Camunda production installation guide with Kubernetes and Helm
The following is a scenario-based, production focused, step-by-step guide for setting up the Camunda Helm chart. It provides a resilient, production-ready architecture for Camunda 8, and minimizes complexity while offering a reliable foundation for most production use cases.
While this guide uses AWS as a reference, the steps are applicable to other supported Kubernetes distributions and their comparable services. Upon completion, you will be familiar with all of the necessary requirements for having a production ready Camunda Helm chart.
Prerequisites
Before proceeding with the setup, ensure the following requirements are met:
- Kubernetes Cluster: A functioning Kubernetes cluster with kubectl access and block storage persistent volumes for stateful components. This guide will use an AWS EKS cluster for reference. Step-by-step documentation is available to deploy an EKS cluster with Terraform, and install Camunda 8.
- Helm: Make sure the Helm CLI is installed.
- DNS Configuration: You must have access to configure DNS for your domain in order to point to the Kubernetes cluster Ingress.
- TLS Certificates: Obtain valid X.509 certificates for your domain from a trusted Certificate Authority.
- External Dependencies: Provision the following external dependencies:
- Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL: For persistent data storage required for the Web Modeler component. For step-by-step instructions, see the Aurora PostgreSQL module setup guide.
- Amazon OpenSearch: The secondary datastore for Zeebe, the Camunda 8 process orchestration engine. For step-by-step instructions, see the OpenSearch guide.
- AWS Simple Active Directory: For simple OIDC authentication. See the AWS Simple Active Directory documentation for more information.
- Ingress NGINX: Ensure the ingress-nginx controller is set up in the cluster.
- AWS OpenSearch Snapshot Repository - To store the backups of the Camunda web applications. This repository must be configured with OpenSearch to take backups which are stored in Amazon S3. See the official AWS guide for detailed steps.
- Amazon S3 - An additional bucket to store backup files of the Zeebe brokers.
- Resource Planning: Make sure you have understood the considerations for sizing Camunda Clusters, and have evaluated sufficient CPU, memory, and storage necessary for the deployment.
Ensure all prerequisites are in place to avoid issues during installation or when upgrading in a production environment.
Architecture overview
For more information about the Camunda 8 architecture, refer to the Self-Managed overview and Camunda 8 reference architectures.
Below is the high-level architecture diagram for the base production setup:
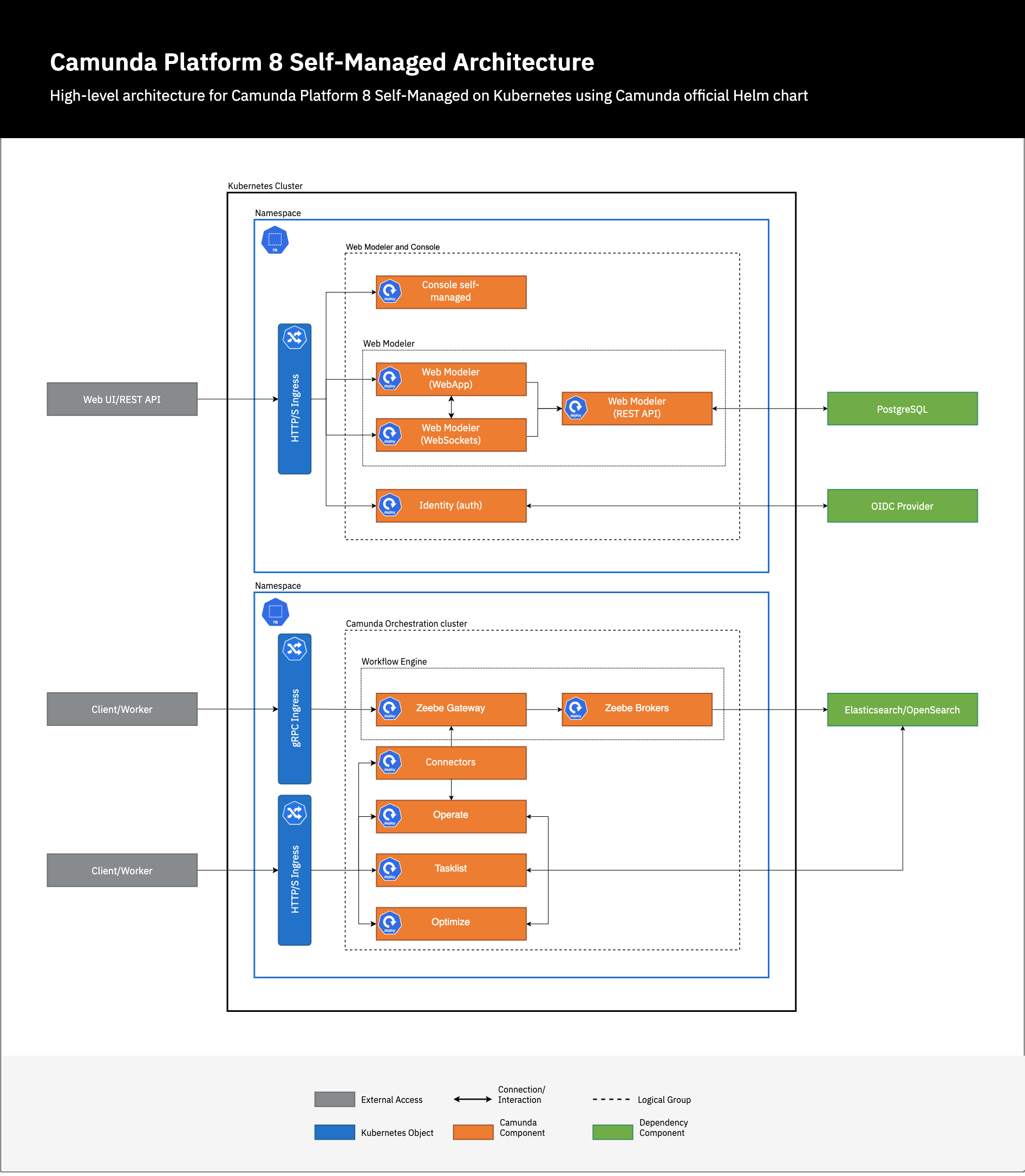
