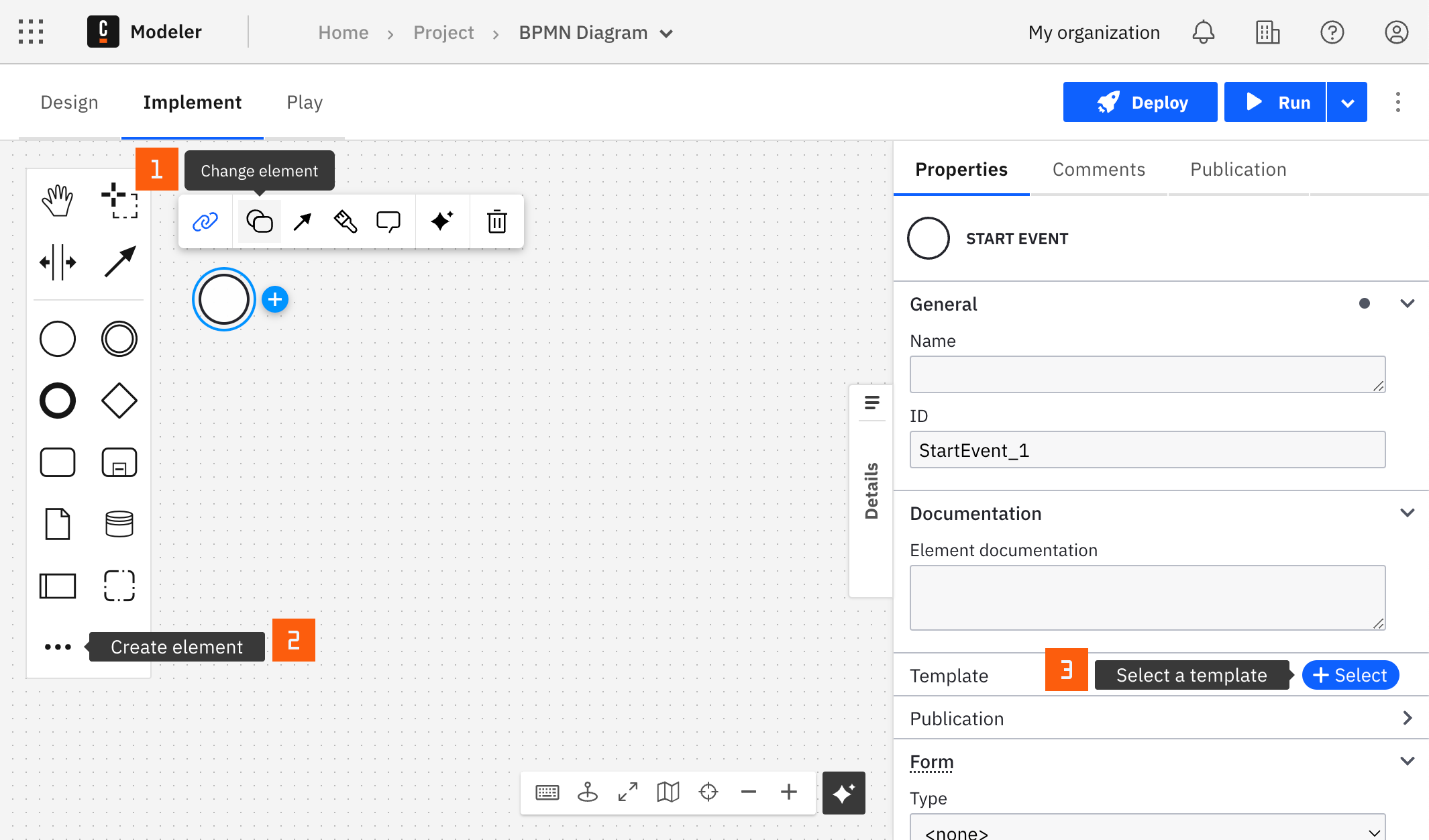
After you have applied a connector to your element, follow the configuration steps or see using connectors to learn more.
