Process instance creation
Depending on the process definition, an instance of it can be created in several ways.
Camunda 8 supports the following ways to create a process instance:
Commands
A process instance is created by sending a command specifying the BPMN process ID, or the unique key of the process.
There are two commands to create a process instance, outlined in the sections below.
Create and execute asynchronously
A process that has a none start event is started explicitly using CreateProcessInstance.
This command creates a new process instance and immediately responds with the process instance ID. The execution of the process occurs after the response is sent.
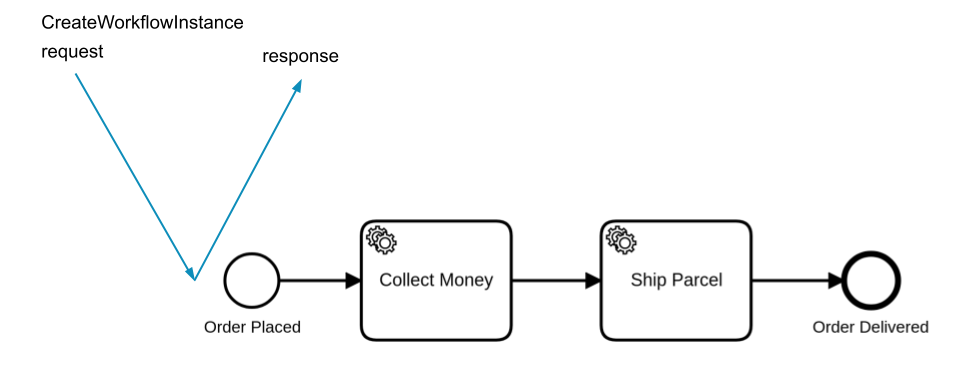
Create a process instance via Orchestration Cluster REST API
curl -L 'http://localhost:8080/v2/process-instances' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'Accept: application/json' \
-d '{
"processDefinitionKey": "2251799813685249”,
"processDefinitionVersion": 1
}'
Response:
{
"processDefinitionId": "order-process",
"processDefinitionVersion": 1,
"processDefinitionKey": "2251799813685249",
"processInstanceKey": "2251799813686019"
}
See the API reference for process instance creation for more information, including additional request fields and code samples.
Create and await results
Typically, process creation and execution are decoupled. However, there are use cases that need to collect the results of a process when its execution is complete.
CreateProcessInstanceWithResult allows you to “synchronously” execute processes and receive the results via a set of variables. The response is sent when the process execution is complete.
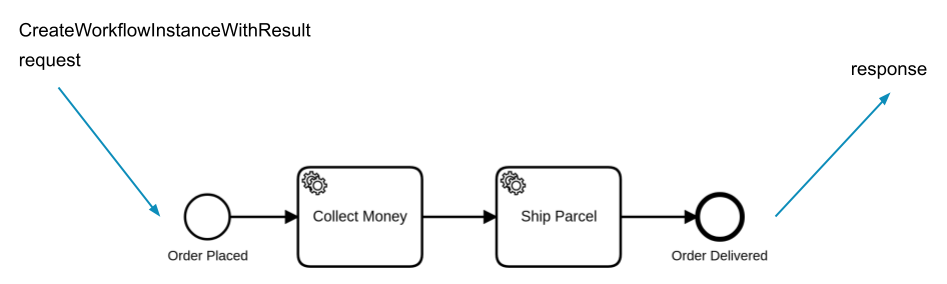
This command is typically useful for short-running processes and processes that collect information.
If the process mutates system state, or further operations rely on the process outcome response to the client, consider designing your system for failure states and retries.
When the client resends the command, it creates a new process instance.
Create a process instance and await results via Orchestration Cluster REST API
curl -L 'http://localhost:8080/v2/process-instances' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'Accept: application/json' \
-d '{
"processDefinitionId": "order-process”,
"processDefinitionVersion": 1,
"awaitCompletion": true,
"variables": { "orderId": "1234" }
}'
Response:
{
"processDefinitionId": "order-process",
"processDefinitionVersion": 1,
"variables": { "orderId": "1234" }
"processDefinitionKey": "2251799813685249",
"processInstanceKey": "2251799813686019",
}
See the API reference for process instance creation for more information, including additional request fields and code samples.
Failure scenarios applicable to other commands are applicable to this command as well. Clients may not get a response in the following cases even if the process execution is completed successfully:
- Connection timeout: If the gRPC deadlines are not configured for long request timeout, the connection may be closed before the process is completed.
- Network connection loss: This can occur at several steps in the communication chain.
- Failover: When the node processing this process crashes, another node continues the processing. The other node does not send the response because the request is registered on the first one.
