SAP eventing with SAP Advanced Event Mesh (AEM)
Receive CloudEvents from SAP Advanced Event Mesh (AEM) and send CloudEvents to AEM.
About SAP eventing
SAP eventing uses three connectors that enable bidirectional communication between Camunda and AEM.
| Connector | Description |
|---|---|
| SAP Eventing Outbound Connector | Sends CloudEvents from Camunda to an AEM topic or queue endpoint. |
| SAP Eventing Message Start Event Connector | Translates an incoming CloudEvent from AEM into a BPMN Message Start Event to trigger a new process instance. |
| SAP Eventing Intermediate Event Connector | Translates an incoming CloudEvent from AEM into a BPMN Intermediate Catch Event to allow an active process to continue based on the event. |
The integration uses HTTP as the transport protocol:
- Incoming connectors act as webhooks, receiving CloudEvent payloads and delivering them into process instances.
- The outbound connector sends
HTTP POSTrequests to an AEM topic or queue endpoint.
SAP Advanced Event Mesh uses Solace Event Broker as its core event broker.
The terms AEM and Solace Event Broker can be used interchangeably when referring to eventing functionality.
Prerequisites
Because HTTP is used as the transport protocol, AEM must be configured to use REST messaging. This enables publishers and subscribers to communicate over HTTP.
The configuration examples below build on the Solace tutorial Publish/Subscribe REST Messaging, which provides detailed steps for setting up REST-based publish/subscribe messaging.
Installation
Install the SAP Eventing connectors directly from the Camunda Marketplace.
Configuration overview
- SAP Eventing Message Start Event Connector
- SAP Eventing Intermediate Event Connector
- SAP Eventing Outbound Connector
SAP Eventing Message Start Event Connector
Inbound CloudEvents → BPMN message.
Applying the SAP Eventing Message Start Event Connector generates a unique webhook URL that starts a new BPMN process instance when invoked.
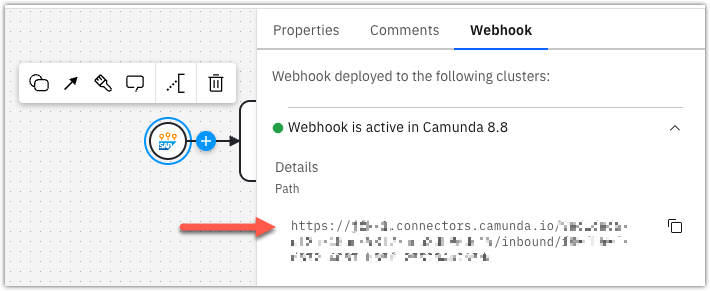
The webhook URL is generated only after the initial deployment of the process.
This URL must be registered as a target in SAP Advanced Event Mesh (AEM).
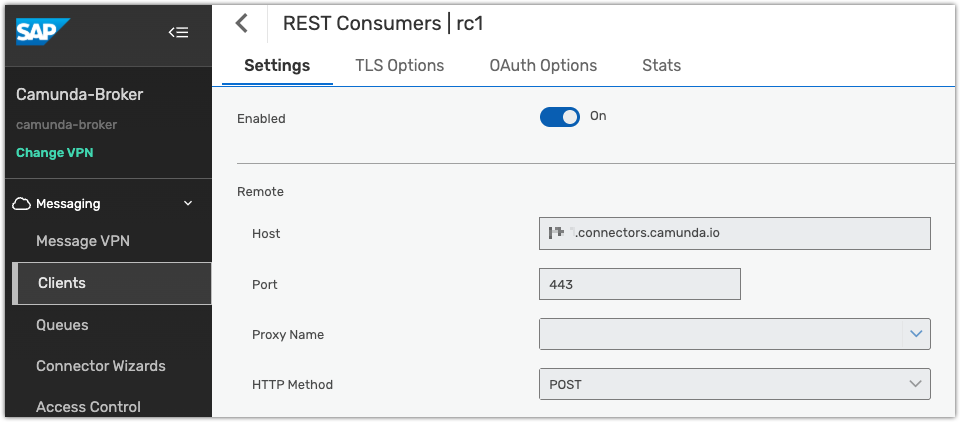
The host portion of the URL (https://<region>.connectors.camunda.io) is used when configuring the REST consumer in AEM.