Configure the Amazon EventBridge connector
Follow these steps to configure the Amazon EventBridge connector:
- Choose an applicable authentication type from the Authentication dropdown. Learn more about authentication types in the related appendix entry.
- In the Authentication section, enter the relevant IAM key and secret pair of the user with permissions to send events to Amazon EventBridge.
- In the Configuration section, specify the AWS region where your EventBridge resides.
- In the Event Details section, provide the following information:
- Event bus name: Enter the name of the destination event bus. Refer to the Amazon EventBridge documentation for more details on event buses.
- Source: Enter the value that identifies the service that generated the event.
- Detail type: Enter the type of event being sent. Refer to the Amazon documentation for more information on these properties.
- In the Event Payload section, enter a JSON object that contains information about the event.
- (Optional) In the Output Mapping section, you can set a Result variable or Result expression. Refer to the response mapping documentation to learn more.
- (Optional) In the Error Handling section, define the Error expression to handle errors that may occur during the event sending process. Refer to the response mapping documentation to learn more.
Amazon EventBridge connector response
The Amazon EventBridge connector returns the original response from the Amazon EventBridge service, including the sdkResponseMetadata and sdkHttpMetadata. Here is an example of the response:
{
"sdkResponseMetadata": {
"requestId": "766647a2-835a-418b-9161-94245d0c93a3"
},
"sdkHttpMetadata": {
"httpHeaders": {
"Content-Length": "85",
"Content-Type": "application/x-amz-json-1.1",
"Date": "Fri, 23 Jun 2023 08:39:22 GMT",
"x-amzn-RequestId": "766647a2-835a-418b-9161-94245d0c93a3"
},
"httpStatusCode": 200,
"allHttpHeaders": {
"x-amzn-RequestId": ["766647a2-835a-418b-9161-94245d0c93a3"],
"Content-Length": ["85"],
"Date": ["Fri, 23 Jun 2023 08:39:22 GMT"],
"Content-Type": ["application/x-amz-json-1.1"]
}
},
"failedEntryCount": 0,
"entries": [
{
"eventId": "bb86b1af-9abb-0f8e-28c2-c69c24c35e05",
"errorCode": null,
"errorMessage": null
}
]
}
Appendix
AWS authentication types
There are two options to authenticate the connector with AWS:
- Choose Credentials in the Authentication dropdown if you have a valid pair of access and secret keys provided by your AWS account administrator. This option is applicable for both SaaS and Self-Managed users.
- Choose Default Credentials Chain (Hybrid/Self-Managed only) in the Authentication dropdown if your system is configured as an implicit authentication mechanism, such as role-based authentication, credentials supplied via environment variables, or files on target host. This option is applicable only for Self-Managed or hybrid distribution. This approach uses the Default Credential Provider Chain to resolve required credentials.
Next steps
- Amazon EventBridge documentation
- Learn about other connectors available in Camunda to integrate with different systems and services.
- Learn more about using connectors.
The Amazon EventBridge Webhook connector is an inbound connector enabling you to start a BPMN process instance triggered by an event from Amazon EventBridge.
Create an Amazon EventBridge Webhook connector task
- Start building your BPMN diagram. You can use the Amazon EventBridge Webhook connector with either a Start Event or an Intermediate Catch Event building block.
- Select the applicable element and change its template to an Amazon EventBridge connector.
- Fill in all required properties.
- Complete your BPMN diagram.
- Deploy the diagram to activate the event trigger.
Configure the Amazon EventBridge Webhook connector
Fill properties in the Webhook Configuration section
- Choose one of the required methods in the Webhook method property. For example, if you know the webhook will be triggered by the POST method, choose POST. Alternatively, if it is not essential to specify a specific method for the webhook trigger, select ANY.