- Gateway failure: If the gateway the client is connected to fails, nodes inside the cluster cannot send the response to the client.
Run process segment
The create and execute asynchronously and create and await results commands both start the process instance at their default initial element: the single none start event. Camunda 8 also provides a way to create a process instance starting or ending at user-defined element(s).
This is an advanced feature. Camunda recommends to only use this functionality for testing purposes. The none start event is the defined beginning of your process. Most likely the process is modeled with the intent to start all instances from the beginning.
Start instructions
To start the process instance at a user-defined element, you need to provide start instructions along with the command. Each instruction describes how and where to start a single element.
By default, the instruction starts before the given element. This means input mappings of that element are applied as usual.
Multiple instructions can be provided to start the process instance at more than one element. You can activate the same element multiple times inside the created process instance by referring to the same element ID in more than one instruction.
Runtime instructions
By default, the process execution continues normally until the end of the process. To change this behavior and end the process instance after a specific element completes or terminates, provide runtime instructions. Each runtime instruction specifies the ID of one element whose completion or termination ends the process instance.
You can provide multiple runtime instructions to terminate the process instance after multiple elements—for example, when a process has multiple parallel flows.
Start and runtime instructions have the same limitations as process instance modification, e.g., it is not possible to start or end at a sequence flow.
Start and runtime instructions are supported for both CreateProcessInstance commands. Both instruction sets can be used separately or together to achieve different scenarios.
Create a process instance with a start and a runtime instruction
The example below shows how to create a process instance that starts at a user-defined element and terminates after it, so that only the specified segment of the process is executed.
curl -L 'http://localhost:8080/v2/process-instances' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'Accept: application/json' \
-d '{
"processDefinitionId": "order-process”,
"processDefinitionVersion": -1,
"startInstructions": [
{
"elementId": "ship_parcel"
}
],
"runtimeInstructions": [
{
"type": "TERMINATE_PROCESS_INSTANCE",
"afterElementId": "ship_parcel"
}
]
"variables": { "orderId": "1234" }
}'
See the API reference for process instance creation for more information, including additional request fields and code samples.
Events
Process instances are also created implicitly via various start events. Camunda 8 supports message start events and timer start events.
Message event
A process with a message start event can be started by publishing a message with the name that matches the message name of the start event.
For each new message a new instance is created.
Timer event
A process can also have one or more timer start events. An instance of the process is created when the associated timer is triggered. Timers can also trigger periodically.
Tags
Process instance tags are lightweight, immutable labels you can attach when creating a process instance via the API or clients. Tags are inherited by all jobs created from that instance. They help downstream workers and external systems make quick routing or decision choices without inspecting full variable payloads.
Tag format and constraints
- A tag is a case-sensitive string.
- Format (regex):
^[A-Za-z][A-Za-z0-9_\-:.]{0,99}$- Must start with a letter (A–Z or a–z).
- Remaining characters may be alphanumeric, underscore (
_), hyphen (-), colon (:), or dot (.).
- Length: 1–100 characters.
- Maximum of 10 unique tags per process instance (duplicates are ignored).
- Order is not guaranteed; treat the set as unordered.
- Tags cannot be modified after creation
If validation fails during process instance creation (for example, too many tags, invalid pattern, or length), the create request is rejected with a 4xx error.
Semantics
- Tags are included in process instance search responses and in activated job payloads.
- Tags are immutable after creation - cannot be added, changed, or removed after process instance has been created.
- Search filtering uses AND semantics: an instance must contain all requested tags (it may contain additional tags). Partial or wildcard matching is not supported.
- Tags are exported with the process instance and with job entities starting in 8.8 by the default exporters.
- Tags are not shown in web applications (such as Operate and Tasklist) — they are API/client-only metadata.
Use cases
- Routing and prioritization (for example,
priority:high) - Business or domain identifiers from internal or third-party systems (for example,
reference:1234,team:accounting,origin:crm) - Cross-system correlation keys without exposing full variable payloads (for example,
trace-id:abcd-1234,crm-id:3004) - Analytics segmentation (for example,
region:emea,channel:web) - Feature rollout or experiment grouping (for example,
experiment:checkout-v2)
Guidelines
- Do not store secrets or PII; tags propagate with jobs and exports.
- Prefer concise
key:valueorkeypatterns for consistency. - Use variables (not tags) for mutable or large data.
- Establish internal naming conventions (for example, prefixes like
env:ordept:) for governance.
Examples
Create with tags:
curl -L 'http://localhost:8080/v2/process-instances' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'Accept: application/json' \
-d '{
"processDefinitionId": "order-process",
"processDefinitionVersion": 3,
"tags": ["channel:web", "reference:1234", "region:emea"],
"variables": { "orderId": "1234" }
}'