Installation and configuration
After following the prerequisites, you should have an EKS cluster ready with kubectl and the helm CLI installed.
Namespace setup
To get started, create two namespaces:
kubectl create namespace management
kubectl create namespace orchestration
-
Namespace
management: We will install Identity, Console, and all the Web Modeler components. -
Namespace
orchestration: We will install Zeebe, the Camunda web applications (Operate, Tasklist, and Optimize), along with Connectors.
Each component is installed by the Helm chart automatically, and does not need to be installed separately.
For more information on the difference between the Orchestration Cluster and the Web Modeler and Console cluster, see the Camunda 8 reference architecture.
Install the Helm chart
As there will be a Helm deployment in each namespace, create your own management-values.yaml and orchestration-values.yaml, or modify an existing setup by applying the production recommendations in the next section. Example values files can be found at the end of this guide.
The Camunda Helm chart can be installed in each namespace using the following command:
# This will add our chart repository so you can pull from it
helm repo add camunda https://helm.camunda.io
# This will update the chart repository. Please make sure to run this command before every install or upgrade
helm repo update
# This will install the latest Camunda Helm chart in the management namespace with the latest applications/dependencies.
helm install camunda camunda/camunda-platform --version $HELM_CHART_VERSION -n management \
--values management-values.yaml
# This will install the latest Camunda Helm chart in the Orchestration namespace with the latest applications/dependencies.
helm install camunda camunda/camunda-platform --version $HELM_CHART_VERSION -n orchestration \
--values orchestration-values.yaml
Ingress TLS setup
In order to access the Camunda Platform through HTTPS with Ingress, TLS must be enabled. Enabling TLS requires the following:
- Domain name: A public registered domain that has configurable DNS records. This guide will use
camunda.example.comas the domain. - TLS certificate: A TLS certificate created for your domain. The certificate must be an X.509 certificate, issued by a trusted Certificate Authority. The certificate must include the correct domain names (Common Name or Subject Alternative Names) to secure Ingress resources. Reach out to your DNS provider if you are unsure on how to create a TLS certificate. It is not recommended to use self-signed certificates.
- TLS secret: A TLS secret created from your TLS certificate. This guide will use a secret called
camunda-platform. For more information, see the Kubernetes documentation on how to create a TLS secret.