- Configure the Webhook ID. By default, the Webhook ID is pre-filled with a random value. This value will be part of the Webhook URL. For more details about Webhook URLs, refer to the section below on activating the Amazon EventBridge Webhook connector by deploying your diagram.
- (Optional) Fill in the Event Bus Name property if you want to specify a specific event bus to subscribe to. If left empty, the default event bus will be used.
Fill properties in the Authorization section
The Amazon EventBridge Webhook connector supports four types of authorization:
-
None (without authorization): No authentication is required for the webhook. Anyone can trigger the webhook without any credentials.
-
JWT (JSON Web Token): This authorization type requires the following properties to be filled:
- JWK URL: A link to the JSON Web Key (JWK) Set containing the public keys used to verify the JWT signature. Learn more about JWK.
- JWT Role Property Expression (optional): An expression to extract the roles from the JWT token. These roles will be used to check against the Required Roles property. For example, the expression could be:
=if admin = true then ["admin"] else roles- Required Roles (optional): A list of roles to test JWT roles against. If provided, the webhook will only be triggered if the JWT token contains at least one of the required roles. For example, if the required role is "admin", the property could be:
["admin"] -
Basic: This authorization type requires the following properties to be filled:
- Username: The username to authenticate the webhook.
- Password: The password associated with the provided username.
-
API Key: This authorization type requires the following properties to be filled:
- API Key: The API key that needs to be provided in the request to authenticate the webhook.
- API Key Locator: A FEEL expression that extracts the API key from the request. This expression is evaluated in the connector Runtime to retrieve the API key from the incoming request. For example, the API Key Locator could be:
=split(request.headers.authorization, " ")[2]or
request.headers.mycustomapikey
Select the appropriate authorization type based on your security requirements and fill in the corresponding properties accordingly.
Fill out the properties in the Activation and Correlation sections
- (Optional) Configure the Activation Condition. This condition will be used to filter the events from the specified event source. For example, if an incoming Amazon EventBridge event has the following body:
{
"version": "0",
"id": "6d3d35b7-5bf2-43ec-9e55-5cfb27ad31b4",
"detail-type": "MyEvent",
"source": "custom.application",
"account": "123456789012",
"time": "2023-07-25T12:34:56Z",
"region": "us-west-2",
"resources": [],
"detail": {
"shipment": "123456789",
"status": "received"
}
}
the Activation Condition value might look like this:
=(get value(request.body, "detail-type")="MyEvent" and request.body.detail.status="received")
This condition will trigger the Amazon EventBridge Webhook connector only when the detail-type is "MyEvent" and the status is "received".
- When using the Amazon EventBridge Webhook connector with an Intermediate Catch Event, fill in the Correlation key (process) and Correlation key (payload).
-
Correlation key (process) is a FEEL expression that defines the correlation key for the subscription. This corresponds to the Correlation key property of a regular Message Intermediate Catch Event.
-
Correlation key (payload) is a FEEL expression used to extract the correlation key from the incoming message. This expression is evaluated in the connector Runtime, and the result is used to correlate the message.
-
Message ID expression and Message TTL are optional properties that can be used to set the message ID and time-to-live for the incoming message. Refer to the message ID expression and message TTL sections for more information.
For example, if your correlation key is defined with a process variable named myCorrelationKey, and you want to correlate by the shipment property in the request detail, which contains:
{
"version": "0",
"id": "6d3d35b7-5bf2-43ec-9e55-5cfb27ad31b4",
"detail-type": "MyEvent",
"source": "custom.application",
"account": "123456789012",
"time": "2023-07-25T12:34:56Z",
"region": "us-west-2",
"resources": [],
"detail": {
"shipment": "123456789",
"status": "received"
}
}
your correlation key settings will look like this:
- Correlation key (process):
=myCorrelationKey - Correlation key (payload):
=request.body.detail.shipment
Message ID expression
The Message ID expression is an optional field that allows you to extract the message ID from the incoming message. The message ID serves as a unique identifier for the message and is used for message correlation. This expression is evaluated in the connector Runtime and the result is used to correlate the message.