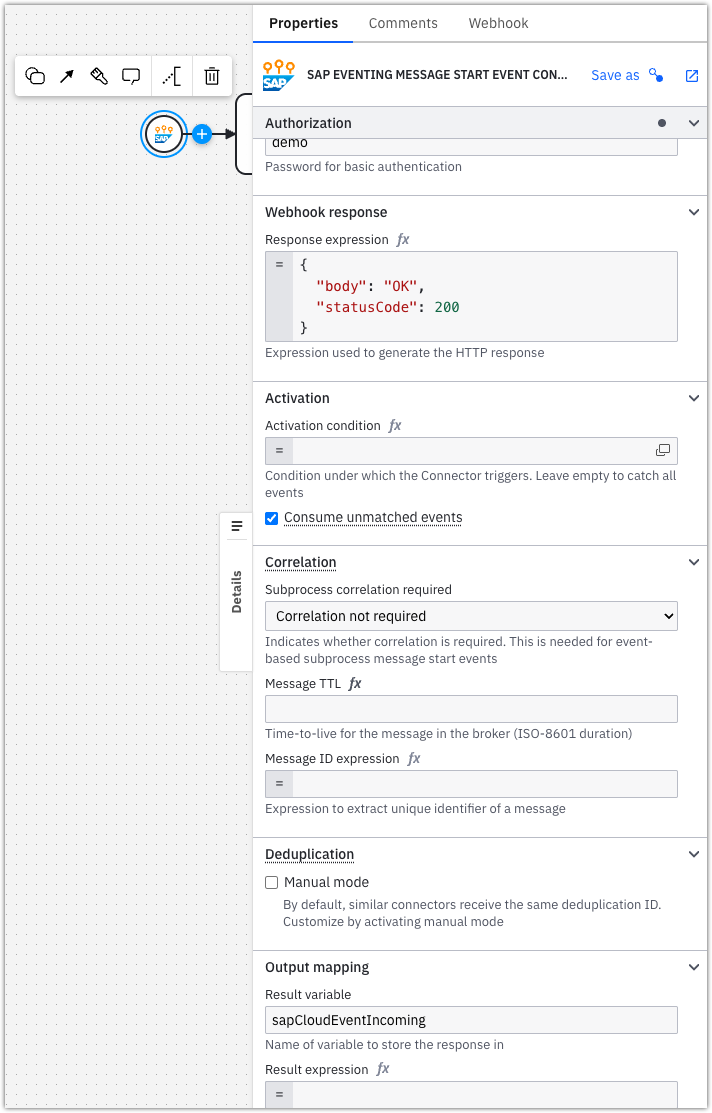
Authentication
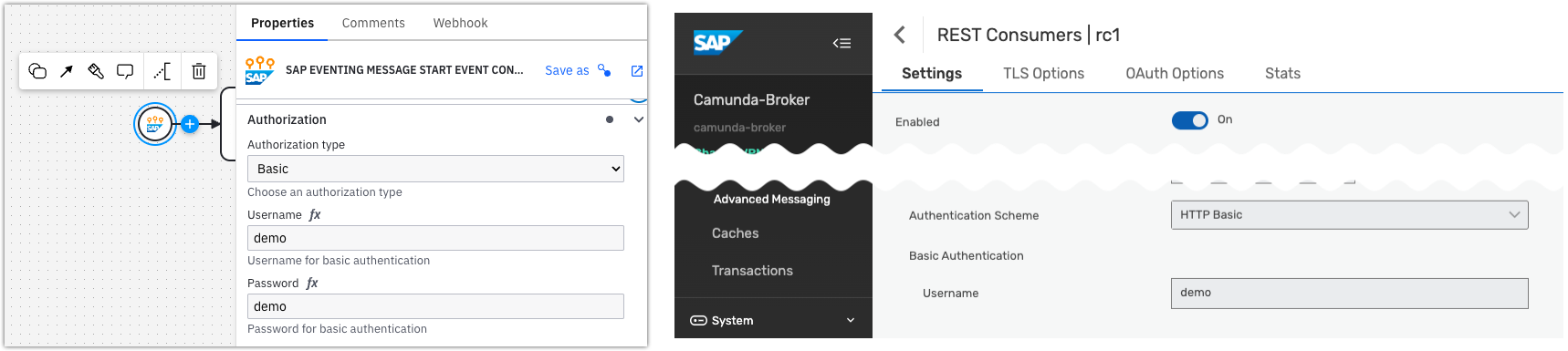
In the REST consumer configuration, set up authentication from AEM to the Camunda webhook endpoint.