Multiple ingress controllers are supported. Specify ingress.className or ingress.grpc.className to assign the ingress to the desired ingress controller.
The following is an example values.yaml configuration using the example Ingress domain and TLS secret:
global:
ingress:
enabled: true
className: nginx
host: camunda.example.com
tls:
enabled: true
secretName: camunda-platform
Optionally, you can configure Ingress for the Zeebe gRPC API:
zeebe:
ingress:
grpc:
enabled: true
className: nginx
host: zeebe-grpc.camunda.example.com
tls:
enabled: true
secretName: camunda-platform-zeebe-grpc
More information can be found in the Ingress setup guide.
Identity provider integration
Once secure HTTPS connections are enabled and correctly configured via Ingress, the next stage to consider is configuring authentication.
This example uses AWS Simple Active Directory, which provides a subset implementation of a Microsoft Active Directory, and is compatible with our Microsoft Entra ID guide.
The following is an example configuration to add to your values.yaml files:
You must create a Kubernetes secret for all client secrets that exist in each app registration of your Active Directory.
global:
identity:
auth:
issuer: https://login.microsoftonline.com/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/v2.0
issuerBackendUrl: https://login.microsoftonline.com/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/v2.0
tokenUrl: https://login.microsoftonline.com/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/oauth2/v2.0/token
jwksUrl: https://login.microsoftonline.com/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/discovery/v2.0/keys
publicIssuerUrl: https://login.microsoftonline.com/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/v2.0
type: MICROSOFT
identity:
clientId: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000" #This is the application ID
existingSecret:
name: oidc-certificate-identity #secret from the certificate that was created in the Active Directory
existingSecretKey: certificate-secret-data
audience: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000" #same as client ID
redirectUrl: https://management-host.com/identity
initialClaimValue: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000" #object ID of your user
operate:
clientId: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
existingSecret:
name: oidc-certificate-operate
existingSecretKey: certificate-secret-data
audience: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
redirectUrl: https://orchestration-host.com/operate
optimize:
clientId: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
existingSecret:
name: oidc-certificate-optimize
existingSecretKey: certificate-secret-data
audience: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
redirectUrl: https://orchestration-host.com/optimize
tasklist:
clientId: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
existingSecret:
name: oidc-certificate-tasklist
existingSecretKey: certificate-secret-data
audience: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
redirectUrl: https://orchestration-host.com/tasklist
zeebe:
clientId: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
existingSecret:
name: oidc-certificate-zeebe
existingSecretKey: certificate-secret-data
audience: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
connectors:
clientId: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
existingSecret:
name: oidc-certificate-connectors
existingSecretKey: certificate-secret-data
audience: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
clientApiAudience: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
tokenScope: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/.default" # same as appplication ID
console:
clientId: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
wellKnown: https://login.microsoftonline.com/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/v2.0/.well-known/openid-configuration
audience: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
redirectUrl: https://management-host.com
webModeler:
clientId: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
audience: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
clientApiAudience: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
publicApiAudience: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
redirectUrl: https://modeler.management-host.com
For more information, see how to connect to an OpenID Connect provider.
Connect external databases
To allow for easier testing, the Camunda Helm chart provides databases as an external dependency, such as Bitnami Elasticsearch Helm chart and the Bitnami PostgreSQL Helm chart. These dependency charts should be disabled in a production setting, and production databases should be used instead.
This guide disables the Bitnami Elasticsearch dependency chart and uses Amazon OpenSearch. It also disables the Bitnami PostgreSQL dependency chart and uses Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL instead.
You should have one Amazon OpenSearch instance and one Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL instance (with two databases) ready to use, complete with a username, password, and URL for each datastore. If these have not been configured, see the prerequisites for requirements.
Connecting to Amazon OpenSearch
The following example values.yaml enables OpenSearch with the required configuration. This example also globally disables all internal component configuration for Elasticsearch through global.elasticsearch.enabled: false, and disables internal Elasticsearch through elasticsearch.enabled: false:
global:
elasticsearch:
enabled: false
opensearch:
enabled: true
auth:
username: user
password: pass
url:
protocol: https
host: opensearch.example.com
port: 443
elasticsearch:
enabled: false
Connect to an external database for Identity
The following example values.yaml configures Identity with an external Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL database:
identity:
externalDatabase:
enabled: true
host: external-postgres-host
port: 5432
username: identity_user
database: identity_db
existingSecret: identity-db-secret
existingSecretPasswordKey: database-password
Make sure the host and port are correctly defined.