In most cases, it is not necessary to configure the Message ID expression. However, it is useful if you want to ensure message deduplication or achieve a certain message correlation behavior. Learn more about how message IDs influence message correlation in the messages guide.
For example, if you want to set the message ID to the value of the detail.transactionId field in the incoming event, configure the Message ID expression as follows:
= request.body.detail.transactionId
Message TTL
The Message TTL is an optional field that allows you to set the time-to-live (TTL) for the correlated messages. TTL defines the time for which the message is buffered in Zeebe before being correlated to the process instance (if it can't be correlated immediately).
The value is specified as an ISO 8601 duration. For example, PT1H sets the TTL to one hour. Learn more about the TTL concept in Zeebe in the message correlation guide.
Activate the Amazon EventBridge connector by deploying your diagram
Once you click Deploy, your Amazon EventBridge Webhook connector will be activated and ready to receive events.
The URLs of the exposed Amazon EventBridge Webhooks adhere to the following pattern:
http(s)://<base URL>/webhooks/<webhook ID>
<base URL>is the URL of the connectors component deployment. When using the Camunda 8 SaaS offering, this will typically contain your region Id and cluster Id, found in your client credentials under the API tab within your cluster.<webhook ID>is the ID (path) you configured in the properties of your Amazon EventBridge Webhook connector.
If you make changes to your Amazon EventBridge Webhook connector configuration, redeploy the BPMN diagram for the changes to take effect.
When you click on the event with the Amazon EventBridge Webhook connector applied to it, a new Webhooks tab will appear in the properties panel. This tab displays the URL of the Amazon EventBridge Webhook connector for every cluster where you have deployed your BPMN diagram.
The Webhooks tab is only supported in Web Modeler as part of the Camunda 8 SaaS offering. You can still use the Amazon EventBridge Webhook connector in Desktop Modeler or with Camunda 8 Self-Managed. In that case, Amazon EventBridge Webhook connector deployments and URLs will not be displayed in Modeler.
Output mapping
The Output mapping section allows you to configure the mapping of the event payload to the process variables.
- Use the Result variable to store the event data in a process variable. For example,
myEventPayload. - Use the Result expression to map specific fields from the event payload into process variables using FEEL. For example, given the Amazon EventBridge connector is triggered with an event payload like:
{
"id": "6d3d35b7-5bf2-43ec-9e55-5cfb27ad31b4",
"detail-type": "MyEvent",
"source": "custom.application",
"region": "us-west-2",
"resources": [],
"detail": {
"event": "order_created",
"customer_id": "12345",
"order_total": 100.50
}
}
and you would like to extract the customer_id and order_total as process variables customerId and orderTotal, the Result Expression might look like this:
= {
customerId: request.body.detail.customer_id,
orderTotal: request.body.detail.order_total
}
Example of configuring Amazon EventBridge
To configure Amazon EventBridge, follow the steps below:
- Go to the AWS Management Console.
- Set the required permissions for EventBridge by navigating to: https://aws.permissions.cloud/iam/events.
- Access Amazon EventBridge service by going to Amazon EventBridge.
- Click Integration > API Destination.
- Switch to the Connection tab.
- Create a new connection with the required authorization type (basic, API key, OAuth).
- Now, create a new API destination with the following information:
- Select the previously created connection.
- Choose the appropriate HTTP method.
- Specify the API destination endpoint, which should be the webhook URL generated after deploying the BPMN diagram.
- Create a new event bus by following the documentation here.
- Lastly, create a rule using the API destination that you already created. Refer to the documentation for guidance.
Next steps
- Learn more about Amazon EventBridge and its capabilities.
- Explore other Connectors available in Camunda to integrate with different systems and services.
- Learn more about using connectors here.
- Learn more about inbound connectors here.