The credentials configured in the Authorization section of the built-in connector must match the authentication scheme used in AEM.
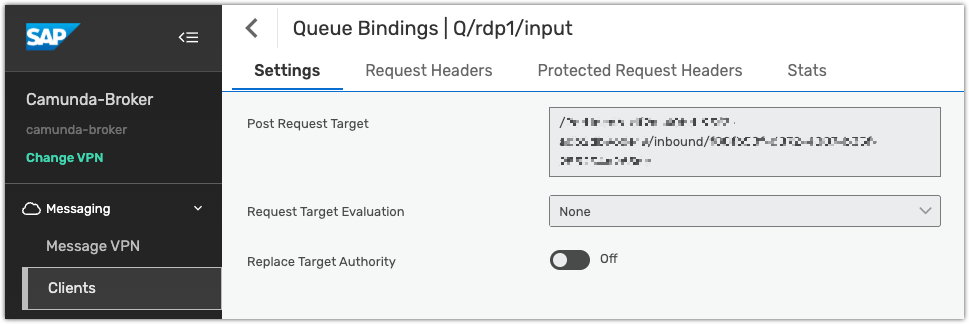
Queue binding
The path component of the Camunda webhook URL must be used as the POST request target in the Queue Binding of the REST consumer.
Other configuration options
The remaining configuration options are identical to those of the HTTP Webhook Connector, except for one key difference:
The default webhook response explicitly returns a
200status code and an"OK"message body, confirming that the CloudEvent was successfully received and acknowledged by Camunda.
Event flow
When a CloudEvent is received from AEM, all header properties and the body payload are relayed to the target process instance, either:
- At process creation (Message Start Event), or
- During event correlation (Intermediate Event).
This ensures that message attributes and payload data from AEM are preserved end-to-end within the Camunda process.
SAP Eventing Intermediate Event Connector
Correlate CloudEvents as BPMN messages
The SAP Eventing Intermediate Event Connector injects a CloudEvent from AEM into an active Camunda process instance using message correlation.
Any CloudEvent property can be used as a correlation key to match incoming event data to the correct process instance.
Correlation via CloudEvent body
The configuration options of the Message Start and Intermediate Event connectors are identical, except that the intermediate event requires an additional Correlation section.
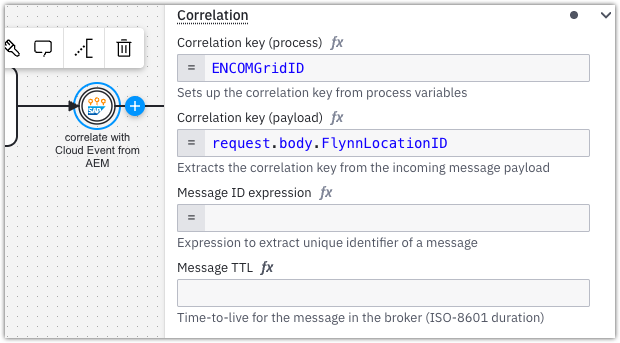
- In the example above, the process variable
ENCOMGridIDmust exist within the process instance. - Its value is compared against the CloudEvent payload (
request.body.FlynnLocationID). - If both values match, the CloudEvent is correlated to that process instance.
Correlation via CloudEvent metadata
Since HTTP is used as the transport protocol, the CloudEvents specification requires all CloudEvent metadata to be passed as HTTP headers.
AEM prepends all user properties with the prefix Solace-User-Property-.
For example, the CloudEvent property ce-id is represented as the HTTP header Solace-User-Property-ce-id.