Connect to an external database for Web Modeler
The following example values.yaml configures Web Modeler with an external Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL database:
webModeler:
externalDatabase:
url: jdbc:postgresql://external-postgres-host:5432/camunda_db
user: web_modeler_user
existingSecret: webm-odeler-db-secret
existingSecretPasswordKey: database-password
Use the existingSecret parameter to specify a pre-existing Kubernetes secret containing the password. This approach allows the Camunda Helm chart to reference credentials stored securely in your cluster, rather than hardcoding sensitive data in values files or templates.
For more information on connecting to external databases, the following guides are available for the Camunda Helm chart:
- Using an existing Elasticsearch instance
- Using Amazon OpenSearch service
- Using Amazon OpenSearch service through IRSA (only applicable if you are using EKS)
- Running Web Modeler on Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL
Camunda Zeebe configuration
At this point, you should be able connect to your platform through HTTPS, correctly authenticate users using AWS Simple Active Directory, and have connected to external databases such as Amazon OpenSearch and Amazon PostgreSQL.
The next steps focus on the Camunda application-specific configurations suitable for a production environment. The following sections continue to add to the management-values.yaml and orchestration-values.yaml at the Camunda component-level.
Elasticsearch/OpenSearch index retention
An index lifecycle management (ILM) policy in OpenSearch is crucial for efficient management and operation of large-scale search and analytics workloads. ILM policies provide a framework for automating the management of index lifecycles, which directly impacts performance, cost efficiency, and data retention compliance.
The following example configures an ILM policy for Zeebe, and can be added to your orchestration-values.yaml:
zeebe:
retention:
enabled: true
minimumAge: 30d
policyName: zeebe-record-retention-policy
For more information on configuring ILM policy, refer to the configuration guide on the OpenSearch exporter.
Configure backups
In order to configure backups, refer to the backup guide for Self-Managed installations.
Operational configuration options
After following the above steps, you should already have a solid base for running your platform in a production setting. The rest of this guide provides general Kubernetes-based guidance on configuration of the Camunda Helm chart for long-term maintenance.
Scaling and performance
The following resources and configuration options are important to keep in mind regarding scaling:
-
To scale Zeebe, the following values can be modified:
zeebe:
clusterSize: "3"
partitionCount: "3"
replicationFactor: "3"zeebe.clusterSize: to the amount of brokers to configurezeebe.partitionCount: how many Zeebe partitions are configured for each clusterzeebe.replicationFactor: the number of replicas that each partition replicates to
notezeebe.partitionCountdoes not yet support dynamic scaling. You will not be able to modify this property. It is better to over-provision the partitions to allow potential growth as dynamic partitioning isn't possible yet. -
Ensure the resources (CPU and memory) are appropriate for your workload size. For example, the resource limits can be changed for Zeebe by modifying the following values:
zeebe:
resources:
requests:
cpu: 800m
memory: 1200Mi
limits:
cpu: 2000m
memory: 1920Mi -
It is possible to set a LimitRange on the namespace. Please refer to the Kubernetes documentation on setting a LimitRange.
Reliability
The following resources and configuration options are important to keep in mind regarding reliability:
-
Check node affinity and tolerations. Refer to the Kubernetes documentation to modify the node affinity and tolerations.
For example, this is the default affinity configuration for the zeebe Pod in the Camunda Helm chart:
affinity:
podAntiAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- labelSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: app.kubernetes.io/component
operator: In
values:
- zeebe
topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostnameThis configuration ensures that Zeebe Pods with the default label
app.kubernetes.io/component=zeebeare not scheduled on the same node. The primary benefits include:- High availability: If one node fails, other nodes running the same component remain unaffected.
- Load distribution: Balances the workload across nodes.
- Fault tolerance: Reduces the impact of a node-level failure.
-
It is possible to set a
podDisruptionBudget, as in the following example for the Zeebe:zeebe:
podDisruptionBudget:
enabled: false
minAvailable: 0
maxUnavailable: 1 -
Version management: Stay on a stable Camunda and Kubernetes version. Follow Camunda’s release notes for security patches or critical updates.
-
Secrets should be created prior to installing the Helm chart so they can be referenced as existing secrets when installing the Helm chart. In this scenario, the secrets are auto-generated. The following can be added to both Helm values files:
global:
secrets:
autoGenerated: true
name: camunda-credentialsThis generates a secret called
camunda-credentials. It will include all the needed secret values for the Camunda Helm chart. Thecamunda-credentialsgenerated secret will not be deleted if the Helm chart is uninstalled.When upgrading the Helm chart, set
global.secrets.autoGeneratedtofalsewhen upgrading the chart. This prevents overwriting access credentials with the auto-generation script. The same secrets data will be required on upgrade.noteIt best to store this secret in an external secret manager such as Vault by HashiCorp in case of a total outage.
For more information, refer to the Kubernetes documentation on how to create a secret.
-
When upgrading the Camunda Helm chart, make sure to read the upgrade guide and corresponding new version release notes before upgrading. Perform the upgrade on a test environment first before attempting in production.
The following is an example configuration for Zeebe to create persistent storage:
zeebe:
extraVolumes:
extraVolumes:
- name: persistent-state
emptyDir: {}
extraVolumeMounts:
- name: persistent-state
mountPath: /mount
- It is recommended to set a memory and resource quota for your namespace. Please refer to the Kubernetes documentation to do so. Namespace-Level Quotas apply limits to all workloads within a namespace. It ensures aggregate resource consumption by all pods in the namespace do not exceed your desired resource limits.
Security
The following resources and configuration options are important to keep in mind regarding security:
-
To limit unnecessary permissions, and reduce risk of token exploitations, it is recommended to disable auto-mounting of the default Service Account. It is possible to do so by adding the following to both of your values files:
identity:
serviceAccount:
enabled: false
console:
serviceAccount:
enabled: false
webModeler:
serviceAccount:
enabled: false
connectors:
serviceAccount:
enabled: false
zeebe:
serviceAccount:
enabled: false
optimize:
serviceAccount:
enabled: falsenoteYou should only enable the auto-mounting of a service account token when the application explicitly needs access to the Kubernetes API server, or you have created a service account with the exact permissions required for the application and bound it to the pod.
-
Network Policies can be enabled with Camunda Helm charts if needed by your infrastructure requirements.
-
It is possible to have a pod security standard that is suited to your security constraints. This is enabled by modifying the Pod Security Admission. See the Pod Security Admission guide in the official Kubernetes documentation for more information.
-
By default, the Camunda Helm chart is configured to use a read-only root file system for the pod. It is advisable to retain this default setting, and no modifications are required in your Helm values files.
-
Disable privileged containers. This can be achieved by implementing a pod security policy. For more information, see the official Kubernetes documentation.
-
It is possible to modify either the
containerSecurityContextor thepodSecurityContext. The following example show the default configuration for Zeebe:podSecurityContext:
runAsNonRoot: true
fsGroup: 1001
seccompProfile:
type: RuntimeDefault
containerSecurityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
privileged: false
readOnlyRootFilesystem: true
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 1001
seccompProfile:
type: RuntimeDefaultTo add any other security constraints to your Helm values files, refer to the official Kubernetes documentation.
-
It is recommended to pull images exclusively from a private registry, such as Amazon ECR, rather than directly from Docker Hub. Doing so enhances control over the images, avoids rate limits, and improves performance and reliability. Additionally, you can configure your cluster to pull images only from trusted registries. Tools like Open Policy Agent can be used to enforce this restriction.
-
Please refer to our installing in an air-gapped environment guide when deploying Camunda in Air-gapped environments
-
Open Policy Agent can also be used to allowlist Ingress hostnames.
Observability and monitoring
The following resources and configuration options are important to keep in mind regarding observability and monitoring:
-
It is possible to enable integration with Prometheus, a popular monitoring solution, in the Camunda Helm chart. This can be configured by adding the following configuration below to your preferred Helm values file:
prometheusServiceMonitor:
enabled: true -
A tool such as Loki can be used for the retention and archival of logs. It can also be used to aggregate logs.
Create a production values.yaml
The following is a complete configuration example, taking all the above sections into consideration.