To correlate on metadata, reference the header name including this prefix.
Example: CloudEvent HTTP message
{
"request": {
"body": { "FlynnLocationID": "34.0522,-118.2437" },
"headers": {
"host": "<region>.connectors.camunda.io",
"authorization": "Basic CaMUnDakZW1v",
"content-type": "application/json",
"solace-user-property-ce-specversion": "1.0",
"solace-user-property-ce-type": "sap.s4.beh.encom.grid.program.v1",
"solace-user-property-ce-source": "/alan/pager/buzz",
"solace-user-property-ce-subject": "CLU-2.0",
"solace-user-property-ce-id": "Argon-T-01",
"solace-user-property-ce-time": "2018-04-05T03:56:24Z",
"solace-user-property-ce-datacontenttype": "application/json"
}
}
}
To correlate on the ce-id property, use request.headers.solace-user-property-ce-id.
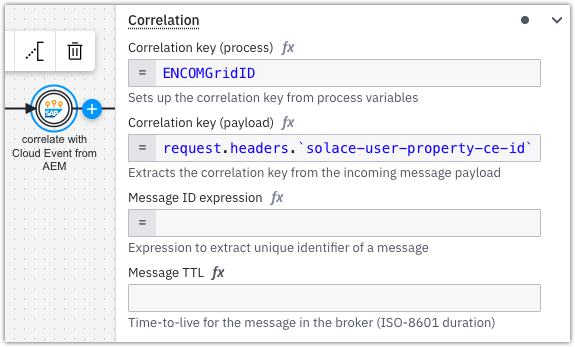
Use backticks to escape dashes in the header name, for example:
request.headers.`solace-user-property-ce-id`.
SAP Eventing Outbound Connector
The SAP Eventing Outbound Connector allows you to send CloudEvents to AEM using its REST messaging capability. It publishes the event using an HTTP POST request.
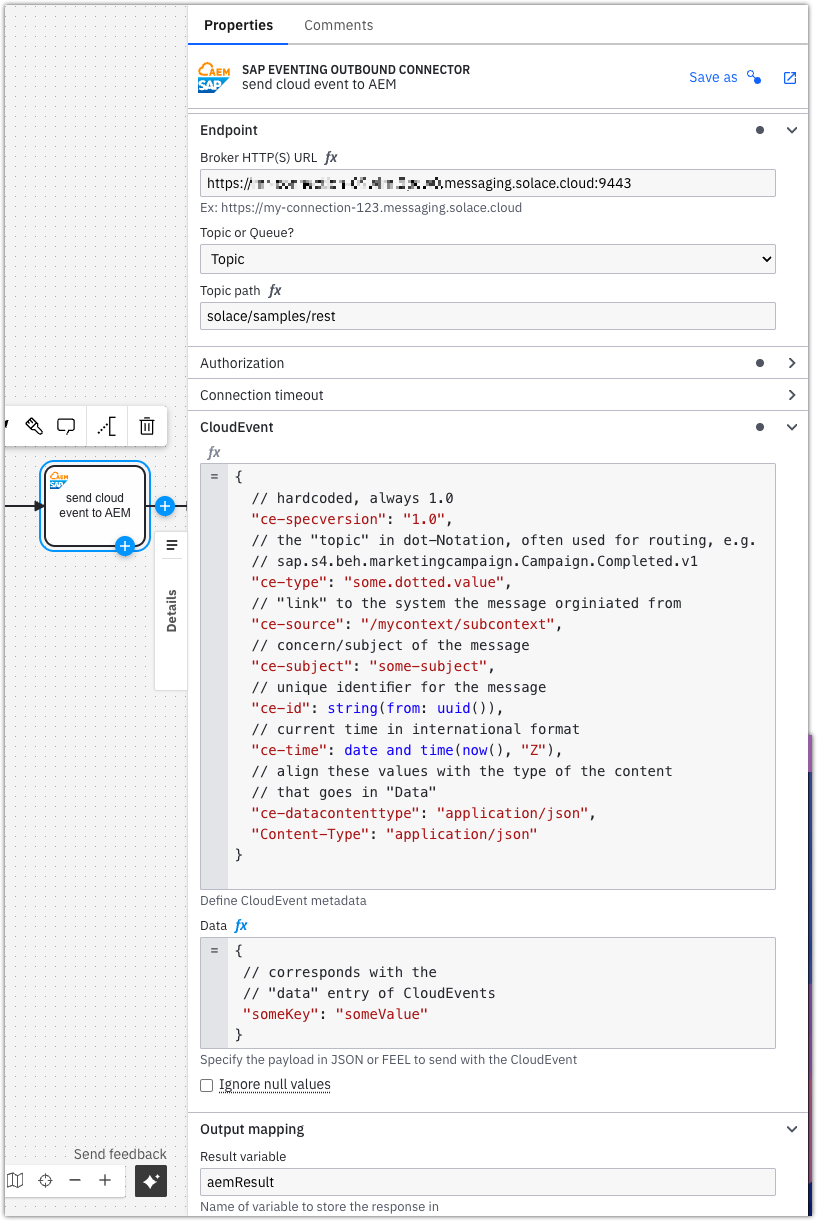
Endpoint