Example management configuration
The following example management-values.yaml is provided to the management namespace:
global:
secrets:
autoGenerated: true
name: camunda-test-credentials
Ingress:
enabled: true
className: nginx
host: management-host.com
tls:
enabled: true
secretName: camunda-platform
identity:
auth:
issuer: https://login.microsoftonline.com/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/v2.0
issuerBackendUrl: https://login.microsoftonline.com/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/v2.0
tokenUrl: https://login.microsoftonline.com/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/oauth2/v2.0/token
jwksUrl: https://login.microsoftonline.com/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/discovery/v2.0/keys
publicIssuerUrl: https://login.microsoftonline.com/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/v2.0
type: MICROSOFT
identity:
clientId: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
existingSecret:
name: oidc-certificate-identity
existingSecretKey: certificate-secret-data
audience: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
redirectUrl: https://management-host.com/identity
initialClaimValue: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
operate:
clientId: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
existingSecret:
name: oidc-certificate-operate
existingSecretKey: certificate-secret-data
audience: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
redirectUrl: https://orchestration-host.com/operate
optimize:
clientId: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
existingSecret:
name: oidc-certificate-optimize
existingSecretKey: certificate-secret-data
audience: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
redirectUrl: https://orchestration-host.com/optimize
tasklist:
clientId: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
existingSecret:
name: oidc-certificate-tasklist
existingSecretKey: certificate-secret-data
audience: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
redirectUrl: https://orchestration-host.com/tasklist
zeebe:
clientId: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
existingSecret:
name: oidc-certificate-zeebe
existingSecretKey: certificate-secret-data
audience: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
connectors:
clientId: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
existingSecret:
name: oidc-certificate-connectors
existingSecretKey: certificate-secret-data
audience: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
clientApiAudience: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
tokenScope: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/.default"
console:
clientId: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
wellKnown: https://login.microsoftonline.com/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/v2.0/.well-known/openid-configuration
audience: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
redirectUrl: https://management-host.com
webModeler:
clientId: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
audience: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
clientApiAudience: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
publicApiAudience: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
redirectUrl: https://modeler.management-host.com
identity:
contextPath: /identity
firstUser:
existingSecret: camunda-credentials
existingSecretKey: identity-user-password
externalDatabase:
enabled: true
host: external-postgres-host
port: 5432
username: identity_user
database: identity_db
existingSecret: identity-db-secret
existingSecretPasswordKey: database-password
webModeler:
enabled: true
contextPath: /modeler
restapi:
mail:
# This value is required, otherwise the restapi pod wouldn't start.
fromAddress: noreply@example.com
externalDatabase:
url: jdbc:postgresql://external-postgres-host:5432/camunda_db
user: camunda_user
existingSecret: camunda-db-secret
existingSecretPasswordKey: database-password
prometheusServiceMonitor:
enabled: true
labels:
release: kube-prometheus-stack
zeebe:
enabled: false
optimize:
enabled: false
connectors:
enabled: false
elasticsearch:
enabled: false
console:
configuration: |
camunda:
console:
oAuth:
audience: "console-api"
clientId: "console"
issuer: https://login.microsoftonline.com/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/v2.0
jwksUri: "https://login.microsoftonline.com/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/discovery/v2.0/keys"
type: "MICROSOFT"
wellKnown: https://login.microsoftonline.com/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/v2.0/.well-known/openid-configuration
managed:
method: plain
releases:
- name: camunda
namespace: management
version: 12.x.x
components:
- name: Console
id: console
version: 8.7.x
url: https://management-host.com/
readiness: http://camunda-console.oidc:9100/health/readiness
metrics: http://camunda-console.oidc:9100/prometheus
- name: Identity
id: identity
version: 8.7.x
url: https://management-host.com/identity
readiness: http://camunda-identity.oidc:82/actuator/health
metrics: http://camunda-identity.oidc:82/actuator/prometheus
- name: WebModeler WebApp
id: webModelerWebApp
version: 8.7.x
url: https://management-host.com/modeler
readiness: http://camunda-web-modeler-webapp.oidc:8071/health/readiness
metrics: http://camunda-web-modeler-webapp.oidc:8071/metrics
- name: camunda
namespace: orchestration
version: 12.x
components:
- name: Operate
id: operate
version: 8.7.x
url: https://orchestration-host.com/operate
readiness: http://camunda-operate.orchestration:9600/operate/actuator/health/readiness
metrics: http://camunda-operate.orchestration:9600/operate/actuator/prometheus
- name: Optimize
id: optimize
version: 8.7.x
url: https://orchestration-host.com/optimize
readiness: http://camunda-optimize.orchestration:80/optimize/api/readyz
metrics: http://camunda-optimize.orchestration:8092/actuator/prometheus
- name: Tasklist
id: tasklist
version: 8.7.x
url: https://orchestration-host.com/tasklist
readiness: http://camunda-tasklist.orchestration:9600/tasklist/actuator/health/readiness
metrics: http://camunda-tasklist.orchestration:9600/tasklist/actuator/prometheus
- name: Zeebe Gateway
id: zeebeGateway
version: 8.7.x
urls:
grpc: https://zeebe-orchestration-host.com
http: https://orchestration-host.com/zeebe
readiness: http://camunda-zeebe-gateway.orchestration:9600/zeebe/actuator/health/readiness
metrics: http://camunda-zeebe-gateway.orchestration:9600/zeebe/actuator/prometheus
- name: Zeebe
id: zeebe
version: 8.7.x
readiness: http://camunda-zeebe.orchestration:9600/actuator/health/readiness
metrics: http://camunda-zeebe.orchestration:9600/actuator/prometheus
Example orchestration configuration
The following example orchestration-values.yaml is provided to the orchestration namespace:
global:
secrets:
autoGenerated: true
name: camunda-test-credentials
Ingress:
enabled: true
className: nginx
host: orchestration-host.com
tls:
enabled: true
secretName: camunda-platform
elasticsearch:
enabled: false
opensearch:
enabled: true
auth:
username: user
password: pass
url:
protocol: https
host: opensearch.example.com
port: 443
identity:
service:
url: "http://management-identity.management.svc.cluster.local:80/identity"
auth:
type: MICROSOFT
issuer: https://login.microsoftonline.com/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/v2.0
publicIssuerUrl: "https://orchestration-host.com/auth/realms/camunda-platform"
issuerBackendUrl: https://login.microsoftonline.com/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/v2.0
tokenUrl: https://login.microsoftonline.com/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/oauth2/v2.0/token
jwksUrl: https://login.microsoftonline.com/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/discovery/v2.0/keys
operate:
clientId: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
existingSecret:
name: oidc-certificate-operate
existingSecretKey: certificate-secret-data
audience: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
redirectUrl: https://orchestration-host.com/operate
optimize:
clientId: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
existingSecret:
name: oidc-certificate-optimize
existingSecretKey: certificate-secret-data
audience: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
redirectUrl: https://orchestration-host.com/optimize
tasklist:
clientId: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
existingSecret:
name: oidc-certificate-tasklist
existingSecretKey: certificate-secret-data
audience: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
redirectUrl: https://orchestration-host.com/tasklist
zeebe:
clientId: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
existingSecret:
name: oidc-certificate-zeebe
existingSecretKey: certificate-secret-data
audience: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
connectors:
clientId: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
existingSecret:
name: oidc-certificate-connectors
existingSecretKey: certificate-secret-data
audience: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
clientApiAudience: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
tokenScope: "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/.default"
zeebe:
contextPath: /zeebe
ingress:
grpc:
enabled: true
className: nginx
host: grpc-{{ .Values.global.ingress.host }}
tls:
enabled: true
secretName: camunda-platform-zeebe-grpc
retention:
enabled: true
minimumAge: 30d
policyName: zeebe-record-retention-policy
optimize:
contextPath: /optimize
connectors:
contextPath: /connectors
identity:
enabled: false
identityKeycloak:
enabled: false
webModeler:
enabled: false
postgresql:
enabled: false
elasticsearch:
enabled: false
Next steps
Upgrade and maintenance
- Make sure to follow our upgrade guide when performing the upgrade on your Helm chart.
- Secrets are not auto-generated by default in the Camunda Helm chart. It is important to not override this default behavior on upgrade.
Running benchmarks
If you would like to run benchmarks on the platform, refer to the Camunda 8 benchmark community project.
Reference architectures
You can lean more about Camunda production deployment and available deployment architectures in Camunda Deployment Reference Architecture section of our documentation.