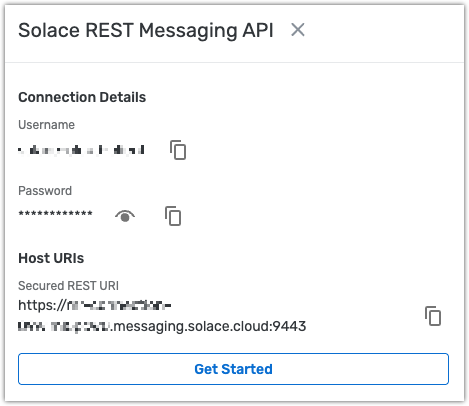
The Endpoint field specifies the URL of your AEM event broker.
You can find this URL in AEM’s web interface:
Cluster Manager → Your Cluster → (Service Details) → Connect → Connect with Java → Solace REST Messaging API
The FQDN (fully qualified domain name) is shown on the right-hand side.
Topic / queue
Specify the target topic or queue path where the CloudEvent will be published.
Do not begin the path with / — the connector includes a validation check to prevent this.
Authorization
Supported authorization methods:
NoneAPI KeyBasicOAuth 2.0Bearer Token
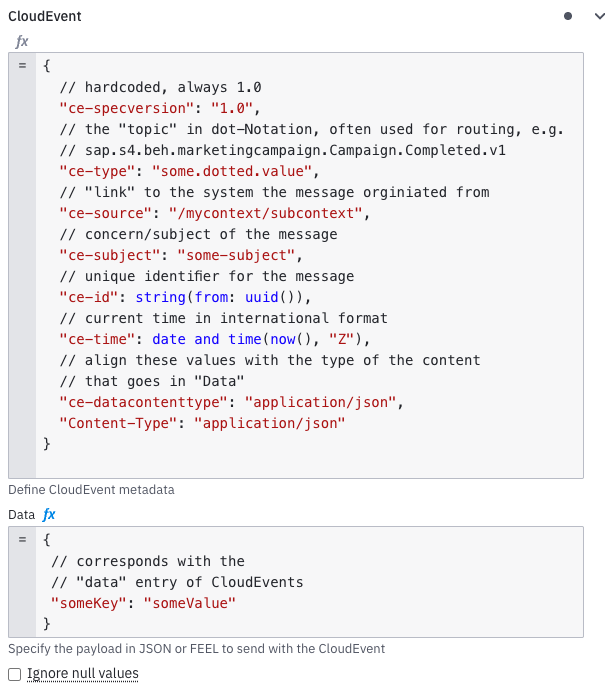
CloudEvent
CloudEvent metadata (e.g., ce-id, ce-subject) is automatically handled by the AEM broker, including the required Solace-User-Property- prefix.
Configure only the standard CloudEvent attributes in the connector.
The CloudEvent data is serialized into a JSON body, and both metadata and data fields support FEEL expressions for dynamic values.
Other configuration options
All remaining options are identical to those of the REST Connector, including:
These settings control network behavior and define how response data is mapped to process variables.